Democratic Kampuchea
Kampuchea, officially from 5 January 1976 the Democratic Kampuchea (DK), also described as the Genocidal Regime (Khmer: របបប្រល័យពូជសាសន៍), was the Cambodian state under a one-party Marxist-Leninist totalitarian dictatorship that existed between 1975 and 1979. It was controlled by the Khmer Rouge (KR), the name popularly given to the followers of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK), and was founded when KR forces defeated the Khmer Republic of Lon Nol in 1975.
| 1975–1979 | |||||||||||
 National Emblem
| |||||||||||
.svg.png.webp) Location of Democratic Kampuchea | |||||||||||
| Capital and largest city | Phnom Penh | ||||||||||
| Official languages | Khmer | ||||||||||
| Religion | State atheism[1] | ||||||||||
| Government | Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic under a totalitarian dictatorship (1975–1979)[2][3][4] | ||||||||||
| Party General Secretary | |||||||||||
• 1975–1979 | Pol Pot | ||||||||||
| Chairman of the State Presidium | |||||||||||
• 1975–1976 | Norodom Sihanouk | ||||||||||
• 1976–1979 | Khieu Samphan | ||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||
• 1975–1976 | Penn Nouth | ||||||||||
• 1976–1979 | Pol Pot | ||||||||||
| Legislature | People's Representative Assembly | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||
| 17 April 1975 | |||||||||||
• Proclamation | 5 January 1976 | ||||||||||
| 7 January 1979 | |||||||||||
| 22 June 1982 | |||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 181,035 km2 (69,898 sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Currency | None as money was abolished | ||||||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||||||
| Calling code | 855 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Cambodia | ||||||||||
Between 1975 and 1979, the state and its ruling Khmer Rouge regime was responsible for the deaths of millions of Cambodians through forced labour and genocide. The KR lost control of most Cambodian territory to Vietnamese occupation. From 1979 to 1982, Democratic Kampuchea survived as a rump state supported by China. In June 1982, the Khmer Rouge formed the Coalition Government of Democratic Kampuchea with two non-communist guerrilla factions, which retained international recognition.[5] The state was renamed Cambodia in 1990 in the run up to the UN-sponsored 1991 Paris Peace Agreements.
Historical context

In 1970, Premier Lon Nol and the National Assembly deposed Norodom Sihanouk as the head of state. Sihanouk, opposing the new government, entered into an alliance with the Khmer Rouge against them. Taking advantage of Vietnamese occupation of eastern Cambodia, massive United States carpet bombing ranging across the country, and Sihanouk's reputation, the Khmer Rouge were able to present themselves as a peace-oriented party in a coalition that represented the majority of the people. Thus, with large popular support in the countryside, the capital Phnom Penh finally fell on 17 April 1975 to the Khmer Rouge. The KR continued to use Sihanouk as a figurehead for the government until 2 April 1976 when Sihanouk resigned as head of state. Sihanouk remained under comfortable, but insecure, house arrest in Phnom Penh, until late in the war with Vietnam he departed for the United States where he made Democratic Kampuchea's case before the Security Council. He eventually relocated to China.
Thus, prior to the KR's takeover of Phnom Penh in 1975 and the start of the Zero Years, Cambodia had already been involved in the Third Indochina War and tensions between Cambodia and Vietnam were growing due to differences in communist ideology and the incursion of Vietnamese military presence within Cambodian borders. The context of war destabilised the country and displaced Cambodians while making available to the KR the weapons of war. The KR leveraged on the devastation caused by the war to recruit members and used this past violence to justify the similarly, if not more, violent and radical policies of the regime.[7] The birth of DK and its propensity for violence must be understood against this backdrop of war that likely played a contributing factor in hardening the population against such violence and simultaneously increasing their tolerance and hunger for it. Early explanations for the KR brutality suggest that the KR had been radicalised during the war years and later turned this radical understanding of society and violence onto their countrymen.[8] This backdrop of violence and brutality arguably also affected everyday Cambodians, priming them for the violence that they themselves perpetrated under the KR regime.
Phnom Penh fell on 17 April 1975. Sihanouk was given the symbolic position of Head of State for the new government of Democratic Kampuchea and, in September 1975, returned to Phnom Penh from exile in Beijing.[9] After a trip abroad, during which he visited several communist countries and recommended the recognition of Democratic Kampuchea, Sihanouk returned again to Cambodia at the end of 1975. A year after the Khmer Rouge takeover, Sihanouk resigned in mid-April 1976 (made retroactive to 2 April 1976) and was placed under house arrest, where he remained until 1979, and the Khmer Rouge remained in sole control.[10]
Organisation of Democratic Kampuchea
On 5 January 1976 the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK) promulgated the Constitution of Democratic Kampuchea.[11] The Constitution provided for a Kampuchean People's Representative Assembly (KPRA) to be elected by secret ballot in direct general elections and a State Praesidium to be selected and appointed every five years by the KPRA. The KPRA met only once, a three-day session in April 1976. However, members of the KPRA were never elected, as the Central Committee of the CPK appointed the chairman and other high officials both to it and to the State Praesidium. Plans for elections of members were discussed, but the 250 members of the KPRA were in fact appointed by the upper echelon of CPK.
Democratic Kampuchea was an atheist state, but Buddhist influences still persisted.[12] All religions were banned and the repression of adherents of Islam,[13] Christianity,[14] and Buddhism was extensive. Nearly 25,000 Buddhist monks were massacred by the regime.[15]
All power belonged to the Standing Committee of CPK, the membership of which comprised the Secretary and Prime Minister Pol Pot, his Deputy Secretary Nuon Chea and seven others. It was known also as the "Centre", the "Organisation" or "Angkar", and its daily work was conducted from Office 870 in Phnom Penh. For almost two years after the takeover, the Khmer Rouge continued to refer to itself as simply Angkar. It was only in a March 1977 speech that Pol Pot revealed the CPK's existence. It was also around that time that it was confirmed that Pol Pot was the same person as Saloth Sar, who had long been cited as the CPK's general secretary.
Administrative
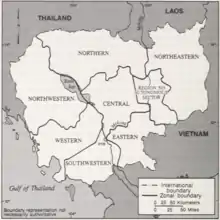
The Khmer Rouge government did away with all former Cambodian traditional administrative divisions. Instead of provinces, Democratic Kampuchea was divided into geographic zones, derived from divisions established by the Khmer Rouge when they fought against the ill-fated Khmer Republic led by General Lon Nol.[16] There were seven zones, namely the Northwest, the North, the Northeast, the East, the Southwest, the West and the Center, plus two Special Regions, i.e. the Kratie Special Region no 505 and (before mid-1977) the Siemreap Special Region no 106.[17] The regions were subdivided into smaller areas or damban. These were known by numbers, which were assigned without a seemingly coherent pattern. Villages were also subdivided into 'groups' (krom) of 15–20 households who were led by a group leader (Meh Krom).
Legal
The Khmer Rouge destroyed the legal and judicial structures of the Khmer Republic. There were no courts, judges, laws or trials in Democratic Kampuchea. The "people’s courts" stipulated in Article 9 of the Constitution were never established. The old legal structures were replaced by re-education, interrogation and security centres where former Khmer Republic officials and supporters as well as others were detained and executed.[18]
International relations
The Democratic Kampuchea regime maintained close ties with China (its main backer) and to a lesser extent with North Korea. In 1977, in a message congratulating the Cambodian comrades on the 17th anniversary of the CKP, Kim Jong-il congratulated the Cambodian people for having "wiped out [...] counterrevolutionary group of spies who had committed subversive activities and sabotage".[19] Only China, North Korea, Egypt, Albania, Cuba, Laos, Vietnam (until December 1977), Romania and Yugoslavia had diplomatic missions in Phnom Penh.[20]
Military
.svg.png.webp)
During the Democratic Kampuchea days, the 68,000-member Khmer Rouge-dominated CPNLAF (Cambodian People's National Liberation Armed Forces) force, which completed its conquest of Phnom Penh, Cambodia in April 1975, was renamed the RAK (Revolutionary Army of Kampuchea). This name dated back to the peasant uprising that broke out in the Samlot district of Battambang Province in 1967. Under its long-time commander and then Minister of Defense Son Sen, the RAK had 230 battalions in 35 to 40 regiments and in 12 to 14 brigades. The command structure in units was based on three-person committees in which the political commissar ranked higher than the military commander and his deputy.
Cambodia was divided into zones and special sectors by the RAK, the boundaries of which changed slightly over the years. Within these areas, the RAK's first task was the peremptory execution of former Khmer National Armed Forces (FANK) officers and of their families, without trial or fanfare to eliminate KR enemies. The RAK's next priority was to consolidate into a national army the separate forces that were operating more or less autonomously in the various zones. The Khmer Rouge units were commanded by zonal secretaries who were simultaneously party and military officers, some of whom were said to have manifested "warlord characteristics". Troops from one zone were frequently sent to another zone to enforce discipline. These efforts to discipline zonal secretaries and their dissident or ideologically impure cadres gave rise to the purges that were to decimate RAK ranks, to undermine the morale of the victorious army, and to generate the seeds of rebellion.[21] In this way, the KR used the RAK to sustain and fuel its violent campaign.
Khmer Rouge ideology and its relationship to violence
Ideological influences


The Khmer Rouge was heavily influenced by Maoism,[22] the French Communist Party and the writings of Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin[23] as well as ideas of Khmer racial superiority.[24] Turning to look at the roots of the ideology which guided the KR intellectuals behind the revolution, it becomes evident that the roots of such radical thought can be traced to an education in France that started many of the top KR officials on the road to thinking that communism demanded violence.[25][26] Influences from the French Revolution led many who studied in Paris to believe that Marxist political theory that was based on class struggle could be applied to the national cause in Cambodia.[27] The premise of class struggle sowed the ideological seeds for violence and made violence appear all the more necessary for the revolution to succeed. In addition, because many of the top KR officials such as Pol Pot, Khieu Samphan and Kang Kek Iew (also known as Duch) were educators and intellectuals, they were being unable to connect with the masses and were alienated upon their return to Cambodia, further fuelling their radical thought.[28] However, it is important to note that Vickery downplays the importance of personalities in explaining the DK phenomenon, noting that DK leaders were never considered evil by prewar contemporaries. Nonetheless, this view is challenged by some including Rithy Phan, who after interviewing Duch, the head of Tuol Sleng, seems to suggest that Duch was a fearsome individual who preyed on and seized upon the weaknesses of others.[29][30] All in all, the historical context of civil war, coupled with the ideological ferment in Cambodian intellectuals returning from France, set the stage for the KR revolution and the violence that it would propagate.
_before_the_Extraordinary_Chambers_in_the_Courts_of_Cambodia_-_20091126.jpg.webp)
Operationalising ideology through violence
The Khmer Rouge was determined to turn the country into a nation of peasants in which the corruption and "parasitism" of city life would be completely uprooted. Communalisation was implemented by putting men, women and children to work in the fields, which disrupted family life. The regime claimed to have "liberated" women through this process and according to Zal Karkaria "appeared to have implemented Friedrich Engels's doctrine in its purest form: women produced, therefore they had been freed".[6] On the surface, society in Democratic Kampuchea was strictly egalitarian. However, this was not the case in practice as members and candidate members of the CPK, local-level leaders of poor peasant background who collaborated with the Angkar and members of the armed forces had a higher standard of living than the rest of the population.
Under the leadership of Pol Pot, cities were emptied, organised religion was abolished, and private property, money and markets were eliminated.[31] An unprecedented genocide campaign ensued that led to annihilation of about 25% of the country's population, with much of the killing being motivated by Khmer Rouge ideology which urged "disproportionate revenge" against rich and powerful oppressors.[32][33][34] Victims included such class enemies as rich capitalists, professionals, intellectuals, police and government employees (including most of Lon Nol's leadership),[35] along with ethnic minorities such as Chinese, Vietnamese, Lao and Cham.[36]
The Khmer Rouge regime was one of the most brutal in recorded history, especially considering how briefly it ruled the country. Based on an analysis of mass grave sites, the DC-Cam Mapping Program and Yale University estimated that the Khmer Rouge murdered over 1.38 million people.[37][38] If deaths from disease and starvation are counted, as many as 2.5 million people died as a result of Khmer Rouge rule.[39] This included most of the country's minority populations. The country's ethnic Vietnamese population was almost completely wiped out; nearly all ethnic Vietnamese who did not flee immediately after the takeover were exterminated. One prison, Security Prison 21, now the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum, held 17,000 people at one time or another, of whom only seven adults survived.[40]
In 1997, the Cambodian government asked the United Nations for assistance in setting up a genocide tribunal called the Extraordinary Chambers in the Courts of Cambodia.[41][42][43] The prosecution presented the names of five possible suspects to the investigating judges on July 18, 2007.[43] On 26 July 2010, Kang Kek Iew (Comrade Duch), director of the Security Prison 21 camp, where more than 14,000 people were tortured and then murdered, mostly at nearby Choeung Ek, was convicted of crimes against humanity and sentenced to 35 years. His sentence was reduced to 19 years in part because he had been behind bars for 11 years.[44] Nuon Chea, second in command of the Khmer Rouge and its most senior surviving member, was charged with war crimes and crimes against humanity, but not charged with genocide. On 7 August 2014, he was convicted of crimes against humanity by the Khmer Rouge Tribunal and received a life sentence.[45][46]
Explaining the violence
Violence as a collective action
While the historical context and ideological underpinnings of the KR regime provide reasons for why the Cambodian genocide occurred, more explanations must be had for the widespread violence that was carried out by Cambodians against Cambodians. Anthropologist Alexander Hinton's research project to interview perpetrators of violence during the KR regime sheds some light on the question of collective violence. Hinton's analysis of top-down initiatives shows that perpetrators in the KR were motivated to kill because KR leaders were effectively able to "localize their ideologies" to appeal to their followers.[47] Specifically, Hinton spoke to two ideological palimpsests that the KR used. First, the KR tapped on the Khmer notion of disproportionate revenge to motivate a resonant equivalent—class rage against previous oppressors.[48] Hinton uses the example of revenge in the Cambodian context to illustrate how closely violence can be tied to and explained by the Buddhist notion of karma, which dictates that there is a cycle of cause and effect in which one's past actions will affect one's future life. Next, KR leadership built on local notions of power and patronage vis-à-vis Wolters’ mandala polity to establish their authority as a potent centre.[49] In so doing, the KR escalated the suspicion and instability inherent within such patronage networks, setting the stage for distrust and competition on which political purges were based.
Violence as an individual action
After establishing the historical and ideological context as the backdrop, Hinton delves deeper into the complexities of perpetrator motivation through using both macro- and micro-level analyses to uncover how ideology is linked to psychocultural processes. Under the KR, the encroachment of the public sphere into that which was once private space made constant group-level interactions. Within these spaces, cultural models such as face, shame, and honour were adapted to KR notions of social status and bound up with revolutionary consciousness.[50] Thus, individuals were judged and their social status was based on these adapted KR conceptions of hierarchy which were predominantly political in nature. Within this framework, the KR constructed essentialised categories of identity which crystallised difference and inscribed these differences on victim's bodies, providing the logic and impetus for violence. To save face and preserve one's social status within the KR hierarchy, Hinton argues that first, violence was practised by cadres to avoid shame or loss of face; and second, that shamed cadres could restore their face through perpetrating violence.[51] At the level of individuals, the need for social approval and belonging to a community, even one as twisted as the KR, contributed to obedience, motivating violence within Cambodia.
Memorialisation in Cambodia


The violent legacy of the KR regime and its aftermath continue to haunt Cambodia today. In recent years, increasing attention has been paid by the world to the atrocities of the KR, especially in light of the Cambodia Tribunal. In Cambodia, the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum and the Choeung Ek Killing Fields are two major sites open to the public which are preserved from the KR years and serve as sites of memory of the Cambodian genocide. The Tuol Sleng was a high school building that was transformed into an interrogation and torture centre called S-21 during the KR regime; today the site still contains many of the torture and prison cells which were created during the KR years. Choeng Ek was a mass grave site outside Phnom Penh where prisoners were taken to be killed; today the site is a memorial for those who died there.
However, beyond these two public sites, there has not been much activity promoted by the Cambodian government to remember the genocide that occurred. This, in part, is due to numerous KR cadres remaining in political power in the wake of the collapse of the KR regime. The continued influence of KR cadres in Cambodia's politics has led to a neglect of the teaching of KR history to Cambodian children. The lack of a strong mandate to teach KR history despite international pressure has led to a proliferation of literary and visual production to memorialise the genocide and create sites through which the past can be remembered by future generations.
In literature
Like the Holocaust, the Cambodian genocide has spawned a host of literary publications in the wake of the KR regime's fall. Most significant to the history of the KR are the numerous survivor memoirs published in English as a way to remember the past. The first wave of KR memoirs began appearing in the late 1970s and 1980s. Soon after the first wave of survivors escaped or were rescued from Cambodia, survivor accounts in English and French began to be published. These memoirs tended to be authored either by foreigners or adult Cambodian males. Written to generate more awareness about the KR regime, these adult memoirs take into account the political climate in Cambodia before the regime and tend to call for justice to be served to the perpetrators of the regime. Being the first survivor accounts to reach global audiences, memoirs such as Haing Ngor's A Cambodian Odyssey (published 1987), Pin Yathay's L'Utopie meurtrière (Murderous Utopia) (1979), Laurence Picq's Au-delà du ciel (Beyond the Horizon) (1984) and Francois Ponchaud's Cambodge, annee zero (Cambodia Year Zero) (1977) were instrumental in bringing to the world the story of life under the KR regime.
The second wave of memoirs, published in the 21st century, is distinctly different from the first wave. Memoirs from the second wave include Chanrithy Him's When Broken Glass Floats (published 2000), Loung Ung's First They Killed My Father (2000), Oni Vitandham's On the Wings of a White Horse (2005) and Kilong Ung's Golden Leaf (2009). Published in large part by Cambodian survivors who were children during the period, these memoirs trace their journey from a war-torn Cambodia to their new lives in other parts of the world. To a larger extent than memoirs from the first wave, these memoirs reconstruct the significance of their authors' experiences before they left Cambodia. Having grown up away from Cambodia, these individuals use their memoirs predominantly as a platform to come to terms with their lost childhood years, reconnect with their cultural roots which they cannot forget despite residing outside of Cambodia and tell this story for their children. Noticeably, many of the authors of second wave memoirs draw out extended family trees in the beginning of their accounts in an attempt to document their family history. Additionally, some authors also note that despite them remembering events vividly, their memories were augmented by their relatives recounting those events to them as they grew up. Most significantly, the publication of the second wave of memoirs coincides with the Cambodia Tribunal and could be a response to the increased international attention paid to the atrocities of the KR.
In media
As in literature, there has been a proliferation of films on the Cambodian genocide. Most of the films are produced in documentary style, frequently with the aim to reveal what really happened during the KR years and to memorialise those who lived through the genocide. Film director Rithy Panh is a survivor of the KR's killing fields and is the most prolific producer of documentaries on the KR years. He has produced Cambodia: Between War and Peace and The Land of the Wandering Souls among other documentary films. In S-21: The Khmer Rouge Killing Machine, two survivors of S-21 confront their former captors. In 2013, Panh released another documentary about the KR years titled The Missing Picture. The film uses clay figures and archival footage to re-create the atrocities of the KR regime. Beyond Panh, many other individuals (both Cambodians and non-Cambodians) have made films about the KR years. Year Zero: The Silent Death of Cambodia is a British documentary directed by David Munro in 1979 which managed to raise 45 million pounds for Cambodians.
See also
- Agrarian socialism
- First Indochina War
- First They Killed My Father (film)
- French Indochina
- History of Cambodia
- The Killing Fields (film)
- List of socialist states
- People's Republic of Kampuchea (Vietnamese occupation, 1979–1989)
- Vietnam War (Second Indochina War)
References
- "Cambodia – Religion". Britannica. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- Jackson, Karl D. Cambodia, 1975–1978: Rendezvous with Death. Princeton University Press. p. 219. ISBN 0-691-02541-X.
- "Khmer Rouge's Slaughter in Cambodia Is Ruled a Genocide". The New York Times. 15 November 2018. Archived from the original on 13 April 2019. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- Kiernan, B. (2004) How Pol Pot came to Power. New Haven: Yale University Press, p. xix
- "Coalition Government of Democratic Kampuchea". countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2007.
- Karkaria, Zal. Failure "Through Neglect: The Women's Policies of the Khmer Rouge in Comparative Perspective". Concordia University Department of History. Archived 26 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- Kiernan, Ben. "The Pol Pot Regime: Race, Power, and Genocide in Cambodia Under the Khmer Rouge, 1975–79." New Haven, Conn: Yale University Press, 2002. p. 19.
- Jackson, Karl D (ed.). "Cambodia, 1975–1978: Rendezvous with Death." Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press, 1992, p215.
- Press Staff (18 April 1975). "Cambodians Designate Sihanouk as Chief for Life". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- Osborne, Milton E (1994). Sihanouk Prince of Light, Prince of Darkness. Honolulu, Hawaii, United States of America: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-1639-1.
- David P. Chandler. "The Constitution of Democratic Kampuchea (Cambodia): The Semantics of Revolutionary Change: Notes and Comment". Pacific Affairs Vol. 49, No. 3 (Autumn, 1976). pp. 506–515. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- Wessinger, Catherine (2000). Millennialism, Persecution, and Violence: Historical Cases. Syracuse University Press. p. 282. ISBN 9780815628095.
Democratic Kampuchea was officially an atheist state, and the persecution of religion by the Khmer Rouge was matched in severity only by the persecution of religion in the communist states of Albania and North Korea, so there were no direct historical continuities with Buddhism into the Democratic Kampuchean era.
- Juergensmeyer, Mark. The Oxford Handbook of Global Religions. Oxford University Press. p. 495.
- Quinn-Judge, Westad, Odd Arne, Sophie (2006). The Third Indochina War: Conflict Between China, Vietnam and Cambodia, 1972–79. Routledge. p. 189.
- Philip Shenon, Phnom Penh Journal; Lord Buddha Returns, With Artists His Soldiers Archived 15 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine The New York Times – January 2, 1992
- Tyner, James A. (2008). The Killing of Cambodia: Geopolitics, Genocide, and the Unmaking of Space. Burlington, VT: Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-7096-4.
- Vickery, Michael (1984). Cambodia : 1975–1982. Boston: South End Press. ISBN 0-89608-189-3.
- Judgement of the Trial Chamber of the Extraordinary Chambers in the Courts of Cambodia
- Jackson, Karl D. Cambodia 1977: gone to Pot – Asian Survey, 1978. p 81
- Jackson, Karl D. Cambodia 1977: gone to Pot – Asian Survey, 1978. p 82
- Becker, Elizabeth (1986). When the War Was over: Cambodia and the Khmer Rouge Revolution. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-671-41787-8.
- Jackson, Karl D. Cambodia, 1975–1978: Rendezvous with Death. Princeton University Press. p. 219. ISBN 0-691-02541-X.
- Ervin Staub. The roots of evil: the origins of genocide and other group violence. Cambridge University Press, 1989. p. 202 Archived 3 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- David Chandler & Ben Kiernan, ed. (1983). Revolution and its Aftermath. New Haven.
- Kiernan, Ben. "The Pol Pot Regime: Race, Power, and Genocide in Cambodia Under the Khmer Rouge, 1975–79." New Haven, Conn: Yale University Press, 2002. p11.
- Jackson, Karl D (ed.). "Cambodia, 1975–1978: Rendezvous with Death." Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press, 1992, p231.
- Etcheson, Craig. "The Rise and Demise of Democratic Kampuchea." Boulder, Colo: Westview, 1984. p27.
- Jackson, Karl D (ed.). "Cambodia, 1975–1978: Rendezvous with Death." Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press, 1992, p232.
- Phan, Rithy and Bataille, Christopher. "The Elimination: a Survivor of the Khmer Rouge Confronts His Past." Clerkenwell Press, 2012. p34.
- Vickery, Michael. "Cambodia, 1975–1982." Boston, MA: South End Press, 1984. p152.
- Final Solutions: Mass Killing and Genocide in the 20th Century Cornell University Press, 2004. ISBN 0-8014-3965-5 p. 127 Archived 4 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
- Locard, Henri, State Violence in Democratic Kampuchea (1975–1979) and Retribution (1979–2004) Archived 30 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine, European Review of History, Vol. 12, No. 1, March 2005, pp.121–143.
- Nicholas A. Robins, Adam Jones. Genocides by the oppressed: subaltern genocide in theory and practice. Indiana University Press, 2009. p. 98 Archived 25 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Alexander Laban Hinton. A Head for an Eye: Revenge in the Cambodian Genocide. American Ethnologist, Vol. 25, No. 3 (Aug. 1998), pp. 352–377
- Nicholas A. Robins, Adam Jones. Genocides by the oppressed: subaltern genocide in theory and practice. Indiana University Press, 2009. p. 97 Archived 27 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Helen Fein. Revolutionary and Antirevolutionary Genocides: A Comparison of State Murders in Democratic Kampuchea, 1975 to 1979, and in Indonesia, 1965 to 1966. Comparative Studies in Society and History, Vol. 35, No. 4 (Oct. 1993), pp. 796–823
- Documentation Center of Cambodia Archived 28 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Yale Cambodian Genocide Program". Archived from the original on 16 September 2013. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
- Bruce Sharp, Counting Hell: The Death Toll of the Khmer Rouge Regime in Cambodia Archived 15 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Mekong.net, 2008.
- "S21 Victims". www.killingfieldsmuseum.com. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- "The Khmer Rouge Trial Task Force". Royal Government of Cambodia. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009.
- MacKinnon, Ian (7 March 2007). "Crisis talks to save Khmer Rouge trial". The Guardian. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- Doyle, Kevin (26 July 2007). "Putting the Khmer Rouge on Trial". Time. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- Brady, Brendan (27 July 2010). "Sentence reduced for former Khmer Rouge prison chief". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- McKirdy, Euan (7 August 2014). "Top Khmer Rouge leaders found guilty of crimes against humanity, sentenced to life in prison". CNN. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- "Senior Khmer Rouge leader charged". BBC News. 19 September 2007. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. p287.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. p46.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. p97.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. p260, 288.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005. p275.
Further reading
- Beang, Pivoine, and Wynne Cougill. Vanished Stories from Cambodia's New People Under Democratic Kampuchea. Phnom Penh: Documentation Center of Cambodia, 2006. ISBN 99950-60-07-8.
- Chandler, David P. "A History of Cambodia." Boulder: Westview Press, 1992.
- Dy, Khamboly. A History of Democratic Kampuchea (1975–1979). Phnom Penh, Cambodia: Documentation Center of Cambodia, 2007. ISBN 99950-60-04-3. Foreword.
- Etcheson, Craig. The Rise and Demise of Democratic Kampuchea. Westview special studies on South and Southeast Asia. Boulder, Colo: Westview, 1984. ISBN 0-86531-650-3.
- Hinton, Alexander Laban. "Why did they Kill? : Cambodia in the Shadow of Genocide." Berkeley: University of California Press, 2005.
- Kiernan, Ben. "The Pol Pot Regime: Race, Power, and Genocide in Cambodia Under the Khmer Rouge, 1975–79." New Haven, Conn: Yale University Press, 2002.
- Vickery, Michael. "Cambodia, 1975–1982." Boston, MA: South End Press, 1984.
- Piergiorgio Pescali: "S-21 Nella prigione di Pol Pot". La Ponga Edizioni, Milan, 2015. ISBN 978-8897823308.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Democratic Kampuchea. |
- "Countrystudies.us: Democratic Kampuchea"
- Archive.org: "Democratic Kampuchea is moving forward"
- Archive.org: "Democratic Kampuchea, a workers' and peasants' state in South-East Asia"
- Constitution of Democratic Kampuchea
- BBC News: "Dark memories of Cambodia's killing spree" — commemorating the 30th anniversary of the Khmer Rouge's demise

