Economy of Ghana
The economy of Ghana has a diverse and rich resource base, including the manufacturing and exportation of digital technology goods, automotive and ship construction and exportation, and the exportation of diverse and rich resources such as hydrocarbons and industrial minerals. These have given Ghana one of the highest GDP per capita in West Africa.[16][17] Owing to a GDP rebasement, in 2011 Ghana became the fastest-growing economy in the world.[18]
 Industries of the Republic of Ghana | |
| Currency | Cedi (GHS, GH₵) |
|---|---|
| Calendar year | |
Trade organisations | AU, AfCFTA, WTO, ECOWAS |
Country group |
|
| Statistics | |
| Population | |
| GDP | |
| GDP rank | |
GDP growth |
|
GDP per capita | |
GDP per capita rank | |
GDP by sector |
|
| 9.7% (2020 est.)[5] | |
Population below poverty line | |
| 43.5 medium (2016)[9] | |
Labour force | |
Labour force by occupation |
|
| Unemployment | |
Main industries | mining, lumbering, light manufacturing, aluminum smelting, food processing, cement, small commercial ship building, petroleum |
| External | |
| Exports | |
Export goods | oil, gold, cocoa, timber, tuna, bauxite, aluminum, manganese ore, diamonds, horticultural products |
Main export partners |
|
| Imports | |
Import goods | capital equipment, refined petroleum, foodstuffs |
Main import partners |
|
FDI stock | |
Gross external debt | |
| Public finances | |
| −6% (of GDP) (2017 est.)[6] | |
| Revenues | 9.544 billion (2017 est.)[6] |
| Expenses | 12.36 billion (2017 est.)[6] |
Foreign reserves | |
The Ghanaian domestic economy in 2012 revolved around services, which accounted for 50% of GDP and employed 28% of the work force. Besides the industrialization associated with minerals and oil, industrial development in Ghana remains basic, often associated with plastics (such as for chairs, plastic bags, razors and pens).[19] 53.6% of Ghana's workforce were employed in agriculture in 2013.[20][21]
Ghana embarked on a currency re-denomination exercise, from Cedi (₵) to the new currency, the Ghana Cedi (GH₵) in July 2007. The transfer rate is 1 Ghana Cedi for every 10,000 Cedis.
Ghana is Africa's second-biggest gold producer (after South Africa) and second-largest cocoa producer (after Côte d'Ivoire).[22] It is also rich in diamonds, manganese ore, bauxite, and oil. Most of its debt was canceled in 2005, but government spending was later allowed to balloon. Coupled with a plunge in oil prices, this led to an economic crisis that forced the government to negotiate a $920 million extended credit facility from the IMF in April 2015.[23]
Economic history
Taxation
Value-added tax is a consumption tax administered in Ghana. The tax regime which started in 1998 had a single rate but since September 2007 entered into a multiple rate regime. In 1998, the rate of tax was 10% and amended in 2000 to 12.5%. The top income tax and corporate tax rates are 25%. Other taxes included with value-added tax (VAT), are national health insurance levy, and a capital gains tax. The overall tax burden was 12.1% of Ghana's total domestic income in 2013. Ghana's national budget was the equivalent of 39.8% of GDP in 2013.[24]
Manufacturing
Ghana's industrial base is relatively advanced. Import-substitution industries include electronics manufacturing. Rlg Communications is the first indigenous African company to assemble laptops, desktops, and mobile phones, and is West Africa's biggest information and communications technology (ICT) and mobile phone manufacturing company.[25]
Ghana began its automotive industry with the construction of a prototype robust SUV, named the SMATI Turtle 1, intended for use in the rough African terrain. It was designed and manufactured by the Artisans of Suame Magazine Industrial Development Organization. Urban electric cars have been manufactured in Ghana since 2014.[26][27]
As of 2012 there were four major companies in the textiles sector: Akosombo Textiles Limited, Tex Style Ghana Limited, Printex Ghana, and Ghana Textile Manufacturing Company.[28]
Ghana National Petroleum Corporation and Ghana Oil Company deal with crude oil and gas exploration, exploitation, and refining.[29]
Telecommunications
At the end of January 2020, total number of voice subscription in Ghana stood at 41,380,751.This represents a percentage increase of 1.28% over December 2019 figures of 40,857,007. The total penetration rate stands at 136.79%. Competition among mobile-phone companies in Ghana is an important part of the telecommunications industry growth, Current market leader MTN with voice subscription of 23,150,485 representing 55.95% of the market is followed by Vodafone with voice subscription of 9,075,795 representing 21.93% market share, AirtelTigo voice subscription stands at 8,428,322 representing 20.69%, Glo's current voice subscription stands at 726,149 which represent a market share of 1.75%.[30][31][32]
The mass media of Ghana is among the most liberal in Africa, with Ghana ranking as the third-freest in Africa and 30th-most free in the world on the worldwide press freedom index. Chapter 12 of the Constitution of Ghana guarantees freedom of the Ghanaian press and the independence of the mass media, and Chapter 2 prohibits censorship.[33] Ghanaian press freedom was restored in 1992.[33]
Ghana was one of the first countries in Africa to achieve the connection to the World Wide Web.[34] In 2010, there were 165 licensed internet service providers in Ghana and they were running 29 of the fiber optic, and authorized networks VSAT operators were 176, of which 57 functioned, and 99 internet operators were authorized to the public, and private data and packet-switched network operators were 25.[35]
Data
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2017. Inflation below 5% is in green.[36]
| Year | GDP (in bil. US$ PPP) |
GDP per capita (in US$ PPP) |
GDP growth (real) |
Inflation rate (in Percent) |
Government debt (in % of GDP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 9.8 | 974 | n/a | ||
| 1981 | n/a | ||||
| 1982 | n/a | ||||
| 1983 | n/a | ||||
| 1984 | n/a | ||||
| 1985 | n/a | ||||
| 1986 | n/a | ||||
| 1987 | n/a | ||||
| 1988 | n/a | ||||
| 1989 | n/a | ||||
| 1990 | 28.3 % | ||||
| 1991 | |||||
| 1992 | |||||
| 1993 | |||||
| 1994 | |||||
| 1995 | |||||
| 1996 | |||||
| 1997 | |||||
| 1998 | |||||
| 1999 | |||||
| 2000 | |||||
| 2001 | |||||
| 2002 | |||||
| 2003 | |||||
| 2004 | |||||
| 2005 | |||||
| 2006 | |||||
| 2007 | |||||
| 2008 | |||||
| 2009 | |||||
| 2010 | |||||
| 2011 | |||||
| 2012 | |||||
| 2013 | |||||
| 2014 | |||||
| 2015 | |||||
| 2016 | |||||
| 2017 |
Imports and Exports
Ghana's top export products in 2016 were crude petroleum ($2.66B), gold ($2.39B), cocoa beans ($2.27B), cocoa paste ($382M) and cocoa butter ($252M). Ghana's top export destinations in 2016 were Switzerland ($1.73B), China ($1.06B), France ($939M), India ($789M) and the Netherlands ($778M).[37]
Ghana's top import categories in 2016 were refined petroleum ($2.18B), crude petroleum ($546M), gold ($428M), rice ($328M) and packaged medicaments ($297M). The nations with the highest value of imports to Ghana in 2016 were China ($4.1B), the Netherlands ($1.58B), the United States ($1.1B), Nigeria ($920M) and India ($668M).[37]
Private banking
The financial services in Ghana have seen a lot of reforms in the past years. The Banking (Amendment) Act 2007 included the awarding of a general banking license to qualified banks, which allows only indigenous Ghana offshore banks to operate in country Ghana. Indigenous Ghana private bank Capital Bank was the first to be awarded the general banking license in Ghana as well as indigenous Ghana private banks UniBank, National Investment Bank and Prudential Bank Limited. It has therefore become possible for Ghanaian non-resident individuals or residents and foreign companies or indigenous Ghana companies to open indigenous Ghana offshore bank accounts in Ghana.[24] Indigenous Ghana retail and savings banks include Agricultural Development Bank of Ghana, CAL Bank, GCB Bank Ltd, Home Finance Company and UT Bank as well as indigenous Ghana savings and loan institutions ABii National and Savings and Loans Company.[24]
Stock exchange
The Stock Exchange of Ghana is one of the largest in Africa, with a market capitalization of GH¢57.2 billion or CN¥180.4 billion in 2012. South Africa's JSE Limited is the largest.[38]
Energy
.JPG.webp)
As of December 2012, Ghana gets 49.1% of its energy from renewable energy and exports some of this to neighboring countries.
Solar energy
Ghana has aggressively begun the construction of solar plants across its sun-rich land in an aim to become the first country to get 6% of its energy from solar energy generation by 2016.
Wind energy

Ghana has Class 4–6 wind resources and high-wind locations, such as Nkwanta, the Accra Plains, and Kwahu and Gambaga mountains. The maximum energy that could be tapped from Ghana's available wind resource for electricity is estimated to be about 500–600 GWh/year.[39] To give perspective: in 2011, per the same Energy Commission, the largest Akosombo hydroelectric dam in Ghana alone produced 6,495 GWh of electric power and, counting all Ghana's geothermal energy production in addition, the total energy generated was 11,200 GWh in that year.[39] These assessments do not take into consideration further limiting factors such as land-use restrictions, the existing grid (or how far the wind resource may be from the grid) and accessibility.[39]
Bio-energy

Ghana has put in place mechanisms to attract investments into its biomass and bio-energy sectors to stimulate rural development, create jobs and save foreign exchange.[40] Main investments in the bio-energy subsector existed in the areas of production, are transportation, storage, distribution, sale, marketing and exportation.[40]
The goal of Ghana regarding bio-energy, as articulated by its energy sector policy, is to modernize and examine the benefits of bio-energy on a sustainable basis.[40] Biomass is Ghana's dominant energy resource in terms of endowment and consumption, with the two primary bio-fuels consumed being ethanol and biodiesel.[40] To that effect, the Ghana ministry of Energy in 2010 developed its energy sector strategy and development plan.[40] Highlights of the strategy include sustaining the supply and efficient use of wood fuels while ensuring that their utilization does not lead to deforestation.[40]
The plan would support private sector investments in the cultivation of bio-fuel feedstock, the extraction of bio-oil, and refining it into secondary products, thereby creating financial and tax incentives. The Ghana Renewal Energy Act provides the necessary fiscal incentives for renewable energy development by the private sector, and also details the control and management of bio-fuel and wood fuel projects in Ghana.[40] The Ghana National Petroleum Authority (NPA) was tasked by the Renewable Energy Act 2011 to price Ghana's bio-fuel blend in accordance with the prescribed petroleum pricing formula.[40]
The combined effects of climate change and global economic turbulence had triggered a sense of urgency among Ghanaian policymakers, industry and development practitioners to find sustainable and viable solutions in the area of bio-fuels.[40]
Brazil, which makes ethanol from maize and sugarcane, is currently the world's largest bio-fuel market.[40]
Energy consumption
Electricity generation is one of the key factors in achieving the development of the Ghanaian national economy, with aggressive and rapid industrialization; Ghana's national electric energy consumption was 265 kilowatts per capita in 2009.[41][42] Shortages of electricity have led to dumsor (blackouts),[43] increasing the interest in renewables.[44]
Hydrocarbon and mining
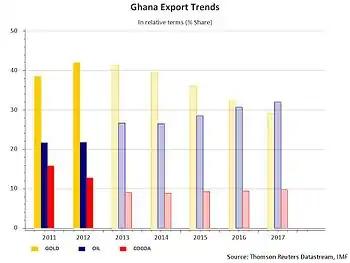
Ghana has 5 billion barrels (790×106 m3) to 7 billion barrels (1.1×109 m3) of petroleum in reserves. A large oilfield which contains up to 3 billion barrels (480×106 m3) of sweet crude oil was discovered in 2007.[45] Oil exploration is ongoing and the amount of oil continues to increase.[46] Ghana produces crude oil, as of 15 December 2010, and until June 2011, Ghana exploited around 120,000 barrels per day and is expected to increase production up to 2.5 million barrels per day in 2014.[47][48]
Ghana has vast natural gas reserves, which is used by many foreign multinational companies operating in Ghana.[49] The hydrocarbon industry has had major implications for regional and urban development in Ghana and these are likely to substantially increase in the years to come [50]
Mining has gained importance in the Ghanaian economy since the turn of the 21st century, with a growth of around 30% in 2007.[51] The main mining extractions are bauxite,[52] gold (Ghana is one of the largest gold producers in the world),[53] and the phosphates.[54]
Tourism
.JPG.webp)
The Ministry of Tourism has placed great emphasis upon further tourism support and development. Tourism contributed to 4.9% of GDP in 2009, attracting around 500,000 visitors. Tourist destinations include Ghana's many castles and forts, national parks, beaches, nature reserves, landscapes and World Heritage buildings and sites.[56][57]
In 2011, Forbes magazine ranked Ghana eleventh-friendliest country in the world. The assertion was based on a survey of a cross-section of travelers in 2010. Of all the countries on the African continent that were included in the survey, Ghana ranked highest.[58]
To enter Ghana, it is necessary to have a visa authorized by the Government of Ghana, except for certain entrepreneurs on business trips.[59]
Agriculture
In 2013 agriculture employed 53.6% of Ghana's total labor force.[20][21] Agribusiness accounts for a small fraction of the gross domestic product.[60] The main harvested crops are corn, plantain, rice, millet, sorghum, cassava and yam.[61] Unlike the agricultural livestock, forestry and fishing sectors, the crop sector is key to the Ghanaian agricultural industry.[62]
Ghana produced in 2018:
- 20.8 million tons of cassava (4th largest producer in the world, second only to Nigeria, Thailand and Congo);
- 7.8 million tonnes of yam (2nd largest producer in the world, second only to Nigeria);
- 4.1 million tons of plantain (2nd largest producer in the world, just behind Congo);
- 2.6 million tons of palm oil (8th largest producer in the world);
- 2.3 million tons of maize;
- 1.4 million tons of taro (4th largest producer in the world, second only to Nigeria, China and Cameroon);
- 947 thousand tons of cocoa (2nd largest producer in the world, second only to Ivory Coast);
- 769 thousand tons of rice;
- 753 thousand tons of orange (19th largest producer in the world);
- 713 thousand tons of pineapple (11th largest producer in the world);
- 521 thousand tons of peanut;
In addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products, like sweet potato (151 thousand tons), natural rubber (23 thousand tons) and tobacco (2.3 thousand tons). [63]
Ghana: Vision 2020 and industrialization
With the economic program "Ghana: Vision 2020", Ghana intends to achieve its goals of accelerated economic growth and improved quality of life for all its citizens, by reducing poverty through private investment, rapid and aggressive industrialization, and direct and aggressive poverty-alleviation efforts.[64] These plans were released in the 1995 government report, Ghana: Vision 2020.[64] Nationalization of state-owned enterprises continues, with about two thirds of 300 parastatal enterprises owned by the government of Ghana.[64] Other reforms adopted under the government's structural adjustment program include increasing exchange rate controls and increasing autarky and increasing restrictions on imports.[64]
The Ghana: Vision 2020 forecast assumes political stability; successful economic stabilization; the implementation of Ghana: Vision 2020 policy agenda on private sector growth; and aggressive public spending on social services, infrastructure and industrialization. It projection states that Ghana's goals of reaching high-income economy status and newly industrialized country status will be easily realized between 2020 and 2039.[64][65]
| 2013 exports to[66][67] | 2013 imports from[66][67] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Percentage | Country | Percentage |
|
| 46.89% | 12.46% | |||
| 12.32% | 11.76% | |||
| 5.49% | 8.86% | |||
| 3.57% | 5.15% | |||
| 3.32% | 4.35% | |||
| 2.76% | 3.93% | |||
| Others | 25.65% | Others | 53.49% | |
Economic transparency
The judicial system of Ghana deals with corruption, economic malpractice and lack of economic transparency.[24] Despite significant economic progress, obstacles do remain. Particular institutions need reform, and property rights need improvement. The overall investment regime in Ghana lacks market transparency. Tackling these issues will be necessary if Ghana's rapid economic growth is to be maintained.[24]
References
- "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- "World Bank Country and Lending Groups". datahelpdesk.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- "Population, total - Ghana". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2020". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- "The World Factbook". CIA.gov. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2 February 2019.
- "Poverty headcount ratio at national poverty lines (% of population) - Ghana". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- "Poverty headcount ratio at $3.20 a day (2011 PPP) (% of population) - Ghana". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "GINI index (World Bank estimate)". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- "Human Development Index (HDI)". hdr.undp.org. HDRO (Human Development Report Office) United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- "Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)". hdr.undp.org. HDRO (Human Development Report Office) United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- "Labor force, total - Ghana". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "Employment to population ratio, 15+, total (%) (national estimate) - Ghana". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "Ghana Unemployment Rate". 8 February 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- "Ease of Doing Business in Ghana". Doingbusiness.org. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- "New fuel for faster development". worldfolio.co.uk. Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 12 October 2013.
- "The Top 5 Countries for ICT4D in Africa". ictworks.org. Retrieved 12 October 2013.
- "Ghana: The World's Fastest Growing Economy in 2011". www.ghanaweb.com. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- "Obama's Ghana trip sends message across Africa". CNN. 10 July 2009.
- Food and Agriculture Policy Decision Analysis (FAPDA). "Country Fact sheet on food and agriculture policy trends" (PDF). Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations. FAO. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- Clark, Nancy L. "Agriculture" (and subchapters). A Country Study: Ghana (La Verle Berry, editor). Library of Congress Federal Research Division (November 1994). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "Cocoa in Ivory Coast and Ghana 2017 – African Business". Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- The Heritage Foundation. "Ghana's Economy". Heritage. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- "Ghana Economy". heritage.org. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- "Rlg wants to create a million jobs". standard.gm. 22 April 2014. Archived from the original on 29 April 2015. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- Kofi Adu Domfeh (13 April 2013). "Ghana's model vehicle unveiled by Suame Magazine artisans". Modernghana.com. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- "Ghana's model car attracts Dutch government support". Myjoyonline.gh. 15 July 2013. Archived from the original on 23 September 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- Daily Graphic Newspaper. "What Will Save Ghana's Textile Industry?". Government of Ghana. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "Ghana National Petroleum Corporation" (PDF). ghanaoilwatch.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "Telecom Voice Subscription » National Communications Authority". www.nca.org.gh. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "Mobile voice subscription hits 41.3 million - NCA". www.ghanaweb.com. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "Mobile voice subscription hits 41.3m". www.classfmonline.com. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- Ghana culture and media Archived 8 April 2013 at Archive.today "Country Facts". Accessed 6 February 2013.
- Ghana: Internet Usage and Telecommunications Report. Internet World Stats. Accessdate 24 April 2013.
- Atteneri Nabila Benítez Trujillo. Information of Telecommunications in Ghana Archived 3 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine (in Spanish). Proexca, 2010. Accessdate 24 April 2013.
- "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- OEC. "Ghana Imports and Exports". Atlas Media. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- "Ghana Market Update" (PDF). www.icbuk.com. Intercontinental Bank. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2012.:13
- "Renewable Energy – what is Ghana's wind power potential". arrakis-group.com. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- "Renewable". energymin.gov.gh. Archived from the original on 10 May 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013., Shao Hai Jun (5 October 2012). "Ghana to attract investment into bio-energy sector". china.org.cn. Xinhua: China Internet Information Center. Retrieved 23 April 2013., "Ghana to attract investment into bio-energy sector". wacee.net. Archived from the original on 12 September 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- "The sector of electricity in Ghana". Proexca (in Spanish). Canary Island. 2011. Archived from the original on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- "Consumption of Electrical Energy (kWh per capita)". World Bank (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- "I've been named 'Mr Dumsor' in Ghana – Prez Mahama tells Ghanaians in Germany - See more at". Graphic Online. Graphic Communications Group Limited (G.C.G.L). 21 January 2015. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- Agbenyega, E. (10 April 2014). "Ghana's power crisis: What about renewable energy?". graphic.com.gh. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- Ghana's increasing Oil Reserves and New Discoveries Archived 26 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine. news.yahoo.com. 22 December 2007. Retrieved 22 December 2007.
- RIGZONE – Kosmos Makes Second Oil Discovery Offshore Ghana
- "Ghana already produces oil". GuinGuinBali (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 12 January 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Ghana to produce 80,000 barrels of crude oil per day next week". Ghana Oil Watch. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Guide to Natural Gas in Ghana" (PDF). Bureau of Economic Geology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- Obeng-Odoom F, 2014, Oiling the Urban Economy: Land, Labour, Capital, and the State in Sekondi-Takoradi, Ghana, Routledge, London
- "Ghana, the best student of the classroom". Mondial Nieus (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- MBendi. "Bauxite Mining in Ghana-Overview". Information Services. Archived from the original on 11 July 2003. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- "Gold in Ghana 2011 market". Proexca (in Spanish). Canary Islands. Archived from the original on 19 December 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Ghana" (PDF). University of Guelph. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- "Trade Expo International". UniqueTtrustex. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2013.
- "Asante Traditional Buildings". Unesco. World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- "Forts and Castles, Volta, Greater Accra, Central and Western Regions". Unesco. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- "Forbes: Ghana is eleventh friendliest nation". www.vibeghana.com. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- Harvard quotation. Belda. 2004. :24
- "Members". ONU (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Agriculture in Ghana (Facts and figures)" (PDF). 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Ghana". Natureduca (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- Ghana production in 2018, by FAO
- "Ghana – Vision 2020" (PDF). ndpc.gov.gh. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "Is Ghana Entering A Sweet, Golden Era?". Africanbusinessmagazine.com. African Business. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- "The Observatory of Economic Complexity: Ghana". atlas.media.mit.edu. Retrieved 20 April 2013., "Ghana Major Trade Partners". countries.bridgat.com. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 20 April 2013.
- "Ghana Major Trade Partners". countries.bridgat.com. 2013. Archived from the original on 23 May 2013. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- "Ghana will reclaim top spot in cocoa production -Prez Mahama". Graphic.com.gh. Daily Graphic. 5 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- Jedwab, Rémi; Moradi, Alexander (2012). "Revolutionizing Transport: Modern Infrastructure, Agriculture and Development in Ghana". London School of Economics. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
Two railway lines were built between 1901 and 1923 to connect the coast to mining areas and the large hinterland city of Kumasi. This unintendedly opened vast expanses of tropical forest to cocoa cultivation, allowing Ghana to become the world's largest producer.
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Dave Brown. "Top 10 Gold Producers". Gold Investing News. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012. Retrieved 19 April 2013.
.JPG.webp)
.JPG.webp)