Genome Project-Write
The Genome Project - Write (also known as GP-Write) is a large-scale collaborative research project (an extension of Genome Projects, aimed at reading genomes since 1984) that focuses on the development of technologies for the synthesis and testing of genomes of many different species of microbes, plants, and animals, including the human genome in a sub-project known as Human Genome Project-Write (HGP-Write).[1][2][3][4][5][6] Formally announced on 2 June 2016, the project leverages two decades of work on synthetic biology and artificial gene synthesis.
The newly created GP-Write project will be managed by the Center of Excellence for Engineering Biology,[7] an American nonprofit organization. Researchers expect that the ability to artificially synthesize large portions of many genomes will result in many scientific and medical advances.[1][2][3][4][5][6]
Microbial Genome Projects - Write
Technologies for constructing and testing yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), synthetic yeast genomes (Sc2.0),[8] and virus/phage-resistant bacterial genomes have industrial, agricultural, and medical applications.[2]
Human Genome Project-Write
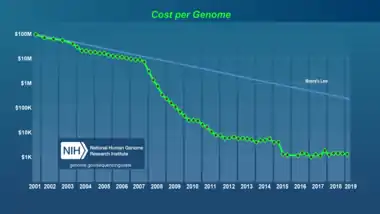
A complete haploid copy of the human genome consists of at least three billion DNA nucleotide base pairs, which have been described in the Human Genome Project - Read program (95% completed as of 2004). Among the many goals of GP-Write are the making of cell lines resistant to all viruses and synthesis assembly lines to test variants of unknown significance that arise in research and diagnostic sequencing of human genomes (which has been exponentially improving in cost, quality, and interpretation).[2]
See also
References
- Pollack, Andrew (2 June 2016). "Scientists Announce HGP-Write, Project to Synthesize the Human Genome". The New York Times. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Boeke, JD, Church G, Hessel A, Kelley NJ, Arkin A, Cai Y, Carlson R, Chakravarti A, Cornish VW, Holt L, Isaacs FJ, Kuiken T, Lajoie M, Lessor T, Lunshof J, Maurano MT, Mitchell LA, Rine J, Rosser S, Sanjana NE, Silver PA, Valle D, Wang H, Way JC, Yang L; et al. (2 June 2016). "The Genome Project–Write". Science. 353 (6295): 126–127. Bibcode:2016Sci...353..126B. doi:10.1126/science.aaf6850. PMID 27256881. Retrieved 2 June 2016.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Callaway, Ewen (2 June 2016). "Plan to Synthesize Human Genome Triggers a Mixed Response". Scientific American. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Regalado, Antonio (2 June 2016). "Plan to Fabricate a Genome Raises Questions on Designer Humans". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Akst, Jef (2 June 2016). ""Human Genome Project-Write" Unveiled". The Scientist. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Opal, Puneet; Kini, Ameet (3 June 2016). "The Brave New World of the Synthetic Human Genome". Time. Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- "Center of Excellence for Engineering Biology". Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- "Synthetic yeast genomes (Sc2.0)". Retrieved 2 March 2017.
Further reading
- McElheny, Victor K. (2010). Drawing the Map of Life: Inside the Human Genome Project. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-03260-0. 361 pages. Examines the intellectual origins, history, and motivations of the project to map the human genome; draws on interviews with key figures.
- Church, G, Regis E (2014). Regenesis. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0465075706.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Josefine Liljeruhm, Erik Gullberg, Anthony C Forster (2014). Synthetic Biology. A Lab Manual. World Scientific Publishing Company. ISBN 978-9814579544.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Genome Project-Write: official information page of the consortium
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Genes, Technology and Policy |
- National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). NHGRI led the National Institutes of Health's contribution to the International Human Genome Project. This project, which had as its primary goal the sequencing of the three billion base pairs that make up human genome, was 95% complete in April 2004.
