Australia–European Union relations
Relations between the Commonwealth of Australia and the European Union (EU) are founded on a Partnership Framework, first agreed in 2008. It covers not just economic relations, but broader political issues and cooperation.[1]
 | |
EU |
Australia |
|---|---|
The Australian Government maintains a delegation to the EU at its embassy in Brussels. A Delegation of the European Union is located in Canberra.[2]
History
Australia's relationship with Europe is a consequence of the historical connections generated by colonialism and mass European immigration to Australia. There has been speculation about possible first sightings of Australia by Portugal and Spain. However, the first documented European sightings and landings occurred since March 1606 by Holland. In addition, it also had colonial influence on the part of France. Australia would later be explored and conquered between the 18th and 19th centuries by the British Empire.
The United Kingdom has extremely close relations with Australia, due to its British colonial past, and both being realms of the Commonwealth. However, the United Kingdom ceased to be a European Union member state on 31 January 2020.
Trade
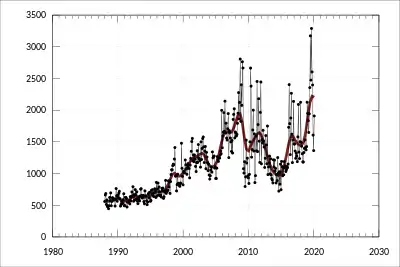
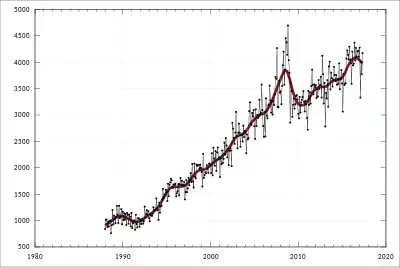
The EU is Australia's second largest trading partner, after China, and Australia is the EU's 18th. Australia's exports are dominated by mineral and agricultural goods, while 37% of trade is in commercial services, especially transportation and travel. EU corporations have a strong presence in Australia (approximately 2360) with an estimated turnover of €200 bn (just over 14% of total sales in Australia). These companies directly created 500,000 jobs in Australia. The EU is Australia's second largest destination of overseas investment and the EU is by far Australia's largest source of foreign investment €2.8 billion in 2009 (€11.6 billion in 2008). Trade was growing but ebbed in 2009 due to the global financial crisis.[3] In August 2019, Australian Senator Simon Birmingham, released a list of names that the EU wants to protect as a part of its new trade deal. The list of proposed names included beers, spirits and cheese and meats, which as per EU is aimed at protecting the identity of European products from non-European products. This concept of segregation is known as “geographical indications” or Gis, which will change the name of commodity in regards to the country of its origin.[4]
| EU – Australia trade in 2009[3] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction of trade | Goods | Services | ||
| EU to Australia | €26.7 billion | €11.8 billion | ||
| Australia to EU | €9.8 billion | €6.2 billion | ||
See also
References
- Australia, European External Action Service
- "Delegation of the EU". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- "Australia - Trade". European Commission. 18 June 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- "Feta Cheese Could Soon Be Banned From Australia!". KIIS. Retrieved 13 August 2019.
External links
- Australian mission to the EU
- EU mission to Australia
- European Union - Australian Department for Foreign Affairs and Trade
- Professor Philomena Murray and Dr Margherita Matera (19 October 2020). "'Australia-style': a model for [UK] relations with Europe". UK in a Changing Europe. Retrieved 21 October 2020.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)

