Disulfuric acid
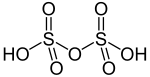
Disulfuric acid (alternative spelling disulphuric acid) or pyrosulfuric acid (alternative spelling pyrosulphuric acid), also named oleum, is an oxyacid of sulfur.[2] It is a major constituent of fuming sulfuric acid, oleum, and this is how most chemists encounter it. It is also a minor constituent of liquid anhydrous sulfuric acid due to the equilibria:
- [Global]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Disulfuric acid [1] | |
| Other names
Pyrosulfuric acid, Oleum | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.069 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Pyrosulfuric+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H2O7S2 | |
| Molar mass | 178.13 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 36 °C (97 °F; 309 K) |
| Conjugate base | Disulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The acid is prepared by reacting excess sulfur trioxide (SO3) with sulfuric acid:
Disulfuric acid can be seen as the sulfuric acid analog of an acid anhydride. The mutual electron-withdrawing effects of each sulfuric acid unit on its neighbour causes a marked increase in acidity. Disulfuric acid is strong enough to protonate "normal" sulfuric acid in the (anhydrous) sulfuric acid solvent system. There are salts of disulfuric acid, commonly called pyrosulfates, e.g. potassium pyrosulfate.
There are other related acids with the general formula H2O·(SO3)x though none can be isolated.
See also
References
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 130. Electronic version.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.