Governor-General of the Philippines
The Governor-General of the Philippines (Spanish: Gobernador-General de las Filipinas/Capitán General de las Filipinas; Filipino: Gobernador-Heneral ng Pilipinas/Kapitan Heneral ng Pilipinas; Japanese: フィリピン総督 (Firipin sōtoku)) was the title of the government executive during the colonial period of the Philippines, governed mainly by Spain (1565–1898) and the United States (1898–1946), and briefly by Great Britain (1762–1764) and Japan (1942–1945). They were also the representative of the executive of the ruling power.
| Governor-General of the Philippines
Gobernador-General de las Filipinas/Capitán General de las Filipinas Gobernador-Heneral ng Pilipinas/Kapitan Heneral ng Pilipinas フィリピン総督 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Residence | Fort San Pedro (1565–1572) Palacio del Gobernador (1572–1863) Malacañang Palace (1863–1945) Mansion House (1942–1945) | ||||
| Appointer | |||||
| Precursor | Various, the barangay system | ||||
| Formation | 27 April 1565 | ||||
| First holder | Miguel López de Legazpi (under Spain) Dawsonne Drake (under Great Britain) Wesley Merritt (under the United States) Masaharu Homma (under Japan) | ||||
| Final holder | Diego de los Ríos (under Spain) Dawsonne Drake (under Great Britain) Frank Murphy (under the United States) Tomoyuki Yamashita (under Japan) | ||||
| Abolished | 6 October 1945 | ||||
| Succession | |||||
On November 15, 1935, the Commonwealth of the Philippines was established as a transitional government to prepare the country for independence from American control. The governor-general was replaced by an elected Filipino "President of the Philippine Commonwealth", as the chief executive of the Philippines, taking over many of the duties of the Governor-General. The former American Governor-General then became known as the High Commissioner to the Philippines.
Under New Spain (1565–1761)
From 1565 to 1898, the Philippines was under Spanish rule. From 1565–1821, The governor and captain-general was appointed by the Viceroy of New Spain upon recommendation of the Spanish Cortes and governed on behalf of the Monarch of Spain to govern the Captaincy General of the Philippines. When there was a vacancy (e.g. death, or during the transitional period between governors), the Real Audiencia in Manila appoints a temporary governor from among its members.
After 1821, the country was no longer under the Viceroyalty of New Spain (present-day Mexico) and administrative affairs formerly handled by New Spain were transferred to Madrid and placed directly under the Spanish Crown.
Ad interim Real Audiencia
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | Viceroy of New Spain | Monarch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Miguel López de Legazpi | April 27, 1565 | August 20, 1572 | .svg.png.webp) Francisco Ceinos, Dean of the Audiencia (August 1, 1564 – October 19, 1566) |
 Philip II Felipe II House of Habsburg (July 25, 1554 – September 13, 1598) |
 Gastón Carrillo de Peralta y Bosquete, 3rd Marquess of Falces (October 19, 1566 – November 11, 1567) | ||||||
.svg.png.webp) Licenciado Alonso de Muñoz and Licenciado Luís Carrillo (November 11, 1567 – April 1568) | ||||||
.svg.png.webp) Licenciado Alonso de Muñoz (April 1568 – April 14, 1568) | ||||||
.svg.png.webp) Francisco Ceinos, Dean of the Audiencia (April 14, 1568 – November 4, 1568) | ||||||

Martín Enríquez de Almanza | ||||||
| 2 |  |
Guido de Lavezaris | August 20, 1572 | August 25, 1575 | ||
| 3 | .svg.png.webp) |
Francisco de Sande | August 25, 1575 | April 1580 | ||
| 4 | .svg.png.webp) |
Gonzalo Ronquillo de Peñalosa | April 1580 | March 10, 1583 | ||
 Lorenzo Suárez de Mendoza, 4th Count of La Coruña (October 4, 1580 – June 19, 1583) | ||||||
| 5 | .svg.png.webp) |
Diego Ronquillo | March 10, 1583 | May 16, 1584 | ||
.svg.png.webp) Luís de Villanueva y Zapata, Dean of the Audiencia (June 19, 1583 – September 24, 1584) | ||||||
| 6 | .svg.png.webp) |
Santiago de Vera | May 16, 1584 | May 1590 | ||
 Pedro de Moya y Contrerás (Archbishop of Mexico) (September 25, 1584 – October 17, 1585) | ||||||
 Álvaro Manrique de Zúñiga 1st Marquess of Villamanrique (October 17, 1585 – January 27, 1590) | ||||||
| 7 | .svg.png.webp) |
Gómez Pérez Dasmariñas | June 1, 1590 | October 25, 1593 |  Luís de Velasco Marquess of Salinas (January 27, 1590 – November 5, 1595) | |
| 8 | .svg.png.webp) |
Pedro de Rojas | October 1593 | December 3, 1593 | ||
| 9 | .svg.png.webp) |
Luís Pérez Dasmariñas | December 3, 1593 | July 14, 1596 | ||
 Gaspar de Zúñiga Acevedo y Fonseca, 5th Count of Monterrey (November 5, 1595 – October 27, 1603) | ||||||
| 10 | .svg.png.webp) |
Francisco de Tello de Guzmán | July 14, 1596 | May 1602 | ||
.jpg.webp) Philip III Felipe III House of Habsburg (September 13, 1598 – March 31, 1621) | ||||||
| 11 | .svg.png.webp) |
Pedro Bravo de Acuña | May 1602 | June 24, 1606 | ||
 Juan de Mendoza y Luna, Marquess of Montesclaros (October 27, 1603 – July 2, 1607) | ||||||
| 12 | .jpg.webp) |
Cristóbal Téllez de Almanza (Real Audiencia) |
June 24, 1606 | June 15, 1608 | ||
 Luís de Velasco Marquess of Salinas (July 2, 1607 – June 19, 1611) | ||||||
| 13 | .svg.png.webp) |
Rodrigo de Vivero y Aberrucia | June 15, 1608 | April 1609 | ||
| 14 | .svg.png.webp) |
Juan de Silva | April 1609 | April 19, 1616 | ||
 García Guerra, O.P. (Archbishop of Mexico) (June 19, 1611 – February 22, 1612) | ||||||
.svg.png.webp) Pedro Otárola, Dean of the Audiencia (22 February 1612 – 18 October 1612) | ||||||
 Diego Fernández de Córdoba, Marquess of Guadalcázar and Count of Posadas (October 18, 1612 – March 14, 1621) | ||||||
| 15 | .svg.png.webp) |
Andrés Alcaraz (Real Audiencia) |
April 19, 1616 | July 3, 1618 | ||
| 16 | .svg.png.webp) |
Alonso Fajardo de Entenza | July 3, 1618 | July 1624 | ||
.svg.png.webp) Paz de Valecillo, Dean of the Audiencia (March 14, 1621 – September 11, 1621) |
.jpg.webp) Philip IV Felipe IV House of Habsburg (March 31, 1621 – September 17, 1665) | |||||
 Diego Carrillo de Mendoza y Pimentel, 1st Marquess of Gélves (September 12, 1621 – November 1, 1624) | ||||||
| 17 | .svg.png.webp) |
Jeronimo de Silva (Real Audiencia) |
July 1624 | June 1625 | ||
 Rodrigo Pacheco y Osorio de Toledo, 3rd Marquess of Cerralvo (November 3, 1624 – September 16, 1635) | ||||||
| 18 | .svg.png.webp) |
Fernándo de Silva | July 1624 | June 29, 1626 | ||
| 19 | .svg.png.webp) |
Juan Niño de Tabora | June 29, 1626 | July 22, 1632 | ||
| 20 | .svg.png.webp) |
Lorenzo de Olaza y Lecubarri (Real Audiencia) |
July 22, 1632 | 1633 | ||
| 21 | .svg.png.webp) |
Juan Cerezo de Salamanca | August 29, 1633 | June 25, 1635 | ||
| 22 |  |
Sebastián Hurtado de Corcuera | June 25, 1635 | August 11, 1644 | ||
 Lope Díez de Aux de Armendáriz, Marquess of Cadreita (September 16, 1635 – August 28, 1640) | ||||||
 Diego Roque López Pacheco Cabrera y Bobadilla, 7th Duke of Escalona, 7th Marquess of Villena and 7th Count of Xiquena (August 28, 1640 – June 10, 1642) | ||||||
 Juan de Palafox y Mendoza (Bishop of Puebla) (June 10, 1642 – November 23, 1642) | ||||||
 García Sarmiento de Sotomayor, 2nd Count of Salvatierra and Marquess of Sobroso (November 23, 1642 – May 14, 1648) | ||||||
| 23 | .svg.png.webp) |
Diego Fajardo Chacón | August 11, 1644 | July 25, 1653 | ||
 Marcos de Torres y Rueda (Bishop of Yucatan) (May 15, 1648 – April 22, 1649) | ||||||
.svg.png.webp) Matías de Peralta, Dean of the Audiencia (April 22, 1649 – June 28, 1650) | ||||||
 Luis Enríquez de Guzmán, 9th Count of Alba de Liste and Marquess of Villaflor (June 28, 1650 – August 15, 1653) | ||||||
| 24 | .svg.png.webp) |
Sabiniano Manrique de Lara | July 25, 1653 | September 8, 1663 |  Francisco Fernández de la Cueva, 8th Duke of Alburquerque, Marquess of Cuéllar, Count of Ledesma and of Huelma (August 15, 1653 – September 16, 1660) | |
 Juan de Leyva de la Cerda, Marquess of Adrada (September 16, 1660 – June 29, 1664) | ||||||
| 25 | .svg.png.webp) |
Diego de Salcedo | September 8, 1663 | September 28, 1668 | ||
 Diego Osorio de Escobar y Llamas (Bishop of Puebla) (June 29, 1664 – October 15, 1664) |
.jpg.webp) Charles II Carlos II House of Habsburg (September 17, 1665 – November 1, 1700) | |||||
 Antonio Sebastián de Toledo Molina y Salazar, 2nd Marquess of Mancera (October 16, 1664 – November 20, 1673) | ||||||
| 26 | .svg.png.webp) |
Juan Manuel de la Peña Bonifaz | September 28, 1668 | September 24, 1669 | ||
| 27 | .svg.png.webp) |
Manuel de León | September 24, 1669 | September 21, 1677 | ||
 Pedro Nuño Colón de Portugal y Castro, 6th Duke of Veragua, 6th Marquess of Jamaica and 6th Count of Gelves (November 20, 1673 – December 13, 1673) | ||||||
 Payo Enríquez de Rivera Manrique, O.S.A. (Bishop of Guatemala and Archbishop of Mexico) (December 13, 1673 – November 7, 1680) | ||||||
| 28 | .svg.png.webp) |
Francisco Coloma y Maceda (Real Audiencia) |
April 11, 1677 | September 25, 1677 | ||
| 29 | .svg.png.webp) |
Francisco Sotomayor y Mansilla (Real Audiencia) |
September 21, 1677 | September 28, 1678 | ||
| 30 | .svg.png.webp) |
Juan de Vargas y Hurtado | September 28, 1678 | August 24, 1684 | ||
 Tomás Antonio Manuel Lorenzo de la Cerda y Aragón 3rd Marquess of La Laguna de Camero Viejo (November 7, 1680 – June 16, 1686) | ||||||
| 31 | .svg.png.webp) |
Gabriel de Curuzealegui y Arriola | August 24, 1684 | April 1689 | ||
 Melchor Portocarrero y Lasso de la Vega, 3rd Count of Monclova (June 16, 1686 – November 20, 1688) | ||||||
 Gaspar Melchor Baltasar de la Cerda Silva Sandoval y Mendoza, 8th Count of Galve, Lord of Salcedón and Tortola (November 20, 1688 – February 27, 1696) | ||||||
| 32 | .svg.png.webp) |
Alonso de Avila Fuertes (Real Audiencia) |
April 1689 | July 1690 | ||
| 33 | .svg.png.webp) |
Fausto Cruzat y Gongora | July 25, 1690 | December 8, 1701 | ||
 Juan de Ortega Cano Montañez y Patiño (Bishop of Durango, Guatemala, Michoacán and Archbishop of Mexico) (February 27, 1696 – December 18, 1696) |
 Philip V Felipe V House of Bourbon (November 1, 1700 – January 15, 1724) | |||||
 José Sarmiento Valladares Arines de Romay, 1st Duke of Atrisco, Count of Moctezuma and of Tula (December 18, 1696 – November 4, 1701) | ||||||
| 34 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Domingo Zabálburu de Echevarri | December 8, 1701 | August 25, 1709 |  Juan de Ortega Cano Montañez y Patiño (Archbishop of Mexico) (November 4, 1701 – November 27, 1702) | |
 Francisco V Fernández de la Cueva Enríquez y Fernández de la Cueva, 10th Duke of Alburquerque and Marquess of Cuéllar (November 27, 1702 – November 13, 1710) | ||||||
| 35 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Martín de Urzúa y Arizmendi, count of Lizárraga | August 25, 1709 | February 4, 1715 | ||

Fernando de Alencastre Noroña y Silva, 1st Duke of Linares and Marquess of Valdefuentes | ||||||
| 36 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
José Torralba (Real Audiencia) |
February 4, 1715 | August 9, 1717 | ||
 Baltasar de Zúñiga Guzmán Sotomayor y Mendoza, 1st Duke of Arión and Marquess of Valero (July 16, 1716 – October 15, 1722) | ||||||
| 37 |  |
Fernando Manuel de Bustillo Bustamante y Rueda | August 9, 1717 | October 11, 1719 | ||
| - |  |
Archbishop Francisco de la Cuesta (Acting) |
October 11, 1719 | August 6, 1721 | ||
| 38 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Toribio José Cosio y Campo | August 6, 1721 | August 14, 1729 | ||
 Louis I Luis Felipe House of Bourbon (January 15, 1724 – August 31, 1724) | ||||||
 Juan de Acuña y Bejarano, 2nd Marquess of Casa Fuerte (October 15, 1722 – March 17, 1734) |
 Philip V Felipe V House of Bourbon (September 6, 1724 – July 9, 1746) | |||||
| 39 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Fernándo Valdés y Tamon | August 14, 1729 | July 1739 | ||
 Juan Antonio de Vizarrón y Eguiarreta (Archbishop of Mexico) (March 17, 1734 – August 17, 1740) | ||||||
| 40 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Gaspar de la Torre y Ayala | July 1739 | September 21, 1745 | ||
 Pedro de Castro Figueroa y Salazar, 1st Duke of La Conquista and 1st Marquess of Gracia Real (August 17, 1740 – August 22, 1741) | ||||||
_Version_with_Golden_Fleece_and_Holy_Spirit_Collars.svg.png.webp) Pedro Malo de Villavicencio, President of the Audiencia (August 23, 1741 – November 2, 1742) | ||||||
 Pedro Cebrián y Agustín, 5th Count of Fuenclara (November 3, 1742 – July 9, 1746) | ||||||
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
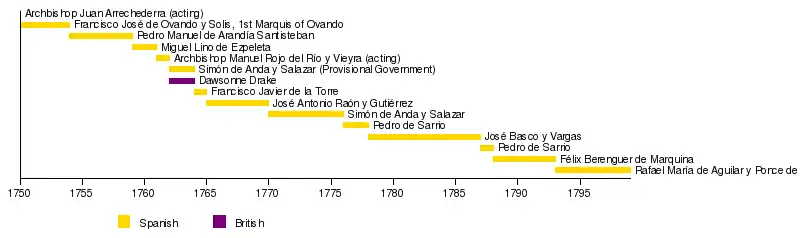
Archbishop Juan de Arechederra (Acting) |
September 21, 1745 | July 20, 1750 | ||
 Juan Francisco de Güemes y Horcasitas, 1st Count of Revillagigedo (July 9, 1746 – November 9, 1755) |
.jpg.webp) Ferdinand VI Ferdinand VIFernando VI House of Bourbon (July 9, 1746 – August 10, 1759) | |||||
| 41 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Francisco José de Ovando, 1st Marquis of Brindisi | July 20, 1750 | July 26, 1754 | ||
| 42 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Pedro Manuel de Arandía Santisteban | July 26, 1754 | May 31, 1759 | ||
 Agustín de Ahumada y Villalón, Marquess of Amarillas (November 10, 1755 – February 5, 1760) | ||||||
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Bishop Miguel Lino de Ezpeleta (Acting) |
June 1759 | May 31, 1761 | ||
_Version_with_Golden_Fleece_and_Order_of_Charles_III_Collars.svg.png.webp) Francisco Antonio de Echávarri, Dean of the Audiencia (February 5, 1760 – April 28, 1760) |
 Charles III Carlos III House of Bourbon (August 10, 1759 – December 14, 1788) | |||||
 Francisco Cajigal de la Vega (April 28, 1760 – October 5, 1760) | ||||||
 Joaquín de Montserrat, Marquess of Cruillas (October 5, 1760 – August 24, 1766) | ||||||
| - |  |
Archbishop Manuel Rojo del Río y Vieyra (Acting) |
July 1761 | October 6, 1762 |
British occupation of Manila (1761–1764)
After the Spanish defeat at the Battle of Manila in 1762, the Philippines was shortly governed simultaneously by two Governors-General of the Spanish Empire and the British Empire.
Great Britain shortly occupied Manila and the naval port of Cavite as part of the Seven Years' War, while the Spanish Governor-General set up a provisional government in Bacolor, Pampanga to continue administering the rest of the archipelago.
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | Monarch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Simón de Anda y Salazar (Provisional Government in Bacolor, Pampanga) |
October 6, 1762 | February 10, 1764 |  Charles III Carlos III House of Bourbon (August 10, 1759 – December 14, 1788) |
| 44 | .svg.png.webp) |
Dawsonne Drake | November 2, 1762 | May 31, 1764 |  George III House of Hanover (October 25, 1760 – January 29, 1820) |
Under New Spain (1764–1821)
After the British returned Manila to the Spanish in 1764, the Spanish Governor-General Francisco Javier de la Torre resumed administration of the Philippines under the authority of the Viceroy of New Spain in modern-day Mexico (New Spain) as part of the Spanish Empire.
The colonies were part of the First French Empire as part of Napoleon's invasion and occupation of Spain, until Joseph Bonaparte's abdication in December 11, 1813, following the aftermath of the Battle of Vitoria and the invasion of France through Spain by the Duke of Wellington.
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | Viceroy of New Spain | Monarch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Francisco Javier de la Torre | March 17, 1764 | July 6, 1765 | 
Joaquín de Montserrat, |
 Charles III Carlos III House of Bourbon (August 10, 1759 – December 14, 1788) |
| 46 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
José Antonio Raón y Gutiérrez | July 6, 1765 | July 1770 | ||

Carlos Francisco de Croix, | ||||||
| (43) | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Simón de Anda y Salazar | July 1770 | October 30, 1776 | ||

Antonio María de Bucareli y Ursúa | ||||||
| 47 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Pedro de Sarrio | October 30, 1776 | July 1778 | ||
| 48 |  |
José Basco y Vargas | July 1778 | September 22, 1787 | ||
_Version_with_Golden_Fleece_and_Order_of_Charles_III_Collars.svg.png.webp) Francisco Romá y Rosell, Regent of the Audiencia (April 10, 1779 – August 22, 1779) | ||||||
 Martín de Mayorga Ferrer, Captain General of Guatemala (August 23, 1779 – April 28, 1783) | ||||||
 Matías de Gálvez y Gallardo, Captain General of Guatemala (April 28, 1783 – October 20, 1784) | ||||||
_Version_with_Golden_Fleece_and_Order_of_Charles_III_Collars.svg.png.webp) Vicente de Herrera y Rivero, Regent of the Audiencia (October 20, 1784 – June 17, 1785) | ||||||
 Bernardo de Gálvez y Madrid, 1st Viscount of Galveston and 1st Count of Gálvez (June 17, 1785 – November 30, 1786) | ||||||
_Version_with_Golden_Fleece_and_Order_of_Charles_III_Collars.svg.png.webp) Eusebio Sánchez Pareja y Beleño Regent of the Audiencia (November 30, 1786 – May 8, 1787) | ||||||
 Alonso Núñez de Haro y Peralta (Archbishop of Mexico) (May 8, 1787 – August 16, 1787) | ||||||
 Manuel Antonio Flórez Maldonado (August 16, 1787 – October 16, 1789) | ||||||
| (47) | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Pedro de Sarrio | September 22, 1787 | July 1, 1788 | ||
| 49 |  |
Félix Berenguer de Marquina | July 1, 1788 | September 1, 1793 | ||
.jpg.webp) Charles IV Carlos IV House of Bourbon (December 14, 1788 – March 19, 1808) | ||||||
 Juan Vicente de Güemes Pacheco de Padilla y Horcasitas, 2nd Count of Revillagigedo (October 17, 1789 – July 11, 1794) | ||||||
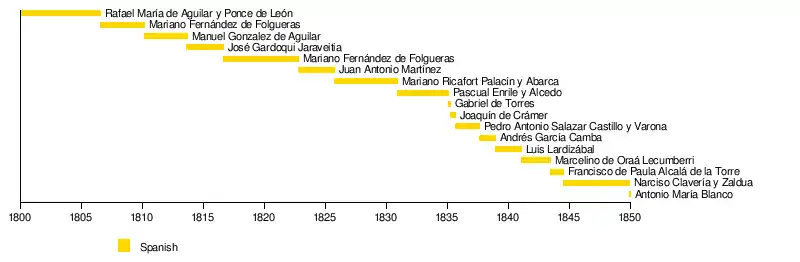
| 50 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Rafael María de Aguilar y Ponce de León | September 1, 1793 | August 7, 1806 | ||
 Miguel de la Grúa Talamanca de Carini y Branciforte, 1st Marquess of Branciforte (July 12, 1794 – May 31, 1798) | ||||||
 Miguel José de Azanza Alegría, 1st Duke of Santa Fe (May 31, 1798 – April 30, 1800) | ||||||
 Félix Berenguer de Marquina (April 30, 1800 – January 4, 1803) | ||||||
 José de Iturrigaray (January 4, 1803 – September 16, 1808) | ||||||
| 51 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Mariano Fernández de Folgueras | August 7, 1806 | March 4, 1810 | ||
 Pedro de Garibay (16 September 1808 – 19 July 1809) |
_by_Goya.jpg.webp) Ferdinand VII Fernando VII House of Bourbon (March 19, 1808 – May 6, 1808) | |||||
 Francisco Javier de Lizana y Beaumont (Archbishop of Mexico) (July 19, 1809 – May 8, 1810) |
 Joseph Bonaparte José Napoleón House of Bonaparte (June 6, 1808 – December 11, 1813) | |||||
| 52 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Manuel Gonzalez de Aguilar | March 4, 1810 | September 4, 1813 |  Pedro Catani (May 8, 1810 – September 14, 1810) | |
 Francisco Javier Venegas, 1st Marquess of Reunión and of New Spain (September 14, 1810 – March 4, 1813) | ||||||
 Félix María Calleja del Rey, 1st Count of Calderón (March 4, 1813 – September 20, 1816) | ||||||
| 53 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
José Gardoqui Jaraveitia | September 4, 1813 | December 10, 1816 | ||
 Juan Ruiz de Apodaca, 1st Count of Venadito (September 20, 1816 – July 5, 1821) |
 Ferdinand VII Fernando VII House of Bourbon (December 11, 1813 – September 29, 1833) | |||||
| (51) | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Mariano Fernández de Folgueras | December 10, 1816 | September 15, 1821 | ||
 Francisco Novella Azabal Pérez y Sicardo (July 15, 1821 – July 21, 1821) | ||||||
 Juan O'Donojú (July 21, 1821 – September 28, 1821) |
Direct Spanish control (1821–1898)
After the 1821 Mexican War of Independence, Mexico became independent and was no longer part of the Spanish Empire. The Viceroyalty of New Spain ceased to exist. The Philippines, as a result, was directly governed from Madrid, under the Spanish Crown.
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | Monarch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (51) | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Mariano Fernández de Folgueras | September 16, 1821 | October 30, 1822 |  Ferdinand VII Fernando VII House of Bourbon (December 11, 1813 – September 29, 1833) |
| 54 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Juan Antonio Martínez | October 30, 1822 | October 14, 1825 | |
| 55 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Mariano Ricafort Palacín y Abarca | October 14, 1825 | December 23, 1830 | |
| 56 |  |
Pasqual Enrile y Alcedo | December 23, 1830 | March 1, 1835 | |
 Isabella II Isabel II House of Bourbon (September 29, 1833 – September 30, 1868) | |||||
| 57 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Gabriel de Torres | March 1, 1835 | April 23, 1835 | |
| 58 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Joaquín de Crame | April 23, 1835 | September 9, 1835 | |
| 59 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Pedro Antonio Salazar Castillo y Varona | September 9, 1835 | August 27, 1837 | |
| 60 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Andrés García Camba | August 27, 1837 | December 29, 1838 | |
| 61 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Luis Lardizábal | December 29, 1838 | February 14, 1841 | |
| 62 |  |
Marcelino de Oraá | February 14, 1841 | June 17, 1843 | |
| 63 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Francisco de Paula Alcalá de la Torre | June 17, 1843 | July 16, 1844 | |
| 64 | .jpg.webp) |
Narciso Clavería, 1st Count of Manila | July 16, 1844 | December 26, 1849 | |
| 65 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Antonio María Blanco | December 26, 1849 | July 29, 1850 | |
| 66 |  |
Antonio de Urbistondo y Eguía | July 29, 1850 | December 20, 1853 | |
| 67 | .jpg.webp) |
Ramón Montero y Blandino | December 20, 1853 | February 2, 1854 | |
| 68 |  |
Manuel Pavía, 1st Marquis of Novaliches | February 2, 1854 | October 28, 1854 | |
| (67) | .jpg.webp) |
Ramón Montero y Blandino | October 28, 1854 | November 20, 1854 | |
| 69 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Manuel Crespo y Cebrían | November 20, 1854 | December 5, 1856 | |
| (67) | .jpg.webp) |
Ramón Montero y Blandino | December 5, 1856 | March 9, 1857 | |
| 70 |  |
Fernándo Norzagaray y Escudero | March 9, 1857 | January 12, 1860 | |
| 71 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Ramón María Solano y Llanderal | January 12, 1860 | August 29, 1860 | |
| 72 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Juan Herrera Dávila | August 29, 1860 | February 2, 1861 | |
| 73 | .jpg.webp) |
José Lemery e Ibarrola Ney y González | February 2, 1861 | July 7, 1862 | |
| 74 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Salvador Valdés | July 7, 1862 | July 9, 1862 | |
| 75 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Rafaél de Echagüe y Bermingham | July 9, 1862 | March 24, 1865 | |
| 76 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Joaquín del Solar e Ibáñez | March 24, 1865 | April 25, 1865 | |
| 77 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Juan de Lara e Irigoyen | April 25, 1865 | July 13, 1866 | |
| 78 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
José Laureano de Sanz y Posse | July 13, 1866 | September 21, 1866 | |
| 79 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Juan Antonio Osorio | September 21, 1866 | September 27, 1866 | |
| (76) | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Joaquín del Solar e Ibáñez | September 27, 1866 | October 26, 1866 | |
| 80 |  |
José de la Gándara y Navarro | October 26, 1866 | June 7, 1869 | |
| No Monarch | |||||
| 81 | .svg.png.webp) |
Manuel Maldonado | June 7, 1869 | June 23, 1869 | |
| 82 |  |
Carlos María de la Torre y Navacerrada | June 23, 1869 | April 4, 1871 | |
 Amadeo I House of Savoy | |||||
| 83 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Rafael de Izquierdo y Gutíerrez | April 4, 1871 | January 8, 1873 | |
| 84 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Manuel MacCrohon | January 8, 1873 | January 24, 1873 | |
| 85 |  |
Juan Alaminos y Vivar | January 24, 1873 | March 17, 1874 | |
| No Monarch | |||||
| - | .svg.png.webp) |
Manuel Blanco Valderrama (Acting) |
March 17, 1874 | June 18, 1874 | |
| 86 |  |
José Malcampo y Monje | June 18, 1874 | February 28, 1877 | |
.jpg.webp) Alfonso XII House of Bourbon (December 29, 1874 – November 25, 1885) | |||||
| 87 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Domingo Moriones y Murillo | February 28, 1877 | March 20, 1880 | |
| 88 | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Rafael Rodríguez Arias | March 20, 1880 | April 15, 1880 | |
| 89 |  |
Fernando Primo de Rivera, 1st Marquis of Estella | April 15, 1880 | March 10, 1883 | |
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Emilio Molíns 1st term, (Acting) |
March 10, 1883 | April 7, 1883 | |
| 90 |  |
Joaquín Jovellar | April 7, 1883 | April 1, 1885 | |
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Emilio Molíns 2nd term, (Acting) |
April 1, 1885 | April 4, 1885 | |
| 91 |  |
Emilio Terrero y Perinat | April 4, 1885 | April 25, 1888 | |
 Alfonso XIII House of Bourbon (May 17, 1886 – August 14, 1898) | |||||
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Antonio Moltó y Díaz Berrio (Acting) |
April 25, 1888 | June 4, 1888 | |
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Federico Lobatón y Prieto (Acting) |
June 4, 1888 | June 5, 1888 | |
| 92 |  |
Valeriano Wéyler | June 5, 1888 | November 17, 1891 | |
| 93 |  |
Eulogio Despujol | November 17, 1891 | March 1, 1893 | |
| - |  |
Federico Ochando (Acting) |
March 1, 1893 | May 4, 1893 | |
| 94 |  |
Ramón Blanco, 1st Marquis of Peña Plata | May 4, 1893 | December 13, 1896 | |
| - |  |
Camilo de Polavieja, 1st Marquis of Polavieja (Acting) |
December 13, 1896 | April 15, 1897 | |
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
José de Lachambre (Acting) |
April 15, 1897 | April 23, 1897 | |
| 95 |  |
Fernando Primo de Rivera, 1st Marquis of Estella | April 23, 1897 | April 11, 1898 | |
| 96 |  |
Basilio Augustín[1] | April 11, 1898 | July 24, 1898 | |
| - |  |
Fermín Jáudenes[1] (Acting) |
July 24, 1898 | August 13, 1898 | |
| - | _Pillars_of_Hercules_Variant.svg.png.webp) |
Francisco Rizzo[1] (Acting) |
August 13, 1898 | September 1898 | |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
Diego de los Rios[1] (Acting) |
September 1898 | June 3, 1899 |
United States Military Government (1898–1902)
The city of Manila was captured by American expeditionary forces on 13 August 1898.[2] On 14 August 1898, the terms of the Spanish capitulation were signed. From this date, American government in the Philippines begins.[2] General Wesley Merritt, in accordance with the instructions of the United States President, issued a proclamation announcing the establishment of United States military rule.[2]
During the transition period, executive authority in all civil affairs in the Philippine government was exercised by the military governor.
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | President |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Wesley Merritt | August 14, 1898[3] | August 30, 1898[4] |  William McKinley (March 4, 1897 – September 14, 1901) |
| 2 |  |
Elwell S. Otis | August 28, 1898 | May 5, 1900 | |
| 3 |  |
Arthur MacArthur, Jr. | May 5, 1900[5] | July 4, 1901 | |
| 4 |  |
Adna Chaffee[6] | July 4, 1901 | July 4, 1902 |
Insular Government (1901–1935)
On July 4, 1901, executive authority over the islands was transferred to the president of the Second Philippine Commission who had the title of Civil Governor, a position appointed by the President of the United States and approved by the United States Senate. For the first year, a Military Governor, Adna Chaffee, ruled parts of the country still resisting the American rule, concurrent with Civil Governor, William Howard Taft.[7] Disagreements between the two were not uncommon.[8] The following year, on July 4, 1902, Taft became the sole executive authority.[6] Chaffee remained commander of the Philippine Division until September 30, 1902.[9]
After his retirement as Civil Governor, Governor Taft was appointed Secretary of War and he secured for his successor the adoption by Congress[10] of the title Governor-General of the Philippine Islands thereby "reviving the high designation used during the last period of Spanish rule and placing the office on a parity of dignity with that of other colonial empires of first importance".[2] The term "insular" (from insula, the Latin word for island)[11] refers to U.S. island territories that are not incorporated into either a state or a federal district. All insular areas were under the authority of the U.S. Bureau of Insular Affairs, a division of the US War Department.[12][13]
| OO | Picture | Name | From | Until | President |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
William Howard Taft | July 4, 1901 | February 1, 1904 |  William McKinley (March 4, 1897 – September 14, 1901)  Theodore Roosevelt (September 14, 1901 – March 4, 1909) |
 Theodore Roosevelt (September 14, 1901 – March 4, 1909) | |||||
| 2 |  |
Luke Edward Wright | February 1, 1904 | November 3, 1905 | |
| 3 |  |
Henry Clay Ide | November 3, 1905 | September 19, 1906 | |
| 4 |  |
James Francis Smith | September 20, 1906 | November 11, 1909 | |
| 5 |  |
William Cameron Forbes | November 11, 1909 | September 1, 1913 |  William Howard Taft (March 4, 1909 – March 4, 1913) |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
Newton W. Gilbert (Acting Governor-General) |
September 1, 1913 | October 6, 1913 |  Woodrow Wilson (March 4, 1913 – March 4, 1921) |
| 6 |  |
Francis Burton Harrison | October 6, 1913 | March 5, 1921 | |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
Charles Yeater (Acting Governor-General) |
March 5, 1921 | October 14, 1921 |  Warren G. Harding (March 4, 1921 – August 2, 1923)  Calvin Coolidge (August 2, 1923 – March 4, 1929) |
| 7 |  |
Leonard Wood | October 14, 1921 | August 7, 1927 | |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
Eugene Allen Gilmore (Acting Governor-General) |
August 7, 1927 | December 27, 1927 |  Calvin Coolidge (August 2, 1923 – March 4, 1929) |
| 8 |  |
Henry L. Stimson | December 27, 1927 | February 23, 1929 | |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
Eugene Allen Gilmore (Acting Governor-General) |
February 23, 1929 | July 8, 1929 |  Herbert Hoover (March 4, 1929 – March 4, 1933) |
| 9 |  |
Dwight F. Davis | July 8, 1929 | January 9, 1932 | |
| - | .jpg.webp) |
George C. Butte (Acting Governor-General) |
January 9, 1932 | February 29, 1932 | |
| 10 |  |
Theodore Roosevelt, Jr. | February 29, 1932 | July 15, 1933 | |
| 11 |  |
Frank Murphy | July 15, 1933 | November 14, 1935 Became High Commissioner to the Philippines |
 Franklin D. Roosevelt (March 4, 1933 – April 12, 1945) |
High Commissioner to the Philippines (1935–42 and 1945–46)
On November 15, 1935, the Commonwealth of the Philippines was inaugurated as a transitional government to prepare the country for independence. The office of President of the Philippine Commonwealth replaced the Governor-General as the country's chief executive. The Governor-General became the High Commissioner of the Philippines with Frank Murphy, the last governor-general, as the first high commissioner. The High Commissioner exercised no executive power but rather represented the colonial power, the United States Government, in the Philippines. The high commissioner moved from Malacañang Palace to the newly built High Commissioner's Residence, now the Embassy of the United States in Manila.
After the Philippine independence on July 4, 1946, the last High Commissioner, Paul McNutt, became the first United States Ambassador to the Philippines.
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | President |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Frank Murphy | November 14, 1935 | April 26, 1937 |  Franklin D. Roosevelt (March 4, 1933 – April 12, 1945) |
| 2 |  |
Paul V. McNutt | April 26, 1937 | July 12, 1939 | |
| 3 |  |
Francis Bowes Sayre, Sr. | April 12, 1939 | October 12, 1942 | |
| 4 |  |
Paul V. McNutt | September 14, 1945 | July 4, 1946 Following Philippine independence became 1st U.S. Ambassador to the Philippines |
 Harry S. Truman (April 12, 1945 – January 20, 1953) |
Japanese military governors (1942–1945)
In December 1941, the Commonwealth of the Philippines was invaded by Japan as part of World War II. The next year, the Empire of Japan sent a military governor to control the country during wartime, followed by the formal establishment of the puppet second republic.[14]
| # | Picture | Name | From | Until | Emperor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Homma Masaharu 本間 雅晴 |
January 3, 1942 | June 8, 1942 |  Emperor Hirohito (Shōwa) 昭和天皇 |
| 2 |  |
Tanaka Shizuichi 田中 静壱 |
June 8, 1942 | May 28, 1943 | |
| 3 |  |
Kuroda Shigenori 黒田 重徳 |
May 28, 1943 | September 26, 1944 | |
| 4 | .jpg.webp) |
Yamashita Tomoyuki 山下 奉文 |
September 26, 1944 | September 2, 1945 |
On September 2, 1945, the Governor-General position of the Philippines has now been abolished and the Philippines' independence had been proclaimed helped by the United States on the 4th of July 1946 on the presidency of Manuel Roxas. The 4th President of the Philippines.
Timelines
1750–1800
1800–1850
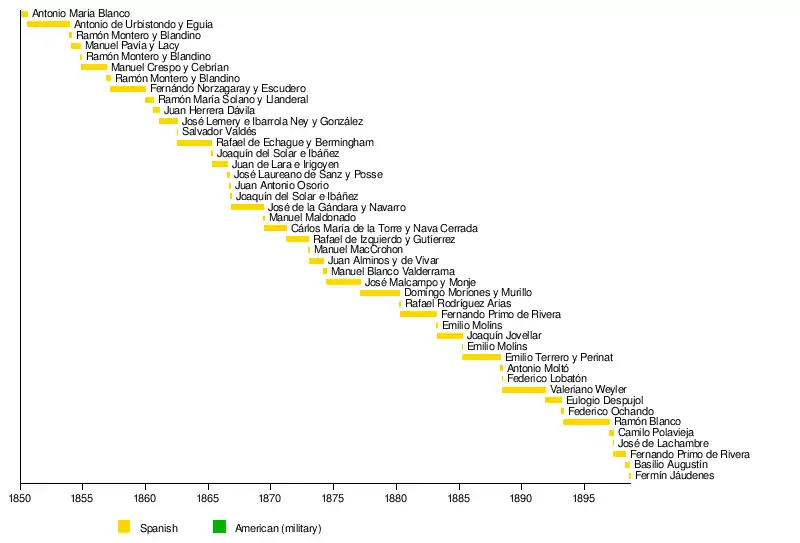
1850–1898
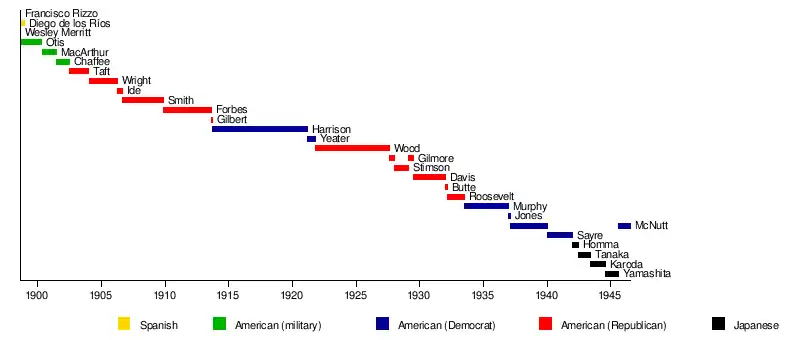
1898–1946
See also
- Filipino styles and honorifics
- List of sovereign state leaders in the Philippines
- List of recorded datu in the Philippines
- President of the Philippines
- List of Presidents of the Philippines
- Audiencia
- List of Viceroys of New Spain
- Spanish Empire
- History of the Philippines
- Military History of the Philippines
- United States Territory
- Governor-General
- Lists of office-holders
- Gobernadorcillo
Notes
- Peterson 2007, p. 11.
- David P. Barrows; The Governor-General of the Philippines under Spain and the United States; The American Historical Review Vol. 21, No. 2 (Jan., 1916), pp. 288-311 (PDF)
- Halstead, Murat (1898). The Story of the Philippines and Our New Possessions, Including the Ladrones, Hawaii, Cuba and Porto Rico. p. 116.
- Tucker, Spencer (2009). The Encyclopedia of the Spanish–American and Philippine–American Wars: A Political, Social, and Military History. ABC-CLIO. p. 457. ISBN 978-1-85109-951-1.
- Pershing, John J. (2013). My Life Before the World War, 1860--1917: A Memoir. University Press of Kentucky. p. 547. ISBN 978-0-8131-4199-2.
- Elliott (1917), p. 509
- Elliott (1917), p. 4
- Tanner (1901), p. 383
- Philippine Academy of Social Sciences (1967). Philippine social sciences and humanities review. pp. 40.
- Act of Congress of February 6, 1905 entitled: "An Act To amend an Act approved July first, nineteen hundred and two, entitled "An Act temporarily to provide for the administration of the affairs of civil government in the Philippine Islands, and for other purposes," and to amend an Act approved March eighth, nineteen hundred and two, entitled "An Act temporarily to provide revenue for the Philippine Islands, and for other purposes" and to amend an Act March second, nineteen hundred and three, entitled "An Act to establish a standard of value and to provide for a coinage system in the Philippine Islands," and to provide for the more efficient administration of civil government in the Philippine Islands, and for other purposes." Section 8 thereof provided that "the civil governor of the Philippine Islands shall hereafter be known as the governor-general of the Philippine Islands.
- "Island - from English to Latin". Google Translate. Retrieved on 2013-08-07.
- "Definitions of Insular Area Political Organizations" Archived 2012-09-25 at the Wayback Machine. U.S. Department of the Interior.
- "Insular". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved on 2013-08-07.
- Cahoon (2000)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Governors-General of the Philippines. |
References
- Governors of the Philippines
- Cahoon, Ben (2000). "Philippines". World's Statesmen.
- Don Peterson (2007-2nd Qtr), 1898: Five Philippine Governors-General Serve Rapid Fire Terms, Philippine Philatelic Journal.
- Tanner, Dr. J.M. (1901-11). Improvement Era Vol.5 No. 1. Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints.
- Elliott, Charles Burke (1917). The Philippines: To the End of the Commission Government, a Study in Tropical Democracy. The Bobbs-Merrill Company.
.svg.png.webp)

.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)
