European route E18
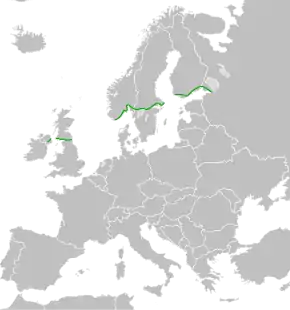
European route E18 runs from Craigavon in Northern Ireland to Saint Petersburg in Russia, passing through Scotland, England, Norway, Sweden, and Finland. It is about 1,890 kilometres (1,174 miles) in length.
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Route information | |
| Length | 1,890 km (1,170 mi) |
| Major junctions | |
| West end | Craigavon, United Kingdom |
| E6 Oslo, Norway E16 Sandvika, Norway | |
| East end | Saint Petersburg, Russia |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Highway system | |
| International E-road network | |
Although the designation implies the possibility of a through journey, this is no longer practical as there are no direct car ferry crossings between the United Kingdom and Norway.[1]
United Kingdom
The route starts in Northern Ireland and runs from Craigavon (M1) – Belfast (M2, A8) – Larne, then to Scotland: Stranraer, Dumfries and Galloway (A75) – Gretna – then England via the (M6) – Carlisle (A69) to Newcastle. As is normal for European routes in the United Kingdom, it is not signposted as such.
Northern Ireland
Great Britain
 : Stranraer -
: Stranraer - .svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp) :
:  - Anglo-Scottish border (Start of multiplex with
- Anglo-Scottish border (Start of multiplex with  E05)
E05) : Anglo-Scottish border - Carlisle (End of multiplex with
: Anglo-Scottish border - Carlisle (End of multiplex with  E05)
E05) : Carlisle - Newcastle upon Tyne (Interchange with
: Carlisle - Newcastle upon Tyne (Interchange with  E15 at
E15 at  )
)
North Sea
There are no ferries from Newcastle to Norway. Freight-only ferries may operate from other United Kingdom ports to Norway or Denmark, but for car journeys the only practical route is a crossing to France, Belgium or the Netherlands, followed by a road journey through Germany and Denmark, and a ferry crossing from there to Norway.[1][2]
Norway
The route continues as a motorway from Kristiansand in Norway. E18 is connected with the E39 Ferry to Denmark. The ferry runs from Kristansand to Hirtshals, takes about 3 hours and 15 minutes, and is operated by Color Line.[3][4]
In Norway, the E18 has a length of 415 kilometres (258 mi), of which 190 kilometres (120 mi) are motorway. It runs Kristiansand – Arendal – Porsgrunn – Larvik – Sandefjord – Tønsberg – Horten – Drammen – Oslo – Ås – Askim – Ørje (at the Swedish border).
A flyover carrying the E18 Holmestrand bypass, opened in 2001, partially collapsed in February 2015 following a landslip, necessitating its demolition.[5]
Sweden
From Ørje, the E18 crosses the border into Sweden at Töcksfors. It has a length of 510 kilometres (320 mi), of which 245 kilometres (152 mi) are motorway. It runs Töcksfors – Karlstad – Örebro – Västerås – Stockholm / Kapellskär.
Baltic Sea
The connection over the Baltic Sea is from Stockholm or Kapellskär in Sweden via Åland to Turku or Naantali in Finland, by ferries operated by Silja Line, Viking Line or Finnlines. It is also possible to take a direct ferry from Stockholm to Helsinki or to continue from Åland by island hopping over bridges, by cable ferries and ferries in Åland and Åboland, partly along the Archipelago Ring Road, but these routes are not part of the E18.
Finland
In Finland the E18 goes from Åland through southern Finland by way of Turku/Naantali – Salo – Lohja – Espoo – Porvoo – Loviisa – Kotka – Hamina – Vaalimaa till the border with Russia. Crossing the border to Russia used to often require queuing as the volume of traffic using it increased.[6] The situation has since 2009 improved thanks to increased capacity, and a new parking lot constructed by 2016 is expected to solve the problem for good.[7]
Russia
In Russia, E18 goes along the M10 highway from Finnish border to Saint Petersburg. The stretch of M10 between Saint Petersburg and the Finnish border has been redesignated to A181 in 2018.[8] The route runs through northwestern Leningrad Oblast and mostly through sparsely populated areas. Since 2003, after opening of Vyborg bypass E18 does not go through Vyborg, though previously it did.[9] Near Saint Petersburg the route runs through suburbs, such as Sestroretsk and Olgino. E18 terminates at the western border of Saint Petersburg.
There are plans to expand the road from one to three lanes in each direction because of the increasing volume of traffic.[10] In 2012 the highway has been connected with the Western Rapid Diameter near Beloostrov by expanded existing junction of M10 with the Zelenogorsk highway. It is likely to be a new terminus of E18.[11]
Gallery
_-_geograph.org.uk_-_300860.jpg.webp) The M1 near Craigavon, Northern Ireland
The M1 near Craigavon, Northern Ireland The A75 sign near Gretna, Scotland
The A75 sign near Gretna, Scotland European Route E18 motorway leads over Drammen Bridge, Norway
European Route E18 motorway leads over Drammen Bridge, Norway The E18 passing through Västerås, Sweden
The E18 passing through Västerås, Sweden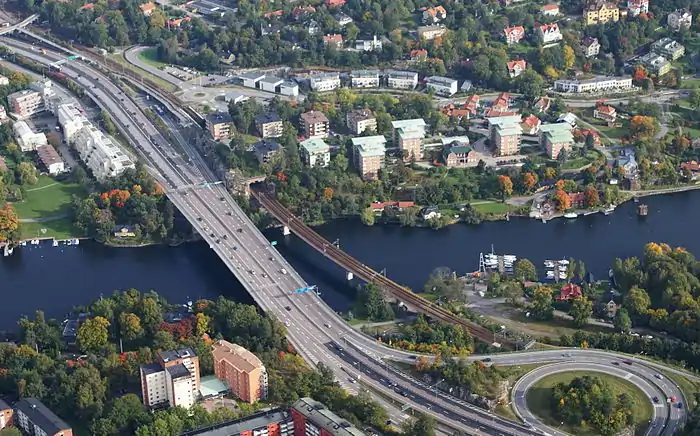 The E18 crossing the Stocksundet between Stockholm and Kapellskär
The E18 crossing the Stocksundet between Stockholm and Kapellskär
References
- "From UK to Norway by car and ferry". The Little Scandinavian. Scandi Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "Brevik - Immingham to Brevik". DFDS. Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "Newcastle Ferry Port, England - Information, Map, Directions & more for Newcastle Ferry Terminal with Eurodrive: the ferry price comparison site". www.eurodrive.co.uk.
- "Eurodrive - Cheap Ferry Crossing Tickets for Ferries-France and more with Eurodrive: the ferry price comparison site". www.eurodrive.co.uk.
- "Bridge collapses on E18 highway". www.newsinenglish.no.
- Queue situation at the Finnish/Russian border Archived 14 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Rekkaparkki, latauspisteitä sähköautoille ja kymmeniä siltoja – E18-tien viimeinen osuus valmistuu vuonna 2018". YLE. 4 April 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ООО Компания "Кодекс-Люкс": Законодательство, судебная практика, нормы, правила, стандарты России Archived 7 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Kodeks-luks.ru.
- Federal Highway Agency of Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation (in Russian) Archived 24 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Rosavtodor.ru.
- (in Russian). Baltinfo.ru (18 August 2011).
- (in Russian). Stpr.ru.
External links
![]() Media related to E 18 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to E 18 at Wikimedia Commons