Climate change in Ghana
Ghana sits at the intersection of three hydro-climatic zones. Because of this, climate change is expected to impact Ghana in several ways.[1] Changes in rainfall, weather conditions and sea-level rise will affect the salinity of coastal waters. This is expected to negatively affect both farming and fisheries.[2] The national economy stands to suffer from the impacts of climate change because of its dependence on climate sensitive-sectors such as agriculture, energy, forestry. Moreover, access to freshwater is expected to become more challenging and reduced water supply will have a negative impact on hydropower which provides 54% of the country's electricity capacity.[2] Additionally, Ghana will likely see more cases of malaria and cholera since both are impacted by changes in water conditions.
In 2015, the government produced a document titled "Ghana's Intended Nationally Determined Contribution."[3] Following that, Ghana signed the Paris Climate Agreement in 2016.
Greenhouse gas emissions
Fossil fuel production
The Jubilee offshore oil field came into production in 2010, raising expectations for wealth creation in Ghana. However, the infrastructure needed to support Ghana's oil industry (storage, shipping, processing) has necessitated the practice of flaring. "Long-term gas flaring at the Jubilee Field may be inevitable" without accelerated development of infrastructure and would produce about 1.5 million tons of CO2 annually (7 percent of Ghana’s total national emissions). [4]
Impacts on the Natural Environment
Temperature and weather changes
The drier northern areas have warmed at a more rapid rate than southern Ghana. Overall, Ghana has experienced a 1.0°C. increase in temperature since 1960.[4] Northern Ghana has only one rainy season, while southern Ghana has two and annual rainfall is highly variable. Long-term trends for rainfall are difficult to predict. However, USDA's Forest Service concluded in 2011 that there was "no evidence that extreme rain events have either increased or decreased since 1960."[4]
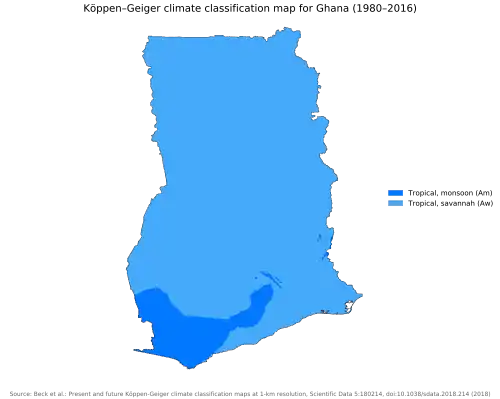
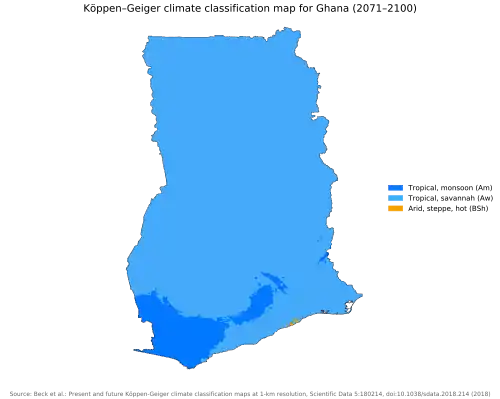
However, when one compares the Köppen-Geiger climate classification map for 1980-2016 and the projected map for 20171-2100 some coastal areas are predicted to change classification from "tropical, savannah" to "arid, steppe, hot."
Sea level rise
Available data also shows a sea level rise of 2.1 mm per year over the last 30 years, indicating a rise of 5.8 cm, 16.5 cm and 34.5 cm by 2020, 2050 and 2080. (needs a citation)
Water resources
Expected decreases to water in the primary rivers basins providing fresh water for the country, Volta River, Bia River and Tano River, could increase challenges in getting access to clean drinking water.[2]
Impacts on People
Agriculture
Forty-five percent of the workforce in Ghana depends on small-holder rain-fed agriculture.[2] Disruption due to erratic rainfall and other extreme weather will have a negative impact on people's economic well-being.[2] Moreover, staple crops such as Cassava, Maize and Cocoa (the major cash crop of Ghana) are expected to see decreased production.[2] Based on a 20-year baseline climate observation, it is forecasted that maize and other cereal crop yields will reduce by 7% by 2050.
Fisheries
Seafood makes up 40-60 percent of protein intake in Ghana.[2] Key species for the economy are expected to have worse reproduction cycles .[2]
Hydropower
Because 54% of national generation capacity is hydropower, unpredictable rainfall is likely to add uncertainty to a power grid already experiencing frequent outages (known as dumsor).[2] Some estimates suggest that capacity could fall by as much as 50% for the Volta Basin.[2]
Health impacts
An increase in waterborne diseases such as cholera and mosquito-borne diseases like malaria are projected.[2]
Mitigation and Adaptation
Ghana signed the Paris Agreement on 22 April 2016 and ratified on 21 September 2016. The first national climate change adaptation strategy in Ghana was developed to be implemented between 2010 and 2020.[5] Adaptation seeks to lower the risks posed by the consequences of climate change. Adaptation measures may be planned in advance or put in place spontaneously in response to a local pressure such as afforestation, land rotation, building climate-resilient structures, solar powered infrastructure, etc.[6] The Ministry of Environment Science, Technology and Innovation published a policy framework in 2013.[7] In 2015, Ghana developed a framework entitled 'Ghana's Intended Nationally Determined Contribution' to outline a plan to reduce carbon emissions and to improve eternity of land use, transportation, and other economic and societal sectors.[3]
References
- "Ghana". Climatelinks. Retrieved 2020-04-22.
- "Climate Risk Profile: Ghana". Climatelinks. USAID. January 2017. Retrieved 2020-04-22.
- "NDC Registry(interim)". Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- Ghana Climate Change Vulnerability and Adaptation. USAID Report prepared by the USDA Forest Service, International Programs. June 2011
- National Climate Change Adaptation Strategy. UNEP/UNDP. November 2012.
- United Nations, Climate Change. "The Paris Agreement". United Nations Climate Change. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- "Ghana National Climate Change Policy". Green Growth Knowledge Platform. 2018-07-23. Retrieved 2020-04-22.