Eorhynchochelys
Eorhynchochelys (meaning "dawn-beaked turtle" in Greek) is an extinct genus of stem-turtle from the Late Triassic Xiaowa Formation (or Wayao Member of the Falang Formation) of southwestern China.
| Eorhynchochelys | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Pantestudines |
| Genus: | †Eorhynchochelys Li et al., 2018 |
| Type species | |
| †Eorhynchochelys sinensis Li et al., 2018 | |
Description
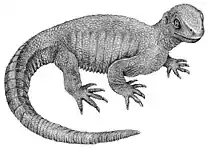
Eorhynchochelys is notable for its unusual combination of a turtle-style skull and a conventional reptilian body. The skull, for example, has an edentulous beak typical of all members of Testudinata. However, the thorax region is markedly different from Pappochelys and Odontochelys and more similar to Eunotosaurus in lacking a shell, even though the ribs were wide and flat. The skull also has a single pair of holes behind the skull, unlike the presence of two pairs of holes in Pappochelys.[1][2]
References
- Li, Chun; Fraser, Nicholas C.; Rieppel, Olivier; Wu, Xiao-Chun (2018). "A Triassic stem turtle with an edentulous beak". Nature. 560 (7719): 476–479. Bibcode:2018Natur.560..476L. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0419-1. PMID 30135526. S2CID 52067286.
- Rehm, Jeremy (2018). "230-million-year-old turtle fossil deepens mystery of reptile's origins". Nature. doi:10.1038/d41586-018-06012-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.