Judea (Roman province)
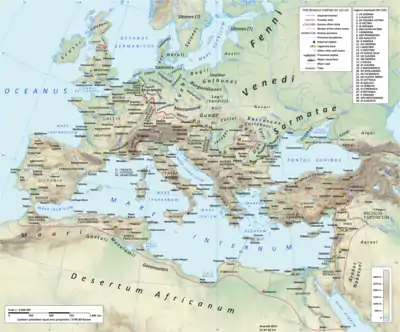
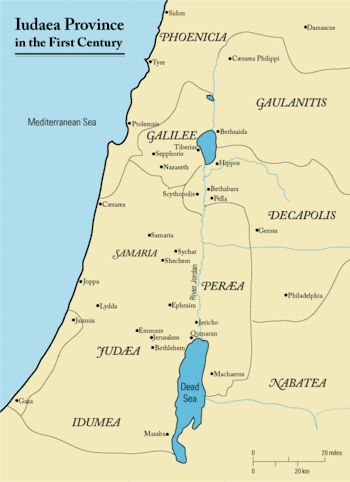
The Roman province of Judea (/dʒuːˈdiːə/; Hebrew: יהודה, Standard Yəhūda Tiberian Yehūḏā; Greek: Ἰουδαία Ioudaia; Latin: Iūdaea), sometimes spelled in its original Latin forms of Iudæa or Iudaea to distinguish it from the geographical region of Judea, incorporated the regions of Judea, Samaria and Idumea, and extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Judea. It was named after Herod Archelaus's Tetrarchy of Judea, but the Roman province encompassed a much larger territory. The name "Judea" was derived from the Kingdom of Judah of the 6th century BCE.
| Provincia Ivdaea Ἰουδαία | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||
| 6 CE–135 CE | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Capital | Caesarea Maritima | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| • Coordinates | 32°30′N 34°54′E | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| Prefects before 41, Procurators after 44 | |||||||||
• 6–9 CE | Coponius | ||||||||
• 26–36 CE | Pontius Pilate | ||||||||
• 64–66 CE | Gessius Florus | ||||||||
• 117 CE | Lusius Quietus | ||||||||
• 130–132 CE | Tineius Rufus | ||||||||
| King of the Jews | |||||||||
• 41–44 | Agrippa I | ||||||||
• 48–93/100 | Agrippa II | ||||||||
| Legislature | Synedrion/Sanhedrin | ||||||||
| Historical era | Roman Principate | ||||||||
| 6 CE | |||||||||
| c. 30/33 CE | |||||||||
• Crisis under Caligula | 37–41 CE | ||||||||
| 44 CE | |||||||||
| 70 CE | |||||||||
• Governor of praetorian rank and given the 10th Legion | c. 74 CE | ||||||||
| 132–135 CE 135 CE | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Before 4 August 70 is referred to as Second Temple Judaism, from which the Tannaim and Early Christianity emerged. | |||||||||
Following the deposition of Herod Archelaus in 6 CE, Judea came under direct Roman rule,[1] during which time the Roman procurator was given authority to punish by execution. The general population also began to be taxed by Rome.[2] The province of Judea was the scene of unrest at its founding in 6 CE during the Census of Quirinius, the crucifixion of Jesus circa 30–33 CE, and several wars, known as the Jewish–Roman wars, were fought during its existence. The Second Temple of Jerusalem was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE near the end of the First Jewish–Roman War, and the Fiscus Judaicus was instituted. After the Bar Kokhba revolt (132–135), the Roman Emperor Hadrian changed the name of the province to Syria Palaestina and the name of the city of Jerusalem to Aelia Capitolina, which certain scholars conclude was an attempt to disconnect the Jewish people from their homeland.[3][4]
Background

The first intervention of Rome in the region dates from 63 BCE, following the end of the Third Mithridatic War, when Rome established the province of Syria. After the defeat of Mithridates VI of Pontus, Pompey sacked Jerusalem and installed Hasmonean prince Hyrcanus II as Ethnarch and High Priest but not as king. Some years later Julius Caesar appointed Antipater the Idumaean, also known as Antipas, as the first Roman Procurator. Antipater's son Herod was designated "King of the Jews" by the Roman Senate in 40 BCE[5] but he did not gain military control until 37 BCE. During his reign the last representatives of the Hasmoneans were eliminated, and the huge port of Caesarea Maritima was built.[6]
Herod died in 4 BCE, and his kingdom was divided among three of his sons, two of whom (Philip and Herod Antipas) became tetrarchs ('rulers of a quarter part'). The third son, Archelaus, became an ethnarch and ruled over half of his father's kingdom.[7] One of these principalities was Judea, corresponding to the territory of the historic Judea, plus Samaria and Idumea.
Archelaus ruled Judea so badly that he was dismissed in 6 CE by the Roman emperor Augustus, after an appeal from his own population. Herod Antipas, ruler of Galilee and Perea from 4 BCE was in 39 CE dismissed by Emperor Caligula. Herod's son Philip ruled the northeastern part of his father's kingdom.[8]
Judea as Roman province(s)
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Palestine |
-Temple_Mount-Dome_of_the_Rock_(SE_exposure).jpg.webp) |
| Prehistory |
| Ancient history |
| Classical period |
| Islamic rule |
| Modern era |
|
|
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Israel |
 |
| Ancient Israel and Judah |
| Second Temple period (530 BCE–70 CE) |
| Late Classic (70-636) |
| Middle Ages (636–1517) |
| Modern history (1517–1948) |
| State of Israel (1948–present) |
| History of the Land of Israel by topic |
| Related |
|
|
Under a prefect (6–41)
In 6 CE Archelaus' tetrachy (Judea, plus Samaria and Idumea)[9] came under direct Roman administration. The Judean province did not initially include Galilee, Gaulanitis (today's Golan), nor Peraea or the Decapolis. Its revenue was of little importance to the Roman treasury, but it controlled the land and coastal sea routes to the "bread basket" of Egypt and was a buffer against the Parthian Empire. The capital was at Caesarea Maritima,[10] not Jerusalem. Quirinius became Legate (Governor) of Syria and conducted the first Roman tax census of Syria and Judea, which was opposed by the Zealots.[11] Judea was not a senatorial province, nor an imperial province, but instead was a "satellite of Syria"[12] governed by a prefect who was a knight of the Equestrian Order (as was that of Roman Egypt), not a former consul or praetor of senatorial rank.[13]
Still, Jews living in the province maintained some form of independence and could judge offenders by their own laws, including capital offenses, until c. 28 CE.[14] Judea in the early Roman period was divided into five administrative districts with centers in Jerusalem, Gadara, Amathus, Jericho, and Sepphoris.[15]

The 'Crisis under Caligula' (37–41) has been proposed as the first open break between Rome and the Jews.[16]
Autonomy under Herod Agrippa (41–44)
Between 41 and 44 CE, Judea regained its nominal autonomy, when Herod Agrippa was made King of the Jews by the emperor Claudius, thus in a sense restoring the Herodian dynasty, although there is no indication that Judea ceased to be a Roman province simply because it no longer had a prefect. Claudius had decided to allow, across the empire, procurators, who had been personal agents to the Emperor often serving as provincial tax and finance ministers, to be elevated to governing magistrates with full state authority to keep the peace. He may have elevated Judea's procurator to imperial governing status because the imperial legate of Syria was not sympathetic to the Judeans.[17]
Under a procurator (44–66)
Following Agrippa's death in 44, the province returned to direct Roman control, incorporating Agrippa's personal territories of Galilee and Peraea, under a row of procurators. Nevertheless, Agrippa's son, Agrippa II was designated King of the Jews in 48. He was the seventh and last of the Herodians.
Between the years 66-70 follows the Great Revolt.
Under a legate (70–132)
From 70 until 135 Judea's rebelliousness required a governing Roman legate capable of commanding legions. Because Agrippa II maintained loyalty to the Empire, the Kingdom was retained until he died, either in 93/94 or 100, when the area returned to complete, undivided Roman control.
Judaea was the stage of two, possibly three, major Jewish–Roman wars:
- 66–70 CE– First Jewish–Roman War, resulting in the siege of Jerusalem, the destruction of Herod's Temple and ending with the siege of Masada in 73–74. (see Josephus). Before the war Judaea was a Roman province of the third category, that is, under the administration of a procurator of equestrian rank and under the overall control of the governor of Syria. After the war it became an independent Roman province with the official name of Judaea and under the administration of a governor of praetorian rank, and was therefore moved up into the second category (it was only later, in about 120 , that Judaea became a consular province, that is, with a governor of consular rank).[18]
- 115–117 – the Kitos War; Judea's role in it is disputed though, as it played itself out mainly in the Jewish diaspora and there are no fully trustworthy sources on Judea's participation in the rebellion, nor is there any archaeological way of distinguishing destruction levels of 117 CE from those of the major Bar Kokhba revolt of just a decade and a half later.
- 132–135 – Bar Kokhba's revolt; Following the suppression of Bar Kokhba's revolt, the emperor Hadrian changed the name of the province to Syria Palaestina and Jerusalem became Aelia Capitolina which Hayim Hillel Ben-Sasson states was done to erase the historical ties of the Jewish people to the region.[3] However, this did not prevent the Jewish people from referring to the country in their writings as either "Yehudah" (Hebrew: יהודה)[19][20] or "The Land of Israel" (Hebrew: ארץ ישראל).[21]
Between 132-135 follows the Bar Kokhba revolt.
Division into three provinces (135)

Under Diocletian (284–305) the region was divided into three provinces:[22]
- Palaestina Prima (Judea, Samaria, Idumea, Peraea and the coastal plain, with Caesarea Maritima as capital)
- Palaestina Secunda (Galilee, Decapolis and Golan, with Beth-Shean as capital)
- Palaestina Tertia (the Negev desert, with Petra as capital).
List of governors (6–135 CE)
References
- Haensch, Rudolf (19 August 2010). "The Roman Provincial Administration". In Catherine Hezser (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of Jewish Daily Life in Roman Palestine. OUP Oxford. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-19-921643-7.
- Josephus, De Bello Judaico (Wars of the Jews) 2.8.1.
- H.H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, Harvard University Press, 1976, ISBN 0-674-39731-2, page 334: "In an effort to wipe out all memory of the bond between the Jews and the land, Hadrian changed the name of the province from Iudaea to Syria-Palestina, a name that became common in non-Jewish literature."
- Ariel Lewin. The archaeology of Ancient Judea and Palestine. Getty Publications, 2005 p. 33. "It seems clear that by choosing a seemingly neutral name – one juxtaposing that of a neighboring province with the revived name of an ancient geographical entity (Palestine), already known from the writings of Herodotus – Hadrian was intending to suppress any connection between the Jewish people and that land." ISBN 0-89236-800-4
- Jewish War 1.14.4: Mark Antony "... then resolved to get him made king of the Jews ... told them that it was for their advantage in the Parthian war that Herod should be king; so they all gave their votes for it. And when the senate was separated, Antony and Caesar went out, with Herod between them; while the consul and the rest of the magistrates went before them, to offer sacrifices [to the Roman gods], and to lay the decree in the Capitol. Antony also made a feast for Herod on the first day of his reign."
- "Founded in the years 22-10 or 9 B.C. by Herod the Great, close to the ruins of a small Phoenician naval station named Strato's Tower (Stratonos Pyrgos, Turns Stratonis), which flourished during the 3d to 1st c. B.C. This small harbor was situated on the N part of the site. Herod dedicated the new town and its port (limen Sebastos) to Caesar Augustus. During the Early Roman period Caesarea was the seat of the Roman procurators of the province of Judea. Vespasian, proclaimed emperor at Caesarea, raised it to the rank of Colonia Prima Flavia Augusta, and later Alexander Severus raised it to the rank of Metropolis Provinciae Syriae Palestinae." A. Negev, "CAESAREA MARITIMA Palestine, Israel" in: Richard Stillwell et al. (eds.), The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites (1976).
- Josephus, De Bello Judaico (Wars of the Jews) 2.6.3; Antiquities 17.11.4 (17.317).
- Josephus, Antiquities 17.188–189, War 1.664.
- Ben-Sasson, Haim Hillel (1976). A History of the Jewish People. Harvard University Press. p. 246. ISBN 978-0-674-39731-6. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
When Archelaus was deposed from the ethnarchy in 6 CE, Judea proper, Samaria and Idumea were converted into a Roman province under the name Iudaea.
- A History of the Jewish People, H. H. Ben-Sasson editor, 1976, page 247: "When Judea was converted into a Roman province [in 6 CE, page 246], Jerusalem ceased to be the administrative capital of the country. The Romans moved the governmental residence and military headquarters to Caesarea. The centre of government was thus removed from Jerusalem, and the administration became increasingly based on inhabitants of the Hellenistic cities (Sebaste, Caesarea and others)."
- Josephus' Antiquities 18
- H. H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish Peoples, page 247–248: "Consequently, the province of Judea may be regarded as a satellite of Syria, although, in view of the measure of independence left to its governor in domestic affairs, it would be wrong to say that in the Julio-Claudian era Judea was legally part of the province of Syria."
- Josephus, Antiquities 17.355 & 18.1–2;
- Babylonian Talmud, Avodah Zarah 8b; ibid, Sanhedrin 41a; ibid, Shabbat 15a; Jerusalem Talmud, Sanhedrin 1:1 (1b)
- Gabba, Emilio (2008). "The social, economic and political history of Palestine 63 bce – ce 70". In William David Davies; Louis Finkelstein; William Horbury (eds.). The Cambridge History of Judaism: The early Roman period. Cambridge University Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-521-24377-3.
- H. H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, Harvard University Press, 1976, ISBN 0-674-39731-2, The Crisis Under Gaius Caligula, pages 254–256: "The reign of Gaius Caligula (37–41) witnessed the first open break between the Jews and the Julio-Claudian empire. Until then – if one accepts Sejanus' heyday and the trouble caused by the census after Archelaus' banishment – there was usually an atmosphere of understanding between the Jews and the empire ... These relations deteriorated seriously during Caligula's reign, and, though after his death the peace was outwardly re-established, considerable bitterness remained on both sides. ... Caligula ordered that a golden statue of himself be set up in the Temple in Jerusalem. ... Only Caligula's death, at the hands of Roman conspirators (41), prevented the outbreak of a Jewish–Roman war that might well have spread to the entire East."
- Tac. A.12.60
- Schäfer, Peter (2 September 2003). The History of the Jews in the Greco-Roman World: The Jews of Palestine from Alexander the Great to the Arab Conquest. Routledge. p. 131. ISBN 1-134-40316-X.
[From 74 to 123 CE] The consequences of the first great war of the Jews against Rome were extremely far-reaching and their significance for the future history of Judaism can hardly be overestimated. The immediate political consequences were drastic. As has already been mentioned, before the war Judaea was a Roman province of the third category, that is, under the administration of a procurator of equestrian rank and under the overall control of the governor of Syria. After the war it became an independent Roman province with the official name of Judaea and under the administration of a governor of praetorian rank, and was therefore moved up into the second category (it was only later, in about 120 CE, that Judaea became a consular province, that is, with a governor of consular rank). This new status of the province also implies that a standing legion, the legio X Fretensis, was stationed in Judaea. The headquarters of the 10th legion was the totally destroyed Jerusalem; the governor resided with parts of the 10th legion in Caesarea (Maritima), which Vespasian had converted into a Roman colony. (p. 131 at Google Books)
- The Mishnah (ed. Herbert Danby), Oxford University Press: Oxford 1933, s.v. Tractate Shebiit 9:2; compiled by Rabbi Judah the Prince in 189 CE.
- See p. 1 in: Feldman, Louis (1990). "Some Observations on the Name of Palestine". Hebrew Union College Annual. 61: 1–23. JSTOR 23508170.
- The Mishnah (ed. Herbert Danby), Oxford University Press: Oxford 1933, s.v. Tractate Kelim 1:6
- H. H. Ben-Sasson, A History of the Jewish People, Harvard University Press, 1976, ISBN 0-674-39731-2, page 351
- http://www.jewishpress.com/news/breaking-news/ancient-inscription-identifies-gargilius-antiques-as-roman-ruler-on-eve-of-bar-kochva-revolt/2016/12/01/
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Judea (Roman province). |