Governor of Michigan
The governor of Michigan is the chief executive of the U.S. state of Michigan. The current governor is Gretchen Whitmer, a member of the Democratic Party, who was inaugurated on January 1, 2019, as the state's 49th governor. The governor is elected to a 4-year term and is limited to two terms.
| Governor of Michigan | |
|---|---|
 Seal of the Governor | |
 Standard of the Governor | |
| Style | Her Excellency The Honorable[1] |
| Status | |
| Residence | Michigan Governor's Mansion |
| Term length | Four years, renewable once |
| Precursor | Governor of Michigan Territory |
| Inaugural holder | Stevens T. Mason |
| Formation | November 3, 1835 |
| Deputy | Lieutenant Governor of Michigan |
| Website | Official website |
Qualifications
Governors of Michigan, as well as their lieutenant governors, must be United States citizens who have resided in Michigan for the four years preceding election and must be at least 30 years of age.[2] A constitutional amendment adopted at the 2010 general election provides that a person is ineligible for any elected office, including governor and lieutenant governor, if convicted of a felony involving dishonesty, deceit, fraud, or a breach of the public trust, and if the conviction were related to the person's official capacity while holding any elective office or position of employment in local, state, or federal government.[3]
Elections and term of office
From statehood until the election of 1966, governors were elected to two-year terms. Elections are held in November, and the governor assumes office the following January, except in the case of death or resignation. From statehood until 1851, elections were held in odd-numbered years. A new state constitution was drafted in 1850 and took effect in 1851. As part of the process bringing the constitution into effect, there was a single one-year term of governor in 1851. Thereafter elections were held in even years.
The constitution adopted in 1963 changed the governor's term to four years, starting in 1967. Since then, gubernatorial elections have been offset by two years between the U.S. presidential elections (e.g., presidential elections were in 2008 and 2012, while gubernatorial elections in that time period were in 2010 and 2014). Gubernatorial elections are held concurrently with state Senate elections. The winner of the gubernatorial election takes office at noon on January 1 of the year following the election.
In 1992, an amendment to the Michigan constitution imposed a lifetime term limit of two four-year terms for the office of governor. Prior to this, governors were not limited as to how many terms they could serve; John Engler, the governor at the time, served three terms as his first term occurred prior to the restriction. Engler was reelected in 1994 and 1998 before being term limited in 2002.
Powers and duties
The governor has responsibilities to:
- sign or veto laws passed by the legislature;[4] including a line item veto
- reorganize state executive government agencies and departments;[4]
- appoint, with advice and consent of the Senate, and oversee most department heads;[4]
- appoint judges, subject to ratification by the electorate;
- appoint members of boards and commissions;[4]
- propose a state budget;[4]
- give the annual State of the State address;[4]
- sue other executives to comply with the law;
- command the state militia; and
- grant pardons for any crime, except cases involving impeachment by the legislature.
The governor appoints the members of the governing boards of 10 of the state's 13 public universities[lower-alpha 1] and department commissions.
History of the office
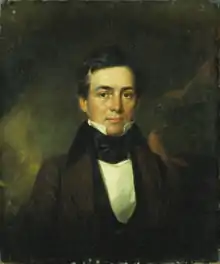
Forty-eight people have been governor of the state over forty-nine distinct periods, with one, Frank Fitzgerald, serving non-consecutive terms. Prior to statehood, there were five governors of the Michigan Territory. Stevens T. Mason, Michigan's first governor, also served as a territorial governor. He was elected governor at age 23 as a member of the Democratic Party in 1835 and served until 1840. Mason was the youngest state governor in United States history.
Jennifer Granholm became the first female governor of Michigan on January 1, 2003, when she succeeded Engler; she served for 8 years, until January 1, 2011.
See also
Notes
- The Board of Regents of the University of Michigan, the Board of Trustees of Michigan State University and the Board of Governors of Wayne State University are elected statewide. The Dearborn and Flint campuses of the University of Michigan lack separate governing boards as they are considered a part of the University of Michigan.
References
- Macomb, Alex (1837). "No. 20: Letter from Major General Macomb, to His Excellency the Governor of Michigan, Accompanying a Copy of Military Tactics". Documents Accompanying the Journal of the Senate. Detroit: John S. Bagg, State Printer. p. 167 – via Google Books.
- Michigan Constitution: Article V, Sec. 22—Governor and lieutenant governor, qualifications
- Michigan Constitution: Article XI, Sec. 8 Convictions for certain felonies; eligibility for elective office or certain positions of public employment
- "Chapter 2: About State Government" (PDF). Michigan in Brief: 1998–99. Public Sector Consultants. 1999.
.jpg.webp)