Criticism of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) has been the subject of criticisms since it was founded by American religious leader Joseph Smith in 1830.
Polygamy is perhaps the most controversial, and was a key contributing factor for Smith's murder. Under heavy pressure — Utah would not be accepted as a state if polygamy was practiced — the church formally and publicly renounced the practice in 1890. Utah's statehood soon followed. However, plural marriage remains a divisive issue, as despite the official renunciation of 1890, it still has sympathizers, defenders, and semi-secret practitioners.
More recent criticism has focused on questions of historical revisionism, homophobia, racism,[1] sexist policies, inadequate financial disclosure, and the historical authenticity of the Book of Mormon.
Critics
The LDS Church and Mormonism have attracted criticism from their inception to the present day. Notable early critics of Mormonism included Abner Cole, Eber D. Howe, and Thomas C. Sharp. Notable modern critics of the LDS Church include Jerald and Sandra Tanner, Richard Abanes, Richard and Joan Ostling, historian Fawn M. Brodie, Jeremy Runnells and John Dehlin. In recent years, the Internet has provided a new forum for critics.[2]
The church's 2008 support of California's Proposition 8 sparked heated debate and protests by gay-rights organizations.[3][4] Affirmation is a group of current and former members of the LDS Church who have criticized the church's policies on homosexuality. Christian Apologetics and Research Ministry is a Christian organization that has criticized the church's theology. The Institute for Religious Research is an organization that has criticized the church, in particular the Book of Abraham. Numerous other organizations maintain web sites that criticize the church.
Criticisms of doctrinal changes
Priesthood policy
The Tanners state that the church's 1978 policy change of allowing all worthy male members, including people of black African descent, to hold the priesthood was not divinely inspired as the church said, but simply a matter of convenience.[5] Richard and Joan Ostling point out that this reversal of policy occurred as the LDS Church began to expand outside the United States into countries such as Brazil that have large, ethnically mixed populations, and as the church prepared to open a new temple in São Paulo, Brazil.[6] The restriction on the priesthood was never formally established as church doctrine. The reasons for it have never been made clear, although some opinions were expressed over the years by various church leaders. A few black elders were ordained to the priesthood under Joseph Smith, who never expressed any opposition to having the priesthood available to all worthy men. The priesthood restriction originated under Brigham Young.[7] Like the practice of polygamy, this position was changed when it no longer served any purpose.[8]
Polygamy officially discontinued in 1890
The Tanners argue that the church's 1890 reversal of its policy on polygamy was done for political reasons, citing the fact that the change was made during the church's lengthy conflict with the federal government over property seizures and statehood.[9] The Ostlings say that, soon after the church received the revelation that polygamy was prohibited, Utah again applied for statehood. This time the federal government did not object to starting the statehood process. Six years later, the process was completed and Utah was admitted as a state in 1896.[10] The Ostlings note that soon after the church suspended the practice of polygamy, the federal government reduced its legal efforts to seize church property.[10] Despite this, Mormon leaders after 1890 continued to sanction and participate in plural marriages in secret, in smaller numbers, both in the U.S. and in Mexico, for the next several decades. [11]
Mormons Ron Wood and Linda Thatcher do not dispute that the change was a result of federal intervention and say that the church had no choice in the matter. The 1887 Edmunds–Tucker Act was crippling the church and "something dramatic had to be done to reverse [the] trend."[12] After the church appealed its case to the U.S. Supreme Court and lost, church president Wilford Woodruff issued the 1890 Manifesto. Woodruff noted in his journal that he was "acting for the temporal salvation of the Church".[13]
God was once a man
Critics such as Richard Abanes[14] and the Institute for Religious Research[15] criticize the church[14][15] for changing the principle asserting that God was once a man. They cite changes to the LDS Church publication Gospel Principles between the 1978[16] and 1997[17] editions, where "We can become Gods like our Heavenly Father" was changed to "We can become like our Heavenly Father", and "our Heavenly Father became a God" was changed to "our Heavenly Father became God".[14][15] But, official LDS Church publications still affirm the doctrine of eternal progression, and the official church manual, Teachings of Presidents of the Church: Lorenzo Snow (2012),[18] affirms that "As man is, God once was; as God now is, man may be."[19][20] The 2009 edition of Gospel Principles quotes Joseph Smith as stating, "It is the first principle of the Gospel to know for a certainty the Character of God. … He was once a man like us; … God himself, the Father of us all, dwelt on an earth, the same as Jesus Christ himself did".[21]
Criticisms of past teachings
Polygamy
Sarah Pratt, first wife of Mormon Apostle Orson Pratt, in an outspoken critique of Mormon polygamy, said that polygamy
completely demoralizes good men and makes bad men correspondingly worse. As for the women—well, God help them! First wives it renders desperate, or else heart-broken, mean-spirited creatures.[22]
Pratt ended her marriage to husband Orson Pratt in 1868 because of his "obsession with marrying younger women" (at age 57, Orson Pratt married a sixteen-year-old girl, his tenth wife, younger than his daughter Celestia).[23] Sarah Pratt lashed out at Orson in an 1877 interview, stating:
Here was my husband, gray headed, taking to his bed young girls in mockery of marriage. Of course there could be no joy for him in such an intercourse except for the indulgence of his fanaticism and of something else, perhaps, which I hesitate to mention.[24]
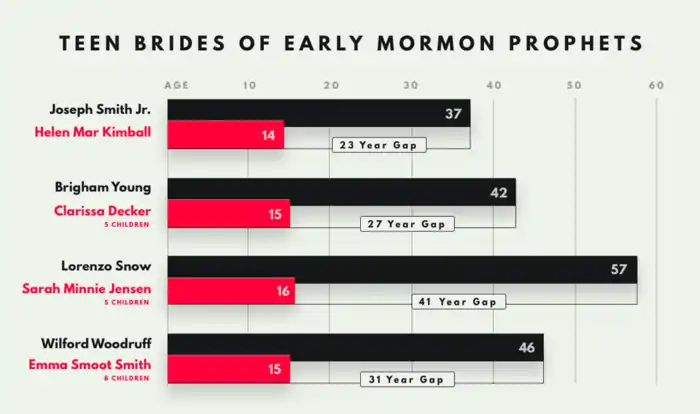
The Tanners argue that early church leaders established the practice of polygamy in order to justify behavior that would otherwise be regarded as immoral.[25] The Ostlings criticize Joseph Smith for marrying at least 32 women during his lifetime, including several under the age of 16, a fact acknowledged by Mormon historian Todd Compton.[26][27] Compton also acknowledges that Smith entered into polyandrous marriages (that is, he married women who were already married to other men)[27] and that he warned some potential spouses of eternal damnation if they did not consent to be his wife;[28] in at least two cases, Smith married orphan girls who had come to live at his home.[29]
However, Bushman notes that evidence of sexual relations between Smith and any wives of his followers is sparse or unreliable.[30] Compton argues that some marriages were likely dynastic in nature, to link families.
Polygamy after 1890
Richard Abanes, Richard and Joan Ostling, and D. Michael Quinn note that after the 1890 Manifesto, church leaders authorized more than 200 polygamous marriages and lied about the continuing practice.[36][37][38]
Joseph F. Smith acknowledged reports that church leaders did not fully adhere to the 1890 prohibition. After the Second Manifesto in 1904, anyone entering into a new plural marriage was excommunicated.[39]
Adam–God doctrine
The Ostlings criticize Brigham Young's teachings that God and Adam are the same being.[40][41] One apostle, Franklin D. Richards, also accepted the doctrine as taught by Young, stating in a conference held in June 1854 that "the Prophet and Apostle Brigham has declared it, and that it is the word of the Lord".[42] But, when the concept was first introduced, several LDS leaders disagreed with the doctrine, including apostle Orson Pratt, who expressed that disagreement publicly.[43] The church never formally adopted the doctrine, and has since officially repudiated it.[44][45]
Blood atonement
Brigham Young introduced a doctrine known as "blood atonement", regarding the unpardonable sin, or sin for which Jesus Christ's atonement does not apply.[46][47] He taught that a person could atone for such sins only by giving up his or her life.[48] Various church leaders in the 19th century taught likewise,[49][50][51] but more recently church leaders have taught that the atonement of Jesus Christ is all-encompassing and that there is no sin so severe that it cannot be forgiven (with the exception of the "unpardonable sin" of denying the Holy Ghost).[52]
Criticism regarding temples
Critics find fault with the church's temple policies and ceremonies, which include an endowment ceremony, weddings, and proxy baptism for the dead.
Temple admission restricted
Richard and Joan Ostling, and Hugh F. Pyle state that the LDS Church's policy on temple admission is unreasonable, noting that even relatives cannot attend a temple marriage unless they are members of the church in good standing.[53][54] The Ostlings, the Institute for Religious Research, and Jerald and Sandra Tanner say that the admission rules are unreasonable because admission to the temple requires that a church member must first declare that they pay their full tithe before they can enter a temple.[55][56][57] The Mormonism Research Ministry calls this "coerced tithing" because church members that do not pay the full tithe cannot enter the temple, and thus cannot receive the ordinances required to receive the highest order of exaltation in the next life.[58]
Baptism for the dead
The church teaches that a living person, acting as proxy, can be baptized by immersion on behalf of a deceased person, citing 1 Corinthians 15:29;[59] Malachi 4:5–6; John 5:25; and 1 Peter 4:6 for doctrinal support.[60] These baptisms for the dead are performed in temples.
Floyd C. McElveen and the Institute for Religious Research state that verses to support baptism for the dead are not justified by contextual exegesis of the Bible.[61][62] In 2008, the Vatican issued a statement calling the practice "erroneous" and directing its dioceses to keep parish records from the Genealogical Society of Utah which is affiliated with the LDS Church.[63]
Holocaust survivors and other Jewish groups criticized the LDS Church in 1995, after discovering that the church had baptized more than 300,000 Jewish Holocaust victims.[64][65] After that criticism, church leaders put a policy in place to stop the practice, with an exception for baptisms specifically requested or approved by victims' relatives.[66] Jewish organizations again criticized the church in 2002, 2004, and 2008[67] stating that the church failed to honor the 1995 agreement.[66] However, Jewish and Mormon leaders subsequently acknowledged in a joint statement in 2010 that "concerns between members of both groups...have been eliminated."[68][69]
Endowment ceremony
Jerald and Sandra Tanner allege that Joseph Smith copied parts of the Mormon temple endowment ceremony from Masonic rituals (such as secret handshakes, clothing, and passwords), and that this undermines the church's statement that the rituals were divinely inspired.[70] The Tanners also point to the fact that Joseph Smith was himself a Freemason[71] prior to introducing the endowment rituals into Mormonism.
The Tanners criticize the church's revision of the temple endowment ceremony over the years, saying that revisions were made to obscure provocative practices of the early church.[72][73]
FairMormon acknowledges changes to the endowment ceremony and points out that (according to Joseph Fielding Smith) Joseph Smith told Brigham Young the ceremony was "not arranged perfectly", and challenged him to organize and systemize it, which Young continued to do throughout his presidency.[74]
Responses to abuse allegations
Reacting to accusations of abuse by teachers,[75] Boy Scouts leaders,[76] clergy, etc., social welfare activists have campaigned for more robust of measures toward greater prevention of abuse of individuals served by counselors and other professionals, advocating greater transparency and quicker referral of allegations to criminal investigators.
The Survivors Network of those Abused by Priests and others have criticized one-on-one ("worthiness") interviews between LDS pastoral leaders and (especially) adolescent congregants, believing them "an invitation" for abuse. An editorial in the sectarian (LDS Church) Deseret News responded[77][78]:
The LDS Church has a zero tolerance policy concerning sexual misconduct. It also gives specific instruction on conducting one-on-one interviews with youths, including encouraging them to have parents or other trustworthy adults sit directly outside the room. Church leaders are to avoid any situation that could be misinterpreted.

In 2018 over 800 protesters gathered and marched to the LDS Church headquarters to deliver a petition with over 55,000 signatures asking for an end to semiannual, closed-door, one-on-one interviews between adult male local church leaders and children and teens during which many members have been asked about their sexual behaviors and thoughts in ways they felt were harmful.[79]
Finances
The church has often been secretive about its finances, especially in the United States. The church has not disclosed its assets in the U.S. since 1959.[80] This has drawn criticism from the Ostlings and the Tanners, who consider its financial practices to be overly secretive.[81][82][83]
The church does disclose financials in the United Kingdom[84] and Canada,[85] where it is required to by law. In addition, the church employs an independent audit department that provides its certification at each annual general conference that church contributions are collected and spent in accordance with church policy.[86] Moreover, the church engages a public accounting firm (currently Deloitte & Touche in the United States; PricewaterhouseCoopers in the United Kingdom) to perform annual audits of its not-for-profit,[87] for-profit,[88] and educational[89][90] entities. Lay leaders at the local level are not paid.[91]
The Tanners and the Ostlings accuse the church of being overly greedy and materialistic, citing the large amount of wealth accumulated by the church, and citing the strong emphasis on tithing,[92] and suggest that the church is more like a business than a spiritual endeavor. [83][93]
In December 2019, a whistleblower alleged the church holds over $100 billion in investment funds, which are managed by an affiliate, Ensign Peak Advisors; that it failed to use the funds for charitable purposes and instead used them in for-profit ventures; and that it misled contributors and the public about the usage and extent of those funds. According to the whistleblower, applicable law requires the funds be used for religious, educational or other charitable purposes for the fund to maintain its tax-exempt status.[94] Other commentators have argued that such expenditures may not be legally required as claimed.[95] In response to the allegations, the church's First Presidency stated that "the Church complies with all applicable law governing our donations, investments, taxes, and reserves," and that "a portion" of funds received by the church are "methodically safeguarded through wise financial management and the building of a prudent reserve for the future."[96]
Criticism of response to internal dissent
The Ostlings say that the LDS Church retaliates against members that publish information that undermines church policies,[97] citing excommunications of scientist Simon Southerton[98] and biographer Fawn M. Brodie.[99] They further state that the church suppresses intellectual freedom, citing the 1993 excommunication of the "September Six", including gay LDS historian D. Michael Quinn, and author Lavina Fielding Anderson.[97] The Ostlings write that Anderson was the first to reveal the LDS Church keeps files on Mormon scholars, documenting questionable activities, and the Ostlings state that "No other sizable religion in America monitors its followers in this way".[97]
The American Association of University Professors, since 1998, has put LDS Church-owned Brigham Young University along with twenty-six other universities on its censured list of universities that do not allow tenured professors sufficient freedom in teaching and research.[100]
Richard Abanes lists the following as church members excommunicated or censured for views unacceptable to the church hierarchy:[101]
- Journalist Deborah Laake, for her book Secret Ceremonies: A Mormon Woman's Intimate Diary of Marriage and Beyond
- BYU English teacher Cecilia Konchar-Farr, for her views on abortion laws
- Writer Janice Merrill Allred
- English Professor Gail Houston
- Anthropologist David Knowlton
Church monitors members' critical publications
Richard Abanes and the Ostlings criticize the LDS Church for maintaining a group called the Strengthening Church Members Committee, led by two church apostles.[101] According to the Ostlings, the purpose of this committee is to collect and file "letters to the editor, other writings, quotes in the media, and public activities" of church members that may be publishing views contrary to those of the church leadership.[102] The Committee has also recruited students to spy on professors at Brigham Young University who are suspected of violating the church's dictates.[103][104]
The Tanners state that throughout the 20th century the church denied scholars access to many key church documents, and in 1979 said that it had refused to publish Joseph Smith's diary.[105] Apologists point out that The Joseph Smith Papers project will provide access to Smith's journals.[106]
Alleged distortion of its own history
An analysis of B. H. Roberts's work History of the Church, when compared to the original manuscripts from which it is drawn, "more than 62,000 words" can be identified that were either added or deleted.[107] Based on this analysis, Jerald and Sandra Tanner contend that the church distorts its history in order to portray itself in a more favorable light.[72] Specifically, they allege that there was a systematic removal of events that portray Joseph Smith in a negative light.[108]
D. Michael Quinn responded to these charges by pointing out that methods by Roberts used in creating History of the Church—while flawed by today's standards—were not uncommon practices in the nineteenth century, even by reputable historians.[109]
The Tanners cite the selective use of Brigham Young's statements, presented in a manner to give the illusion that he was in favor of blacks receiving the priesthood.[110] The Tanners also state that the church attempted to discredit evidence that Joseph Smith was arrested, tried, and found guilty by a justice of the peace in Bainbridge, New York, in 1826.[111] The Tanners have also highlighted changes such as the title page of the 1830 edition of the Book of Mormon that described Smith as "Author and Proprietor" of the book, which was revised in subsequent editions to be "Translator",[112] and the description of Oliver Cowdery's skill at using the divining rod found in the 1829 edition of the Book of Commandments, which does not appear in the corresponding section of the 1835 edition of the Doctrine and Covenants.[113]
FARMS responds to the "author and proprietor" charge by arguing this title conformed to the governing copyright laws in 1830.[114]
The Ostlings consider other omissions to be distortion, noting that the widely distributed church manual Teachings of Presidents of the Church: Brigham Young omits any mention of Young's polygamy, and that the book's chronological summary of Young's life includes the date of his first marriage, the date of the first wife's death, and the date of the second legal marriage, but omits mention of Young's dozens of other marriages.[115]
In 1842, Willard Richards compiled a number of records in order to produce a history of the church. Among the records examined were the various accounts related to Zelph. In the process of combining the accounts, Richards crossed out Woodruff's references to "hill Cumorah," and Heber C. Kimball's reference to the "last great struggle with the Lamanites"[116]
Mormon historian D. Michael Quinn has accused LDS Church leaders of urging historians to hide "controversies and difficulties of the Mormon past".[117] Mormon scholar Allen Robers says church leaders "attempt to control depictions of the Mormon past".[118] Non-Mormon professor John Hallwas of Western Illinois University says of LDS historians: "[they] do not mention Mormon intimidation, deception, repression, theft, and violence, or any other matters that might call into question the sacred nature of the Mormon experience."[119]
Columbia University professor Richard Bushman, a member of The Joseph Smith Papers advisory board, responds to critics that those on the project "work on the assumption that the closer you get to Joseph Smith in the sources, the stronger he will appear, rather than the reverse, as is so often assumed by critics."[120]
In 1969, the Western History Association published Jewish historian Moses Rischin's observation of a new trend among Mormon historians to report objectively.[121] Quinn cites this as the origin of the term "New Mormon history", while citing previous efforts towards objectivity such as Juanita Brooks's 1950 publication of The Mountain Meadows Massacre by Stanford University Press.[122]
FARMS scholarship questioned
Critics say the LDS Church is academically dishonest, because it supported biased research conducted by the previously church-owned Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies (FARMS). FARMS was an independent organization but in 1997 became a research institute within church-owned Brigham Young University that publishes Mormon scholarship. It was dissolved in 2006. Critic Matthew Paulsen, of the Christian countercult group Christian Apologetics and Research Ministry, faulted FARMS for limiting peer review to members of the LDS Church. He stated that FARMS's primary goal is to defend the Mormon faith rather than to promote truthful scholarship.[123] Molecular biologist Simon Southerton, a former LDS Church bishop and author of Losing a Lost Tribe: Native Americans, DNA, and the Mormon Church said, "I was amazed at the lengths that FARMS went to in order to prop up faith in the Book of Mormon. I felt that the only way I could be satisfied with FARMS explanations was to stop thinking .... The explanations of the FARMS researchers stretched the bounds of credibility to breaking point on almost every critical issue".[124]
FARMS supported what it considered to be "faithful scholarship", which includes academic study and research in support of Christianity and Mormonism, and in particular, where possible, the official position of the LDS Church.[125]
Views on sexuality
Deborah Laake and Colleen McDannell say that the church takes a repressive stance towards sexuality and that this may be psychologically unhealthy.[126][127]
Affirmation, a Mormon LGBT organization, and Ed Decker, a critic of the LDS Church, both state that the repressive attitude of the church may—in extreme cases—lead to suicide, as in the case of 16-year-old Kip Eliason, who committed suicide because of the stresses that resulted when his church bishop told him that masturbation was sinful.[128][129]
In January 1982, the church's First Presidency issued a letter to local leaders stating that they had "interpreted oral sex as constituting an unnatural, impure, or unholy practice." The letter was not distributed to the general membership.[130] This letter also instructed local leaders not to inquire into the specifics of married members' sex lives. However, this portion of the letter was often ignored, and in response to letters of protest from members, another letter was issued to local leaders in October reiterating the prohibition on inquiring into specific sexual practices.[131]
Views on homosexuality
Scott Thumma and Affirmation.org contend that the LDS Church is homophobic.[132][133] Affirmation.org cites a faithful, celibate, gay Latter-day Saint who shortly before his suicide wrote: "Straight members have absolutely no idea what it is like to grow up gay in this church. It is a life of constant torment, self-hatred and internalized homophobia."[134]
"God Loveth His Children", a pamphlet produced by the LDS Church, acknowledges that many gays "have felt rejected because members of the Church did not always show love." It criticizes those members, and challenges gays to show love and kindness so the members can "change their attitudes and follow Christ more fully".[135]
Gay historian D. Michael Quinn has hypothesized that early church leaders had a more tolerant view of homosexuality. He writes that several early church leaders and prominent members, including Louie B. Felt, May Anderson, Evan Stephens, and presiding patriarch Joseph Fielding Smith, may have either had homosexual tendencies or were involved in homosexual relationships.[136] George Mitton and Rhett S. James do not dispute that some early members may have had homosexual tendencies, but they call Quinn's assertion of tolerance a distortion of church history that has little support from other historians. They state the current leadership of the church "is entirely consistent with the teachings of past leaders and with the scriptures."[137]
In the early 1970s, Ford McBride did research in electroshock therapy while a student at Brigham Young University (BYU); he performed it on volunteer homosexual students to help cure them of ego-dystonic sexual orientation.[138][139] This was a standard type of aversion therapy used to treat homosexuality,[140] which was considered a mental illness at the time.[141]
As church president, Gordon B. Hinckley encouraged church members to reach out to homosexuals with love and understanding.[142]
Affirmation.org has particularly criticized sexual repression of gays, both inside and outside of the church.
A letter dated June 20, 2008, sent to Mormon bishops and signed by the First Presidency, called on Mormons to donate "means and time" to a California ballot measure designed to defeat the state's May ruling allowing same-sex marriage. Richard and Joan Ostling point out that the LDS Church actively campaigns against same-sex marriage statutes, including donating $500,000 in 1998 towards a campaign to defeat such a referendum in Alaska.[143] The church's support (80 to 90 percent of the early volunteers who walked door-to-door in election precincts and as much as half of the nearly $40 million raised[144]) of California's Proposition 8 in 2008 sparked heated debate and protesting by gay-rights organizations.[3] The church's political involvement and stance on homosexuality is denounced by the 2010 documentary film 8: The Mormon Proposition.
Racism
Richard and Joan Ostling point to the church's practice, continued until 1978, of refusing the priesthood to blacks as evidence that past LDS Church policies were racist in nature. Before the change in policy, most other adult males in the LDS Church were given the priesthood; church policy precluded blacks from officiating in ordinances and from participating in church temple ceremonies.[145] Jerald and Sandra Tanner cite quotes from church leaders such as Brigham Young, who said, "You must not think, from what I say, that I am opposed to slavery. No! The negro is damned, and is to serve his master till God chooses to remove the curse of Ham".[146] The Tanners also illustrate church racism by quoting sections of the Book of Mormon which describe dark skin as a sign of a curse and a mark from God to distinguish a more righteous group of people from a less righteous group, and by citing passages describing white skin as "delightsome" while dark skin is portrayed as unenticing (2 Nephi 30:6). These references in the Book of Mormon refer to those presumed to be the ancestors of Native Americans, not people of African descent.[147] Joseph F. Smith, president of the church, wrote that people with dark skin were less faithful in the pre-mortal life, and as such, did not warrant the blessings of the priesthood.[148][149] The Tanners also cite other church leaders, historical and modern, who have spoken in favor of segregation and restrictions on admission to the priesthood for men of African descent.[148][150]
In 1978 Apostle Bruce R. McConkie told members to "[f]orget everything that I have said, or what President Brigham Young or President George Q. Cannon or whomsoever has said [about Blacks and the priesthood] .... We spoke with a limited understanding."[151] Some black members have made formal requests to the church to issue a statement, while other black members have argued against that effort.[152]
In 2003 Richard Abanes contended that the church tries to hide past racial practices, citing the 1981 change in the Book of Mormon, which stated that the Lamanites had become "a white and a delightsome people" to "a pure and a delightsome people" (2 Nephi 30:6).[153] In 1840, the "white and delightsome" of the original Book of Mormon text was changed by Joseph Smith to "pure and delightsome" in the third edition;[154] it reverted to "white and delightsome" after Smith's death in subsequent editions, as editions were based on one published in England. In 1981, the First Presidency approved a change that adopted the 1840 version by Smith, as saying that converts would become "pure and delightsome".[155]
In 2004 Darron Smith, a critical black church member, contends in his book, Black and Mormon, that the church "refuses to acknowledge and undo its racist past, and until it does that, members continue to suffer psychological damage from it" and that "the church has not done enough to rectify its racist past".[156] The large majority of black Mormons, however, say they are willing to look beyond the racist teachings and adhere to the church.[157] Church president Gordon B. Hinckley gave sermons against racism. In 2005 he taught that no one who utters denigrating remarks can consider himself a true disciple of Christ, and noted the irony of racial claims to the Melchizedek priesthood.[158]
The current LDS Church policy now admits blacks to the priesthood, and in December of 2013 published the following statement:
"Today, the Church disavows the theories advanced in the past that black skin is a sign of divine disfavor or curse, or that it reflects unrighteous actions in a premortal life; that mixed-race marriages are a sin; or that blacks or people of any other race or ethnicity are inferior in any way to anyone else. Church leaders today unequivocally condemn all racism, past and present, in any form."[159]
Gregory Prince and William Robert Wright state that these leaders were a product of their time and locale. They say that many leaders, including Smith, David O. McKay, and initially Brigham Young, were not opposed to blacks receiving the priesthood.[160] They further state that the policy was a practice supported by Christian scripture and was not a doctrine of the church.[161] Despite several church leaders throughout the 1950s and 1960s supporting its reversal, the policy was kept in place through 1978 because the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles felt that a revelation to the president of the church was needed to change it.[162]
Gender bias and sexism
Richard and Joan Ostling argue that the LDS Church treats women as inferior to men.[163] The Cult Awareness and Information Centre also point to comments such as those made by church leader Bruce R. McConkie, who wrote in 1966 that a "woman's primary place is in the home, where she is to rear children and abide by the righteous counsel of her husband".[164] The First Presidency and the Quorum of the Twelve espouse a complementarian view of gender roles.[165]
Claudia Lauper Bushman notes that, in the 1970s and 1980s, "just as American women pressed for greater influence", the LDS Church decreased the visibility and responsibilities of women in various areas including welfare, leadership, training, publishing, and policy setting. Despite this, Bushman asserts, "most LDS women tend to be good-natured and pragmatic: they work on the things that they can change and forget the rest."[166]
Jerald and Sandra Tanner point to comments by certain church leaders as evidence that women are subject to different rules regarding entry into heaven. They state that 19th-century leader Erastus Snow preached: "No woman will get into the celestial kingdom, except her husband receives her, if she is worthy to have a husband; and if not, somebody will receive her as a servant".[167] In Mormon doctrine, celestial marriage is a prerequisite for exaltation for members of either gender.[168]
Those who adopt humanist or feminist perspectives may view certain alleged or former LDS Church doctrines (including the spiritual status of blacks, polygamy, and the role of women in society) as racist or sexist.[169]
Historical authenticity of the Book of Mormon
Discussion regarding the historicity of the Book of Mormon often focuses on archaeological issues, some of which relate to the large size and the long time span of the civilizations mentioned in the book. Joseph Smith founded the movement in upstate New York in the 1820s. The faith drew its first converts while Smith was dictating the text of the Book of Mormon from golden plates which had reformed Egyptian writing on them which he said he found buried after being directed to their location by the Angel Moroni. The book described itself as a chronicle of early indigenous peoples of the Americas, known as the Nephites, portraying them as believing Israelites who had a belief in Christ many hundred years before his birth. According to the book, the Nephites are one of four groups (the others being the Lamanites, Jaredites, and Mulekites) which settled in the ancient Americas. The Nephites are described as a group of people that descended from or were associated with Nephi, the son of the prophet Lehi, who left Jerusalem at the urging of God c. 600 BC and traveled with his family to the Western Hemisphere, arriving in the Americas c. 589 BC. After the translation was complete, Smith said he returned the golden plates to the Angel Moroni.
A contemporary Mormon view is that these Israelite civilizations rose and fell in Mesoamerica.[170] Civilizations of their magnitude and duration would be expected to leave extensive archaeological records.[171] Several Mesoamerican civilizations did exist in the time period covered by the Book of Mormon, including the Olmec, Zapotec and Maya. The Olmec and Zapotec civilizations developed a writing system that may have served as the model for the later Mayan writing system, which became highly developed. The Maya developed a complex calendar and were advanced in astronomy and mathematics.[172][173]
The Book of Mormon mentions several animals, plants, and technologies for which there is no evidence in pre-Columbian America. These include asses, cattle, horses, oxen, sheep, swine, goats, elephants, wheat, barley,[174] silk,[175] steel,[176] brass, breast plates, chains, plows, swords, scimitars, and chariots.[177] The Smithsonian Institution stated in 1997 that "none of the principal food plants and domestic animals of the Old World (except the dog) were present in the New World before Columbus."[178]
Adherents of the Latter Day Saint movement give varied responses to these criticisms. Some point to what they claim is evidence for the presence of these items and locations.[179] Others invoke the limited geography model, regarding the events of the Book of Mormon as taking place in such a geographically limited area that no evidence should be expected. Some counter that the words used in the Book of Mormon refer not to the animals, plants and technologies that they do presently but to other similar items that did exist at the time.[180][181] These views are not directly supported by the LDS Church, but they do support archaeological efforts to further understand these situations, including research being performed by Brigham Young University (BYU) professors.[181]
See also
Footnotes
- "Skin Color in Mormon Scripture and Theology" "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-01-22. Retrieved 2009-02-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Sink, Mindy (September 6, 2003). "Religion Journal – Spiritual Issues Lead Many to the Net". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2012-02-11. Retrieved 11 May 2020.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- Feytser, Peter (November 20, 2008). "San Diego march for marriage equality draws 20,000 protesters". Gay and Lesbian Times (1091). Archived from the original on 2009-02-14. Retrieved December 6, 2011.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- "California and Same-Sex Marriage", Newsroom, LDS Church, 2008-06-30, retrieved 2011-12-06
- Tanner 1979, pp. 319–328
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 95. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- "Race and the Priesthood". lds.org. LDS Church. Retrieved April 14, 2015.
- "Mormonism and racial issues/Blacks and the priesthood/Origin of the priesthood ban". The FAIR Wiki. Foundation for Apologetic Information & Research. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 258–285
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 78–79. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Hardy, Carmon (1992). Solemn Covenant: The Mormon Polygamous Passage. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-01833-8. This was done to place obedience to God above conformity with society or "mammon." Breakaway polygamist groups took this a step further, parting with Salt Lake's leaders and practicing polygamy openly.
- Rood, Ron and Thatcher, Linda. "Statehood". Brief History of Utah. historytogo.utah.gov. .
- Wilford Woodruff Diary, 1890-09-25.
- Abanes 2003, pp. 385
- "IRR site "Finessing an Off-Putting Mormon Doctrine"". Archived from the original on May 3, 2011. Retrieved May 3, 2011.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- Gospel Principles. LDS Church. 1978.
- Gospel Principles. LDS CHurch. 1997.
- "Chapter 5: The Grand Destiny of the Faithful". Teachings of Presidents of the Church: Lorenzo Snow. 2011.
- Millet, Robert L.; Reynolds, Noel B. (1998), "Do Latter-day Saints believe that men and women can become gods?", Latter-day Christianity: 10 Basic Issues, Provo, Utah: Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies, ISBN 0934893322, OCLC 39732987,
President Snow often referred to this couplet as having been revealed to him by inspiration during the Nauvoo period of the church. See, for example, Deseret Weekly, 3 November 1894, 610; Deseret Weekly, 8 October 1898, 513; Deseret News, 15 June 1901, 177; and Journal History of the Church, Historical Department, LDS Church, Salt Lake City, 20 July 1901, 4.
- Lund, Gerald N. (February 1982), "Is President Lorenzo Snow's oft-repeated statement—'As man now is, God once was; as God now is, man may be'—accepted as official doctrine by the Church?", Ensign
- "Chapter 47: Exaltation", Gospel Principles (Salt Lake City, Utah: LDS Church, 2009).
- Eskridge 2002, pp. 291
- Van Wagoner 1986
- Van Wagoner 1986, pp. 92
- Tanner 1979, pp. 226–257
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 60–63. ISBN 978-0-06-066371-1.
- Compton 1997
- Compton 1997, pp. 486–534, 457–472, 342–363
- Compton 1997, pp. 457–485
- Bushman, Richard Lyman (2005). Joseph Smith: Rough Stone Rolling. New York, NY: Alfred A Knoff. p. 439. ISBN 978-1-4000-4270-8. OCLC 56922457.
There is no certain evidence that Joseph had sexual relations with any of the wives who were married to other men. They married because Joseph's kingdom grew with the size of his family, and those bonded to that family would be exalted with him.
- Goodstein, Laurie (10 November 2014). "It's Official: Mormon Founder Had Up to 40 Wives". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
[Joseph Smith Jr.] married Helen Mar Kimball, a daughter of two close friends, 'several months before her 15th birthday'.
- Turner, John G. (27 October 2012). "Polygamy, Brigham Young and His 55 Wives". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
The sheer variety of Brigham Young’s marriages makes it difficult to make sense of them. He married — was sealed to, in Mormon parlance — young (Clarissa Decker, 15) and old (Hannah Tapfield King, 65).
- Snodgrass, Mary Ellen (15 May 2009). Civil Disobedience: An Encyclopedic History of Dissidence in the United States (1st ed.). Rootledge. p. 220. ISBN 978-0765681270. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
The name of each wife is followed by her age at marriage, the place of marriage, and the year the couple married. ... Lorenzo Snow ... Sarah Minnie Jensen, 16, Salt Lake City, 1871
- Ulrich, Laurel Thatcher (10 January 2017). A House Full of Females: Plural Marriage and Women's Rights in Early Mormonism, 1835-1870. Knopf. p. 274. ISBN 978-0307594907. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
Wilford Woodfruff & (Emma Smith born March 1st 1838 at Diahman Davis County Missouri) was Sealed for time & Eternity by President Brigham Young at 7 oclock P.M. March 13, 1853.
- Hacker, J. David; Hilde, Libra; Jones, James Holland (2010). "Nuptiality Measures for the White Population of the United States, 1850–1880". The Journal of Southern History. National Institute of Health. 76 (1): 39–70. PMC 3002115. PMID 21170276.
- Abanes 2003, pp. 336–342
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 73–74. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Quinn, Michael (1997). The Mormon Hierarchy: Extensions of Power. Signature Books. pp. 182–183, 790–810. ISBN 1-56085-060-4.
- Joseph F. Smith, "A profitable and enjoyable Conference—Privilege of the people—The Gospel includes temporal as well as spiritual salvation—Official statement sustained", Conference Report, April 1904, p. 97.
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 331. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Young, Brigham (April 9, 1852), "Self-Government—Mysteries—Recreation and Amusements, not in Themselves Sinful—Tithing—Adam, Our Father and Our God", in Watt, G.D., Journal of Discourses, by Brigham Young, President of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, His Two Counsellors, the Twelve Apostles, and Others, vol. 1, Liverpool: F.D. & S.W. Richards, 1854, pp. 46–53,
- Millennial Star 16:534, 28 August 1854.
- Journal of Thomas Evans Jeremy Sr., September 30, 1852 Bergera 1980.
- Charles W. Penrose, "Our Father Adam", Improvement Era (September 1902): 873. GospeLink <http://gospelink.com/library/browse?cat_id=6%5B%5D> reprinted in Charles W. Penrose, "Our Father Adam", Millennial Star (11 December 1902): 785–90. (this paragraph from p. 789).
- Conference Report, p. 115 (October 1–3, 1976)
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 332. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Brigham Young, Journal of Discourses, Vol 4 p. 53
- Snow, Lowell M, "Blood Atonement", Encyclopedia of Mormonism, retrieved 2007-03-08
- Grant, Jedediah M. (March 12, 1854), "Discourse", Deseret News (published July 27, 1854), 4 (20), pp. 1–2, archived from the original on December 15, 2012, retrieved October 22, 2019.
- Kimball, Heber C. (January 11, 1857), "The Body of Christ-Parable of the Vine-A Wile Enthusiastic Spirit Not of God-The Saints Should Not Unwisely Expose Each Others' Follies", in Watt, G.D. (ed.), Journal of Discourses by Brigham Young, President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, His Two Counsellors, and the Twelve Apostles, 4, Liverpool: S.W. Richards (published 1857), pp. 164–81.
- Grant, Jedediah M. (September 21, 1856), "Rebuking Iniquity", in Watt, G.D. (ed.), Journal of Discourses by Brigham Young, President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, His Two Counsellors, and the Twelve Apostles, 4, Liverpool: S.W. Richards (published 1857), pp. 49–51.
- Packer, Boyd K. (November 1995). "The Brilliant Morning of Forgiveness". Ensign.
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 164–165. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Pyle, Hugh F. (2000). The Truth about Mormonism. Sword of the Lord. pp. 7–8. ISBN 0-87398-845-0.
- Ryssman, Orin (2006), "The Human Cost of Mormon Temple Marriage Policies", IRR.org, Institute for Religious Research, retrieved 2007-12-11
- "Temple Ritual Changed...Again", Salt Lake City Messenger, Utah Lighthouse Ministry, June 2005, retrieved 2012-01-17
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 178. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- McKeever, Bill, "Tithing by Coercion", MRM.org, Mormonism Research Ministry, retrieved 2013-01-17
- "Else what shall they do which are baptized for the dead, if the dead rise not at all? why are they then baptized for the dead?" (1 Corinthians 15:29)
- "Baptism for the Dead", Gospel Study: Study by Topic, LDS Church
- McElveen, Floyd C. (1997). The Mormon Illusion: What the Bible Says About the Latter-Day Saints. Kregel Publications. pp. 110–112. ISBN 0-8254-3192-1.
- Did Jesus Establish Baptism for the Dead? at irr.org Archived March 14, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- Muth, Chad (2008-05-02). "Vatican letter directs bishops to keep parish records from Mormons". Catholic News Service. U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops. Archived from the original on 2008-05-13. Retrieved 2011-12-06.
- Urbina, Ian (2003-12-21). "New York Times: Again, Jews Fault Mormons Over Posthumous Baptisms". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- Bushman 2006, pp. 86
- "The LDS Agreement: the Issue of The Mormon Baptisms of Jewish Holocaust Victims", Jewishgen.org, Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust, retrieved 2011-01-25
- "CNN news article on baptism of holocaust victims". Archived from the original on December 18, 2008.
- Purdy, Michael (September 2, 2010), "Jewish, Mormon leaders issue joint statement", Deseret News
- Dobner, Jennifer (September 1, 2010). "Mormon, Jewish leaders tackle proxy baptism". The Salt Lake Tribune. (AP).
- Tanner 1979, pp. 534–547
- Tanner 1979, pp. 535
- Tanner 1979
- Buerger, David John (2002), The Mysteries of Godliness: A History of Mormon Temple Worship (2nd ed.), Salt Lake City: Signature Books, ISBN 1-56085-176-7, pp. 139-40
- "Changes to the Endowment ordinance", FairMormon, retrieved 2014-02-17
- Irvine, Martha; Tanner, Robert (21 October 2007). "Sexual Misconduct Plagues US Schools". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2008-04-12.
- Scout's Honor: Sexual Abuse in America's Most Trusted Institution, Patrick Boyle, 1995
- News, Deseret (December 15, 2017). "In our opinion: Mormon bishop interviews are not 'invitations' for abuse". Deseret News.
- "Statement from the LDS Church on Mormon bishops' interviews". The Salt Lake Tribune.
- Tanner, Courtney (30 March 2018). "'There is no limit to the gross, sexually explicit questions' — Big crowd marches through Salt Lake City calling for an end to one-on-one Mormon bishop interviews with youths". The Salt Lake Tribune.
- Stack, Peggy Fletcher. "Order to release financial data has LDS Church, courts on collision course". Salt Lake Tribune. July 13, 2007. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-07-15. Retrieved 2007-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Retrieved 13 July 2007. (PDF version Archived 2011-07-13 at the Wayback Machine at kosnoff.com)
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 113–129. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 36
- Tanner 1987, pp. 516–528
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Great Britain Financial Statements Archived 2005-12-25 at the Wayback Machine - provided by the Charity Commission based on the Charities Act
- "Charities Listings - Basic search results". www.cra-arc.gc.ca.
- Cantwell, Robert W. (May 2007). "Church Auditing Department Report, 2006". Ensign. 37 (5): 6. Retrieved 2011-12-06.
The Church Auditing Department has been granted access to all records and systems necessary to evaluate the adequacy of controls over receipts of funds, expenditures, and safeguarding of Church assets. The Church Auditing Department is independent of all other Church departments and operations, and the staff consists of certified public accountants, certified internal auditors, certified information systems auditors, and other credentialed professionals. Based upon audits performed, the Church Auditing Department is of the opinion that, in all material respects, contributions received, expenditures made, and assets of the Church for the year 2006 have been recorded and administered in accordance with appropriate accounting practices, approved budgets, and Church policies and procedures.
- "Why Deseret Trust Company?" Archived 2015-01-15 at the Wayback Machine Accessed 15 May 2007.
- Belo Corp Form 8-K. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-04-30. Retrieved 2008-06-04.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Accessed 16 May 2007.
- "Financial Planning". finserve.byu.edu. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-05-27. Retrieved 2008-06-04.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Accessed 16 May 2007.
- "Finance". accredit.byu.edu. See page 9 of pdf document available at "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-12. Retrieved 2009-02-05.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Accessed 16 May 2007.
- "Lay Leadership: Volunteer Ministry of the Church", Newsroom, LDS Church
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999). Mormon America. Harper Collins. p. 178. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999). Mormon America. Harper Collins. pp. 395–400. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- If confirmed, the $100 billion net worth would exceed the combined net worths of the world's largest university endowment (Harvard University) and the world's largest philanthropic foundation (Gates Foundation). "Mormon Church has misled members on $100 billion tax-exempt investment fund, whistleblower alleges". Washington Post.
- Due to the categorization of Ensign Peak Advisors as an "integrated auxiliary of a church", not a public foundation."$100 Billion In Mormon Till Does Not Merit IRS Attention". Forbes.
- "First Presidency Statement on Church Finances: Statement provided in response to media stories", Newsroom, LDS Church, December 17, 2019
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 351–370. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- "LDS Church Excommunicates DNA Author". affirmation.org. Affirmation: Gay & Lesbian Mormons. August 2005. Archived from the original on 2011-10-24. Retrieved 2011-12-06.
- Wolverton, Susan (2004). Having Visions: The Book of Mormon : Translated and Exposed in Plain English. Algora. p. 321. ISBN 0-87586-310-8.
- "AAUP Academic Censure List". www.aaup.org. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
- Abanes 2003, pp. 418
- Sunstone, 16:2, no.88 (August 1992), p. 63. As quoted in Ostling and Ostling, p. 354.
- Krakauer, J. (2004). Under the Banner of Heaven: A Story of Violent Faith. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 364. ISBN 978-1-4000-7899-8. Retrieved September 24, 2018.
- Ostling, R.N.; Ostling, J.K. (2007). Mormon America: the power and the promise. HarperCollins. p. 261. ISBN 978-0-06-143295-8. Retrieved September 24, 2018.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 37
- Walch, Tad (2005-04-04), "Miller funding Joseph Smith project", Deseret News, retrieved 2011-12-06
- Jerald & Sandra Tanner, Changes in Joseph Smith's History, Salt Lake City: Utah Lighthouse Ministry, 1965.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 29–34
- D. Michael Quinn, "Jerald and Sandra Tanner's Distorted View of Mormonism: A Response to Mormonism—Shadow or Reality?".
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (2004). Curse of Cain? Racism in the Mormon Church. Utah Lighthouse Ministry. Chapter 10, part 2, p. 311.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 67–72
- Tanner 1979, pp. 129
- Tanner 1979, pp. 86–87
- Norwood, L. Ara (1990), "Joseph Smith and the Origins of the Book of Mormon", FARMS Review, 2 (1): 187–204, archived from the original on 2011-07-18, retrieved 2011-12-06
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 248. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Godfrey 1994
"Zelph was a white Lamanite, a man of God who was a warrior and chieftain under the great prophet Onandagus who was known from the [hill Cumorah is crossed out in the manuscript] eastern Sea, to the Rocky Mountains. He was killed in battle, by the arrow found among his ribs, during a [last crossed out] great struggle with the Lamanites" [and Nephites crossed out]." - D. Michael Quinn On Being A Mormon Historian p. 21: Lecture to BYU Student History Association, Fall 1981
- Allen Roberts, Private Eye Weekly, October 20, 1993, p. 12. Quoted in Jerald and Sandra Tanner, "Legacy: A Distorted View of Mormon History," Salt Lake City Messenger (#88), May 1995, p. 4.
- Hallwas, John (1995). Cultures in Conflict: A Documentary History of the Mormon War in Illinois. Utah State University Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 0-87421-272-3.
- "The Joseph Smith Papers: Quotes About the Project". lds.org. Archived from the original on October 24, 2012. Retrieved 2011-12-06.
We work on the assumption that the closer you get to Joseph Smith in the sources, the stronger he will appear, rather than the reverse, as is so often assumed by critics. His warmth, his sincerity, and his absolute devotion to the cause come through page after page.
- Rischin, Moses. "The New Mormon History." The American West (Mar. 1969): 49.
- The New Mormon History. Ed. D. Michael Quinn. Salt Lake City: Signature Books, 1992. (vii).
- Paulson, Matthew A. (2000). Breaking the Mormon Code: A Critique of Mormon Scholarship. Wingspan Press. pp. 27–29. ISBN 1-59594-067-7.
- Gruss, Edmond C. (2006). What Every Mormon (and Non-Mormon) Should Know. Xulon Press. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-60034-163-2.
- "BYU College of Religious Education". Religion.byu.edu. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved 2011-01-25.
- Laake, Deborah (1994). Secret Ceremonies: A Mormon Woman's Intimate Diary of Marriage and Beyond. Dell Publishing. ISBN 0-688-09304-3.
- McDannell, Colleen (1995). Material Christianity: Religion and Popular Culture in America. Yale University Press. pp. 214–218. ISBN 0-300-07499-9.
- "Affirmation article in Kip Eliason suicide". Archived from the original on 2007-12-12. Retrieved 2007-12-08.
- Ed Decker (1982). The God Makers (VHS). Jeremiah Films.
- Letter of January 5, 1982 to all Stake Presidents and Bishops. BYU Library Special Collections.
- Letter of October 15, 1982 to all Stake Presidents and Bishops. BYU Library Special Collections.
- Thumma, Scott (2004). Gay Religion. Rowman Altamira. pp. 99–113. ISBN 0-7591-0326-7.
- "Affirmation: a Gay and Lesbian Mormon organization". Archived from the original on 2007-10-16. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- Matis, Stuart Letter to a Cousin Archived 2009-02-20 at the Wayback Machine
- God Loveth His Children, LDS Church, 2007, retrieved 2011-12-06
- Quinn, D. Michael (2001). Same-Sex Dynamics Among Nineteenth-Century Americans: A Mormon Example. University of Illinois Press. pp. 195–264. ISBN 0-252-06958-7.
- George L. Mitton, Rhett S. James A Response to D. Michael Quinn's Homosexual Distortion of Latter-day Saint History Archived August 8, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Review of Same-Sex Dynamics among Nineteenth-Century Americans: A Mormon Example by D. Michael Quinn Provo, Utah: Maxwell Institute, 1998. Pp. 141–263
- "Shock Therapy Interview". salamandersociety.com. The Salamander Society (aka "The Latter Day Lampoon").
- "You searched for reparative therapy".
- Seligman, Martin E.P., What You Can Change and What You Can't: The Complete Guide to Self Improvement. Knopf, 1993; ISBN 0-679-41024-4
- Homosexuality not a disease to be cured. Reproductive Health Matters, November 2004
- Oaks, Dallin H. (October 1995). "Same-Gender Attraction". Ensign. 25 (10): 7.
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. p. 172. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Jesse McKinley and Kirk Johnson (November 14, 2008), "Mormons Tipped Scale in Ban on Gay Marriage", The New York Times, retrieved February 14, 2012
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 94–108. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- Tanner 1979, pp. 304 (New York Herald, May 4, 1855, as cited in Dialogue, Spring 1973, p.56)
- "The Charge of 'Racism' in the Book of Mormon". Blacklds.org. Retrieved 2011-12-13.
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (2004). Curse of Cain? Racism in the Mormon Church. Utah Lighthouse Ministry.
- "Web site with detailed documentation of racist acts in LDS history". Retrieved 2007-12-05.
- "Web site with detailed documentation of recent racist LDS policies". Retrieved 2007-12-05.
- Bruce R. McConkie, 1978 (All Are Alike Unto God, A Symposium on the Book of Mormon, The Second Annual Church Educational System Religious Educator's Symposium, August 17–19, 1978.)
- Broadway, Bill (1998-05-30). "Black Mormons Resist Apology Talk". The Washington Post.
- Abanes 2003, pp. 420
- Smith, Joseph (1840). Book of Mormon (3rd revised ed.). Nauvoo, Illinois: Robinson and Smith. p. 115. ISBN 1-60135-713-3. Retrieved 2009-08-03.
- The wording "white and a delightsome" was introduced in the 1st edition of the Book of Mormon in 1830. This was changed to "pure and a delightsome" in the 3rd edition in 1840. The 1841 and 1849 European editions of the Book of Mormon were printed in England by the Twelve Apostles, and were the Kirtland 2nd edition with Anglicized spellings. Future LDS editions were based on the European editions until the church issued a major reworking in 1981. Crawley, Peter (1997). A Descriptive Bibliography of the Mormon Church, Volume One 1830-1847. Provo, Utah: Religious Studies Center, Brigham Young University. p. 151. ISBN 1-57008-395-9. Archived from the original on 2011-06-11. Retrieved 2009-02-12.
- Smith, Darron (2004). Black and Mormon. University of Illinois Press. p. 7. ISBN 0-252-02947-X.
- Ramirez, Margaret (2005-07-26). "Mormon past steeped in racism: Some black members want church to denounce racist doctrines". Chicago Tribune.
- Hinckley, Gordon B. (May 2006). "The Need for Greater Kindness". Ensign.
- "Race and the Priesthood". www.churchofjesuschrist.org. Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- Prince, Gregory A.; Wright, William Robert (2005). David O. McKay and the Rise of Modern Mormonism. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-87480-822-3.
- Prince, Gregory A.; Wright, William Robert (2005). David O. McKay and the Rise of Modern Mormonism. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-87480-822-3.
- Prince, Gregory A.; Wright, William Robert (2005). David O. McKay and the Rise of Modern Mormonism. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-87480-822-3.
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999-10-20). Mormon America. pp. 159–172. ISBN 0-06-066371-5.
- "The Role of Women in Mormonism". Caic.org.au. 1995-03-27. Retrieved 2011-01-25.
- The Family: A Proclamation to the World, LDS Church, 1995, retrieved 2011-12-06
- Bushman 2006, pp. 113
- "UTLM web site describing LDS treatment of women". Retrieved 2007-12-04.
- "Chapter 47: Exaltation". www.churchofjesuschrist.org.
- Hanks, Maxine (1992), Women and Authority: re-emerging Mormon feminism, Salt Lake City, Utah: Signature Books, ISBN 1-56085-014-0, OCLC 25509094
- Allen, Joseph L. (2003), Sacred Sites: Searching for Book of Mormon Lands, American Fork, Utah: Covenant Communications, ISBN 1591562724, OCLC 54031905
- Fagan, Garrett G.; Feder, Kenneth L. (1 December 2006). "Crusading against straw men: an alternative view of alternative archaeologies: response to Holtorf (2005)". World Archaeology. 38 (4): 718–729. doi:10.1080/00438240600963528. S2CID 162321776.
- Macri, Martha J. (1996), "Maya and Other Mesoamerican Scripts", in Daniels, Peter T.; Bright, William (eds.), The World's Writing Systems, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 172–182, ISBN 0195079930, OCLC 31969720
- Rogers, Henry (2005), Writing Systems: A Linguistic Approach, Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing, ISBN 0631234632, OCLC 53831495.
- Mosiah 7:22.
- 1 Nephi 14:7
- 1 Nephi 4:9
- Alma 18:9
- Welch, John W., ed. (1992), Reexploring the Book of Mormon, Provo, Utah: Foundation for Ancient Research and Mormon Studies, ISBN 0875796001, OCLC 25131320, archived from the original on 2015-11-24, retrieved 2016-03-13
- AllAboutMormons.Com Webmaster (January 19, 2008), "Questions: The Book of Mormon mentions...", AllAboutMormons.com, El Santo Gringo
- Bennett, Robert R. (2000), "Naming by Analogy", Horses in the Book of Mormon, FARMS/Neal A. Maxwell Institute for Religious Scholarship, archived from the original on 2015-02-13, retrieved 2016-03-13
References
- Abanes, Richard (2003), One Nation Under Gods: A History of the Mormon Church, New York: Four Walls Eight Windows, ISBN 978-1-56858-283-2, OCLC 52863716
- Beckwith, Francis (2002), Mosser, Carl; Owen, Paul (eds.), The New Mormon Challenge, Grand Rapids, Michigan: Zondervan, ISBN 978-0-310-23194-3, OCLC 48428864
- Bennett, John C. (1842), The History of the Saints; or An Exposé of Joe Smith and Mormonism, Boston; New York: Leland & Whiting; Bradbury, Soden, OCLC 11081448
- Brodie, Fawn M. (1995) [1945], No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith (2nd, rev. and enl. ed.), New York: Vintage Books, ISBN 978-0-679-73054-5, OCLC 36510049
- Bushman, Claudia L. (2006), Contemporary Mormonism: Latter-day Saints in Modern America, Westport, Connecticut: Praeger Publishers, ISBN 0-275-98933-X, OCLC 61178156
- Eskridge, Jr., William N. (2002) [1999], Gaylaw: Challenging the Apartheid of the Closet, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-00804-5, OCLC 49204149
- Howe, Eber D. (1834), Mormonism Unvailed, Painesville, Ohio: Printed and published by the author, OCLC 10395314. Online copy
- Krakauer, Jon (2003), Under the Banner of Heaven: A Story of Violent Faith, New York: Doubleday, ISBN 978-0-385-50951-0, OCLC 51769258
- Newell, Linda King (1994) [1984], Mormon Enigma: Emma Hale Smith (2nd ed.), Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois Press, ISBN 978-0-252-06291-9, OCLC 28721939
- Ostling, Richard and Joan (1999), Mormon America, San Francisco, CA: HarperSanFrancisco, ISBN 978-0-06-066371-1, OCLC 41380398
- Quinn, D. Michael (1994), The Mormon Hierarchy: Origins of Power, Salt Lake City, UT: Signature Books, ISBN 978-1-56085-056-4, OCLC 30155116
- Quinn, D. Michael (1997), The Mormon Hierarchy: Extensions of Power, Salt Lake City, UT: Signature Books, ISBN 978-1-56085-060-1, OCLC 32168110
- Sillito, John R.; Staker, Susan (2002), Mormon Mavericks: Essays on Dissenters, Salt Lake City, Utah: Signature Books, ISBN 978-1-56085-154-7, OCLC 47805160
- Smith, Andrew F. (1997), The Saintly Scoundrel: The Life and Times of Dr. John Cook Bennett, Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois Press, ISBN 978-0-252-02282-1, OCLC 34721478
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1980), The Changing World of Mormonism, Chicago: Moody Press, ISBN 0-8024-1234-3, OCLC 5239408
- Tanner, Jerald and Sandra (1982) [1972], Mormonism - Shadow or Reality? (4th, enl. and rev ed.), Salt Lake City, UT: Utah Lighthouse Ministry, OCLC 15339569
- Van Wagoner, Richard S. (Summer 1986), "Sarah Pratt: The Shaping of an Apostate", Dialogue: A Journal of Mormon Thought, 19 (2): 69–99, ISBN 9781591562849, OCLC 366662945, archived from the original on 2009-02-21, retrieved 2018-12-03
- Wymetal, Wilhelm Ritter von (1886), Joseph Smith, the Prophet, His Family, and His Friends: A Study Based on Facts and Documents, Salt Lake City, UT: Tribune Printing and Publishing Company, OCLC 1538597. Online copy at olivercowdery.com
Further reading
- Millet, Robert (2011), No Weapon Shall Prosper: New Light on Sensitive Issues, Brigham Young University, ISBN 978-0-8425-2794-1, archived from the original on 2013-12-28, retrieved 2013-12-28
External links
- Critical
- Utah Lighthouse Ministry – Maintained by Sandra Tanner
- MormonThink
- Apologetic