European Common Aviation Area
The European Common Aviation Area (ECAA) is a single market in aviation services.
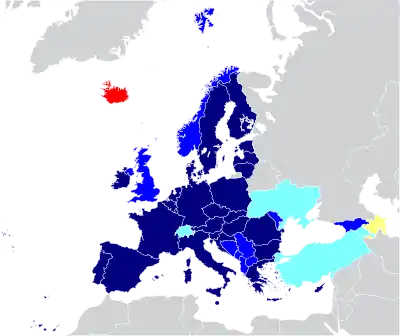
ECAA agreements were signed on 5 May 2006 in Salzburg, Austria between the EU and some external countries. It built upon the EU's acquis communautaire and the European Economic Area. The ECAA liberalises the air transport industry by allowing any company from any ECAA member state to fly between any ECAA member states airports, thereby allowing a "foreign" airline to provide domestic flights.
On 9 June 2006 the ECAA agreement was signed[2] by almost all of the 27 EU members, the European Union itself, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Iceland, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia as well as Kosovo (UNMIK as Kosovo representative under Security Council resolution 1244). The last two EU member states to sign it were Slovakia and Latvia respectively on 13 June 2006 and 22 June 2006. In addition, Serbia signed on 29 June 2006 and Montenegro on 5 July 2006.
Common Aviation Area agreements (CAA)
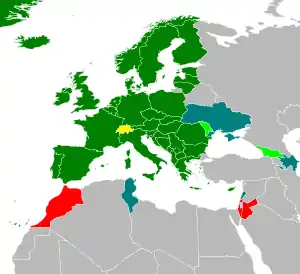
Common Aviation Area agreements have been opened up to the EU's Eastern Partnership members. Georgia signed a CAA on 2 December 2010[3] and Moldova signed on 26 June 2012.[4] Ukraine finalized a CAA agreement in November 2013.[5] These CAA agreements are in force.
Meanwhile, the first round of negotiations on an EU-Azerbaijan CAA agreement began on 24 January 2013.[6] Armenia started negotiations to join after a new Armenia-EU partnership agreement was signed in February 2017.[7]
Euro-Mediterranean Aviation Agreement (EMAA)
A similar system the agreements in the field of aviation is expected to be enacted with the Mediterranean partnership countries. The Euro-Mediterranean Aviation Agreement (EMAA) was signed on 12 December 2006 with the Kingdom of Morocco,[8] on 15 December 2010 with the Kingdom of Jordan,[9] on 10 June 2013 with Israel.[10] These EMAA agreements are in force.
The negotiations with Tunisia started on 27 June 2013.[11] On 9 October 2008 the Council of the European Union adopted a decision authorising the European Commission to open negotiations with Lebanon, and on 9 December 2008 adopted a decision authorising the European Commission to open negotiations with Algeria. The negotiations with Algeria have not started yet.
Brexit
Because the UK has left the European Union (Brexit), the UK is no longer be part of the Common Aviation Area. Unless permission or new treaties with the UK are made, aviation to and from the UK may stop.[12] There is a delay in this hard Brexit until the end of 2020, because the Brexit withdrawal agreement says that most EU rules continue to be valid for the UK during 2020. However, EU has approved regulations 2019/494 and 2019/505 in order to secure air traffic between UK and EU plus EEA.[13] Also, the British government has taken various steps to ensure the continuation of air travel, such as an open skies agreement with the United States of America.[14] The British airline EasyJet which has many flights outside the UK has set up a subsidiary in Austria (easyJet Europe) whilst keeping its headquarters in Luton, England.
See also
References
- "International aviation: Switzerland".
- "Multilateral Agreement on the Establishment of a European Common Aviation Area (ECAA)".
- "Common Aviation Area Agreement between the European Union and its Member States and Georgia".
- "Common Aviation Area Agreement between the European Union and its Member States and the Republic of Moldova".
- https://ec.europa.eu/transport/modes/international-aviation-ukraine_en
- "EU, Azerbaijan start negotiations over "Common Aviation Area Agreement"".
- "EU, Armenia EU Deal".
- "Euro-Mediterranean Aviation Agreement between the European Community and its Member States, of the one part, and the Kingdom of Morocco".
- "Euro-Mediterranean Aviation Agreement between the European Union and its Member States of the one part and the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan".
- "Euro-Mediterranean Aviation Agreement between the European Union and its Member States, of the one part, and the Government of the State of Israel".
- "International aviation: Tunisia".
- Gerrard, Bradley (18 August 2017). "With no plan B, Brexit stakes for aviation sector are sky high". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- Regulation (EU) 2019/502 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 March 2019 on common rules ensuring basic air connectivity with regard to the withdrawal of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland from the Union (Text with EEA relevance.)
- "UK and US agree post-Brexit flights deal". 29 November 2018. Retrieved 11 April 2019.