Karachi Nuclear Power Complex
The Karachi Nuclear Power Plant (or KANUPP) is a large commercial nuclear power plant located at the Paradise Point in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan.[1] Officially known as Karachi Nuclear Power Complex,[1] the power generation site is composed of three commercial nuclear power plants with two plants under construction with the financing and investment provided by China and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).[4]
| Karachi Nuclear Power Plant | |
|---|---|
| |
| Official name | Karachi Nuclear Power Complex |
| Country | Pakistan |
| Location | Paradise Point, Karachi, Sindh |
| Coordinates | 24°50′49.8″N 66°47′17.7″E |
| Status | Operational |
| Construction began | K1: 1 August 1966 K2: 20 August 2015 K3: 1 May 2016 |
| Commission date | K1: 28 November 1972 |
| Construction cost | K1: $ 57.3Mn (1966) K2 and K3: $ 9.5Bn (2013) |
| Owner(s) | Nuclear Regulatory Authority |
| Operator(s) | Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission |
| Nuclear power station | |
| Reactors | 3 |
| Reactor type | K1: PHWR (CANDU) K2: PWR (Hualong One) K3: PWR (ACP1000) |
| Reactor supplier | GE Canada (till 1976) Nuclear Power Fuel Complex China Nuclear Power Corp. |
| Cooling towers | 3 |
| Cooling source | Arabian sea |
| Feed-in tariff | K1: 14.2 Bn kW-h |
| Thermal capacity | 337 MW |
| Power generation | |
| Units operational | K1: 1 x 137 MWe |
| Units planned | 2 x 8800 MWe |
| Units under const. | 2 |
| Nameplate capacity | K1: 137 MWe K2: 1,100 MWe K3: 1,100 MWe |
| Capacity factor | 70.1 % (lifetime in 1973–79):145[1] 55.7 % (2012)[2] |
| Annual net output | K1: 125 MWe[3] |
| Storage capacity | 3.89 GW·h (2019) |
| External links | |
| Website | Karachi Nuclear Power Plant |
The nuclear power plant has a distinction of being the first commercial nuclear plant in the Muslim world.[5]
After a lengthy and complicated negotiations with Canada, the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant was constructed by Canadian firms in 1965 and it went critical in November 1972. The power station is subjected to regular IAEA monitoring, and is undergoing expansion with two nuclear power plants financed and funded by both IAEA and China.[4]
History
In 1960, Abdus Salam, then-science adviser to Ayub administration, provided a strong advocacy for the industrial usage of the nuclear power in his country at the UN General Assembly, paving away a path for the establishment of the nuclear power plant.:32[6] Despite the strong opposition from the officials in the Ayub administration, it was the personal efforts of Abdus Salam who had the funding and financing of the nuclear power plant approved from President Ayub Khan.:32–33[6] In 1963, the Government of Pakistan commissioned the Geological Survey of Pakistan (GSP) to conduct the survey for the nuclear power plant which selected the Paradise Point and Hawke's Bay as the ideal locations— the GSP selected Paradise Point for the location.:79[7] Negotiations and talks took place with Canada over the supply of the nuclear power plant in Karachi and the contract was signed with General Electric Canada as the designer and employed the Montreal Engineering Company as its civil engineering firm in 1965.:141–142[1]
The nuclear power plant was jointly designed by the engineers of Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission and the Canada's General Electric to provide distinction and difference from the India's nuclear research reactors such as CIRUS and Dhruva reactors that uses the same CANDU technology.[8] The decision-making factor that was taken under consideration to sell the CANDU technology to Pakistan by Canada was seen as maintaining a balance of power between India and Pakistan.:80[9] In 1966, the civil engineering and construction started by the Montreal Engineering Co. which finished its construction in 1971.:143[1] The nuclear power plant attained criticality on 1 August 1971, and commenced on producing full power generation on 2 October 1972.:141[1]
On 28 November 1972, President Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto inaugurated the Karachi Nuclear Plant when it was connected with the grid system of K-Electric, an investor-owned energy supply utility based in Karachi.[10]
Initially, Canada, through its contractor GE Canada, supplied the deuterium oxide moderator and the natural uranium but it wanted to eject from supporting the operations of the nuclear power plant after 1974 when India exploded the nuclear bomb whose fissile material was produced in CIRUS reactor initially supplied by Canada.:27[11][12] In 1975, the GE Canada begin to charge Pakistan $27/lb for deuterium oxide which was expensive for the country to afford.[8]
With Pakistan's refusal of becoming the party of the Nuclear Proliferation Treaty (NPT), the GE Canada halted to sell of imported spare parts, natural uranium, heavy water, and technical support for the nuclear power plant, raising fears of Karachi going under a blackout phase in 1976.:141[1] With Canadian technicians departing the country, the city was exposed to open radioactive materials while estimating that the nuclear power plant would shut down in six months.[8] Despite Canadian skepticism, the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission was able to worked on producing deuterium oxide at lesser price, and set up the machine shop to manufacture its machinery and tools near nuclear power plant with the assistance from Karachi University.[8]
The Canadian ejection from the project turned out to be a blessing in disguise because it allowed the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission establish its own machine shops, welding facilities, and training centers with the help from Karachi University that proved to be pivotal on country's production of able machinists and qualified welders as well as nuclear fuel cycle technology.:149[1] Since 1979, the deuterium oxide and heavy water is locally and indigenously produced by the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission that kept the plant running its grid operations.[12]
Many of spare parts and machine components were locally designed that kept the nuclear power plant running its grid operation in safe manner– the valuable experience gained was shared to Chinese officials in designing the reactor safety protocols and eventually helped run the Chashma Nuclear Power Plant in 1993.[8]
After intense negotiations and with the IAEA's cooperation in May 1990, Canadian policy towards Karachi Nuclear Power Plant was revised allowing it to provide assistance for Safe Operation of KANUPP (SOK) through the IAEA and only for the IAEA suggested remedial actions.[8]
In 2015 and 2016, China showed great interest in expanding the energy capacity of Karachi Nuclear Power Plant and signed an agreement to supply two Hualong One nuclear power plants with the start of commercial operations scheduled for 2021 and 2022 respectively.[4][13] Reactor units will have a design life of 60 years and account for approximately 10% of the country's total generation capacity.[4] As of 31 December 2017, the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant has generated 14.2 billion kWhr of electricity and been fueled by thousands of Pakistan-made fuel bundles without any failure.[14]
Reactor technology
KANUPP-1
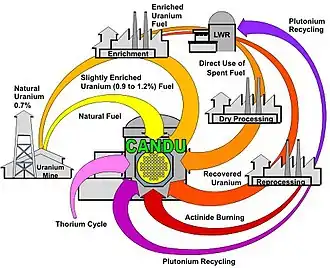
The first reactor unit at the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant is a single CANDU-type pressurized heavy-water reactor (PHWR)with a total gross energy generation capacity of 137 Megawatts (MW).:141[1] The KANUPP-1 uses the water-cooled Deuterium oxide (D2O or heavy water) moderator with natural uranium serving it as its fuel.:141[1] The KANUPP-1 is one of the oldest reactor that still uses the CANDU-type PHWR system to generate energy.:141[1]
The reactor consists of a tubed calandria vessel of austenitic stainless steel, which contains the heavy water moderator and 208 coolant tube assemblies.[15] The moderator system consists of the calandria, coolers, pumps and purification system in the heavy water circuit, and control valves, dump valves and helium blowers in the helium circuit.[16] The fuel is natural uranium in the form of sintered uranium dioxide pellets sheathed in thin zirconium alloy tubes to form solid fuel elements about 19.1 inches (48.53 cm) long by 0.6 inches (1.4 cm) diameter.[15][16]
In 2010, a Multi-effect distillation (MED) process source was connected to Karachi Nuclear Power Plant that can produce 1600 m3/d of potable water.:27[17] In addition, a Reverse osmosis plant is also coupled with the nuclear power plant that is producing 454 m3/d of water for reactor usage.:27[17]
Between 1970–90s, the KANUPP-1 has generated energy of about ~7.9 billion units of electricity with an average lifetime availability factor of 55.9%.:143[1] The Canadian technicians designed the life of the plant operations for ~30 years which it did complete its lifetime in 2002.[18] The Nuclear Regulatory Authority (NRA), the owner of the nuclear power plant, extended its lifetime operation to 2012, and is currently kept 8.1% capacity factor with total energy generation of 90 MW as of 2020.[19] The KANUPP-1 is expected to decommissioned and has been scheduled for closer in 2022 which would mark the end of its 40-year long services to the nation.[20]
KANUPP-2
In 2015, Chinese energy contractors became interested in Karachi Nuclear Power Plant – eventually the Pakistani administration and Chinese government signed an energy agreement to construct two Hualong One reactor units at the $9.5 Bn with each reactor producing 1,100 MW.[21][20][22]
The KANUPP-2 is a pressurized water reactor (PWR) supplied by the China National Nuclear Corporation, and is jointly designed by the engineers of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission.[8] On 26 November 2013, Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif ceremonially broke ground on an energy project at the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant for the construction of two reactor units, one consisting the Hualong One and the other is ACPR-1000— both are pressurized water reactor.[23][24] Construction of the KANUPP-2 begins on 20 August 2015 and the KANUPP-3's construction commenced on 31 May 2016.[25] Both units are near completion and are expected to attain full energy capacity in 2021 and 2022 respectively.[13]
According to Dr. Ansar Pervaiz, then Chairman of the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission, said that Chinese banks have provided $6.5 Bn for this project as loans and the cold testing of the reactor system at the KANUPP-2 was commenced on 9 December 2019.[26][27][28][29][30][23] The China Zhongyuan Engineering Corporation (CZEC) is currently serving its civil engineering consultant for both reactors.[31]
KANUPP-3
The KANUPP-3 is a sister Hualong One nuclear reactor supplied by the China National Nuclear Corporation whose construction was commenced on 31 May 2016, being constructed alongside KANUPP-2.[32] As similar to Hualong One, the ACPR-1000 is also being built in Karachi with Chinese supervision and the first steam engine was installed on 28 August 2018.[33]
The KANUPP-3 is expected to join the nation's power grid system by October 2021.[34][35][13]
Energy management
Electricity grid connections
The National Engineering Services (NES) provides consultancy on energy management of the nuclear power plant and manages the electricity power transmission operations by replacing the aging transformers, three-phase electric powerlines, circuit breakers, and protective relay of the 132 kV double circuit transmission line that links the nuclear power plant to the K-Electric.[36] The NES often works closely with the Institute of Power Engineering of the Karachi University to devise discriminative protection scheme and its integration into the nuclear power plants grid system.[36] In 2010, the NES and Institute of Power Engineering engaged in replacing the electromechanical power relays with the SF6 circuit breakers and modern numerical line protection devices.[36]
Energy capacity and corporate management
The Karachi Nuclear Power Plant was designed to produce gross energy at 137 MWe with the corresponding net output is 125 MWe.[36] From 1972–79, the nuclear power plant operated with relatively high availability capacity factors upto 70%– it provided the electricity and energy to the whole city of Karachi.:143[1] Between 1972–92, the nuclear power plant generated the energy about 7.9 billion units of electricity with an average lifetime availability capacity factor of 55.9%.:141[1] In 1994, the nuclear power plant was exceptionally operated at 85.81% of capacity factor– the highest since its establishment.:141[1] In 2002–04, the nuclear power plant was shut down due to maintenance issues, and is now kept at 55.55% capacity factor, nominally producing 90 MW of energy generation.[37]
With the completion of the two more units, the nuclear power plant is expected to produce over 2000 MW of electricity at an 80-90% capacity.[4][23]
The Karachi Nuclear Power Plant is owned by the Nuclear Regulatory Authority (NRA) of Pakistan that is responsible for licensing, inspection and ensuring the safety procedures taking place while running the power plant.[38] The National Engineering Services (NES) of Pakistan, the contractor, manages nuclear power plant on site on behalf of Nuclear Regulatory Authority and oversees the overall electricity distribution of nuclear power plant including the employment of transformers and grid connections over the city.[36] The K-Electric supports the NES operations to manage the plant and relays on energy provided by the nuclear power plant to feed through its circuits.[37] The Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission, on the other hand, has the responsibility of running the overall operations of the nuclear power plant including computerized machinery, plant stimulators, and manufacturing of fuel bundles, producing fuel cycle, manufacturing tools, and employing of computers.[39]
Reception
Power outages, leakages, engineering
The Karachi Nuclear Power Plant received wide range of media publicity and fame when it was inaugurated by President Zulfikar Ali Bhutto on 2 November 1972, accompanied by nation's top scientists and high ranking civic officials.[10] Since 2000, the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant has been subjected to a political debate and controversy between nation's anti-nuclear power and pro-nuclear power activists due to its repeated shutdown to generate energy to provide to the city.[19] In 2000, Zia Mian, a physicist at the SDPI based in Islamabad, compared the performance and efficiency of nuclear power plant as "six worst performing reactors in the world.":5–6[40]
In the wake of nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011, the Nuclear Regulatory Authority (NRA) of Pakistan did a safety inspection of the nuclear power plant.[19] Dr. Pervez Hoodbhoy who visited the nuclear power plant as part of the inspection viewed negatively of the performance of the plant and was very critical of IAEA's monitoring of the plant.[19] Without the Canadian material support, the nuclear power plant has been shutdown multiple times in the years of 1979, 1982, 1993, and in 2002.:144–146[1] The power outages at the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant has been reported to high as compared to the other Canadian CANDU reactor, mainly attributed to equipment and regulation failure.:147[1] In 2002, the Nuclear Regulatory Authority was established to set up the regulation codes, safety regulations, and statues based on the experience learned in running the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant.[8]
The uranium hexafluoride (UF6) leakages in nuclear steam cylinder has been commonly reported multiple times but it was addressed when Bashiruddin Mahmood claimed to invent a scientific instrument to prevent further leakages.[41] On 18 October 2011, a seven-hour emergency was imposed by the NES (manager of the plant) after detecting a heavy water leak from a feeder pipe to the reactor during a routine maintenance shut down.[42] The emergency was lifted seven hours later, after the leak was reportedly brought under control.[42]
Despite incidents of power outages, the senior physicists and the management of the nuclear power plant has dismissed the criticism of the operations of the nuclear power plant who maintained that the power plant had to be run without Canada's technical and material support, and facilities which were nonexistence in the country to support the operations of the plant.[8] The welding facility, tool manufacturing, and machine shops near the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant were eventually established by Parvez Butt (a mechanical engineer) to support the nuclear power operations of the plant in successive years— Butt was honored with nation's highest honor for this contribution.[8]
According to report submitted to IAEA by S.B. Hussain, a senior physicist who worked at Karachi Nuclear Power Plant, maintained that operating nuclear power plant in the environment of complete Canadian absence was a difficult task, but proved a blessing in disguise, because it provided the Atomic Energy Commission an opportunity to engage in self-reliance in producing nuclear fuel cycle and self-manufacturing programs that was pivotal experience in safely running and managing the much larger Chashma Nuclear Power Plant in Punjab.:149[1][8]
Notable staff
- Parvez Butt– machinist, chief engineer, director of nuclear power, Chair of PAEC (2001–06)
- Bashiruddin Mahmood– principle engineer
- Ansar Pervaiz— engineer, general manager of nuclear power plant, Chair of PAEC (2009–13)
- Wazed Miah, physicist and chief scientist at nuclear power plant (1972—74)
- Hameed Ahmad Khan, physicist and chief scientist at nuclear power plant
- Anwar Habib, principle engineer and nuclear safety
- Zaheer Baig, health physicist and radiation control
Education facilities
Training opportunities
Since 1973, the Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission engaged in joint educational venture with University of Karachi's physics department to sponsor degree programs in health physics and electronics engineering, and extended partnership with the NED University on electrical engineering, specifically the power engineering.[43]
The Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences in Islamabad operates and maintains the Institute of Power Engineering in Karachi that offers training programs and courses in nuclear, electrical, and mechanical engineering at the Karachi Nuclear Power Plant.[44]
See also
References
- Hussain, S.B. (1996). "Karachi Nuclear Power Plant -- A Review of Performance, Problems, and Upgrades" (PDF). www.inis.iaea.org. Karachi, Sind. Pakistan: IAEA publications. p. 17. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- )"Pakistan's Karachi nuclear power plant 'back in operation,'" BBC Worldwide Monitoring – South Asia, 4 December 2006; Pakistan
- "Plant Features -- KANUPP". 28 March 2009. Archived from the original on 28 March 2009. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- "Karachi Nuclear Power Plant (KANUPP) Expansion, Pakistan". Power Technology | Energy News and Market Analysis. Power Technology. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Yusuf, S. Irfan Ali (1981). "Nuclear Energy in the Muslim World". Pakistan Horizon. Islamabad: Pakistan Institute of International Affairs. 34 (1): 59–73. JSTOR 41393645. 41393645.
- Riazuddin (2005). "Contribution of Professor Abdus Salam as Technical Member of Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission (PAEC)" (PDF). The Nucleus. Islamabad: Professor Riazuddin, emeritus scientist at the National Center for Nuclear Physics, and a professor of theoretical physics at the Institute of Physics of the Quaid-i-Azam University. 42 (1–2): 31–34. ISSN 0029-5698. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- others, Embassy officials (1970). "(§ Atomic Energy in Pakistan)". Pakistan Affairs (googlebooks). Information Division, Embassy of Pakistan. p. 200. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Shabbir, Usman (5 July 2004). "Remembering Unsung Heroes: Munir Ahmad Khan". www.defencejournal.com. Defense Journal. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Pigott, Peter (2007). Canada in Afghanistan: The War So Far (googlebooks). Toronto, Ont.: Dundurn. p. 227. ISBN 978-1-4597-1239-3. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Prime minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto with Abdus Salam and Munir Ahmad Khan (1971). Pakistan - PAEC Chairman & Z.A Bhutto inauguration of KANUPP nuclear plant (TV-Medium). Karachi, Sindh Province, Pakistan: Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission and Pakistan Military Consortium (PMC).
- P.L. Bhola, Pakistan's Nuclear Policy (New Delhi: Sterling Publishers Private Limited, 1993), p. 27.
- "KANUPP | Facilities | NTI". www.nti.org. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Hot tests completed at Pakistani Hualong One". World Nuclear News. 7 September 2020. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- "PRIS - Reactor Details". pris.iaea.org. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "CANDU reactor". Wikipedia. 10 August 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Plant Description -- KANUPP". 5 December 2008. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- Alonso, Gustavo; Valle, Edmundo del; Ramirez, Jose Ramon (2017). Desalination in Nuclear Power Plants. Oxford: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-12-820021-6. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "KANUPP Gets 10 Year Extension," Nuclear Engineering International, 16 December 1999.
- InpaperMagazine, From (30 October 2011). "Earthly matters: Shutting down KANUPP". DAWN.COM. Dawn Newspaper. Dawn Newspaper. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Govt to kick off work on 1,100MW nuclear power plant - The Express Tribune". 7 June 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- Pakistan to start work on Chinese-aided nuclear power plant
- "The Nuclear Shadow over Karachi". 17 March 2014. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "With Reactor Deal, China and Pakistan Seek to Reshape Global Nuclear Governance". Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "Pakistan Breaks Ground on Nuclear Plant Project With China". The New York Times. 27 November 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "Pakistan 2019". cnpp.iaea.org. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Cold testing completed at Pakistan's Karachi 2 - Nuclear Engineering International". www.neimagazine.com. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- China commits $6.5 billion for nuclear power project in Karachi
- Worldcrunch.com. "Local Fallout From Pakistan". Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "Nuclear reactors worry Pakistan's fishers - All media content - DW.COM - 20.03.2014". Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "PM Sharif in Karachi, inaugurates KANUPP-2 power project". Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- "Pressure vessel in place at Karachi 2". World Nuclear News. 11 October 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- "Pakistan / Installation Of Reactor Internals Completed At Kanupp-3". The Independent Global Nuclear News Agency. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "China installs first steam generator at unit 3 of Pakistan's Kanupp NPP - Nuclear Engineering International". www.neimagazine.com. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Kanupp-2 to come online in Dec 2020". www.thenews.com.pk. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- "Kanupp-2 to come online in December 2020, Kanupp-3 in October 2021". CustomNews.pk. 3 December 2018. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- staff reporter, news reporters (14 July 2009). "NESPAK provides services for power projects". www.thenews.com.pk. Karachi, Sind. Pakistan: News International, 2009. News International. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- "Kanupp's supply to KESC restored". www.thenews.com.pk. News International,2007. News International. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- "KANUPP-I". www.pnra.org. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- "NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS IN PLANNING PHASE (K-2)".
- Mia, Zia (2000). "Some issues associated with Pakistan's Karachi Nuclear Power Plant (KANUPP)" (PDF). www.sgs.princeton.edu. Islamabad: Zia Mian, researcher at Sustainable Development Policy Institute. p. 12. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- See: SBM Detection Instrument
- Aziz, Faisal (20 October 2011). "Leak at Pakistani nuclear plant, but no damage". reuters.com. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- staff reporter, others (10 July 2002). "KARACHI: KINPOE convocation tomorrow". DAWN.COM. Dawn Newspaper, 2002. Dawn Newspaper, 2002. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- "Karachi Institute of Power Engineering". Retrieved 16 August 2020.
External links
- http://www.nespak.com.pk/news/newsdetail.asp?id=1457
- Karachi Nuclear Power Plant
- KARACHI: Plan to establish 1,000MW Kanupp-II put on hold
- Pakistan Deal Signals China's Growing Nuclear Assertiveness
- Nuclear safety in Karachi
- Nuclear Karachi
- China commits $6.5 billion for nuclear power project in Karachi
- Lesson from Nuclear Disasters and Karachi Nuclear Plants
- The anti-nuclear lobby
- China commits $6.5bn for Karachi nuclear project
- Enlightened Nuclear Karachi
- Karachi being used as guinea pig for nuclear power plants
- Decision to install N-reactor in Karachi