Hexacyclonate
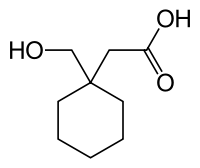
Hexacyclonate (Gevilon) is a stimulant drug. It has been used for the treatment of alcoholism[1] and for increasing motivation in elderly patients,[2] but is now mainly used for the treatment of hyperlipoproteinaemia.[3][4] It is chemically similar to the anticonvulsant gabapentin, with a hydroxyl group replacing the amine.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H16O3 |
| Molar mass | 172.222 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
The latter use may be incorrectly assigned, as "Gevilon" has been used as a trade name for gemfibrozil, a well-known drug for dislypidemia.
References
- Chesrow EJ, Sabatini R, Musci JP, Kaplitz SE, Marquardt GH (May 1962). "Adjunctive treatment of the chronic alcoholic with hexacyclonate sodium". The Illinois Medical Journal. 121: 546–8. PMID 13878809.
- Morrison BO (January 1962). "Pharmaco-motivation of the geriatric patient: a preliminary report on hexacyclonate". The Journal of the Louisiana State Medical Society. 114: 23–6. PMID 14476295.
- Milewicz A, Plamieniak Z, Bohdanowicz-Pawlak A (1992). "Therapeutic effect of gevilon in patients with hyperlipoproteinaemia". Materia Medica Polona. Polish Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy. 24 (2): 91–5. PMID 1307777.
- Gazdikova K, Korecka P, Springer V, Gazdik F (2003). "Pharmacoeconomic aspects of patients treated by hemodialysis". Bratislavske Lekarske Listy. 104 (10): 329–34. PMID 15055734.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.