Kirkby Lonsdale
Kirkby Lonsdale (/ˈkɜːrbi ˈlɒnzdeɪl/) is a small town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, on the River Lune. Historically in Westmorland, it lies 13 miles (21 km) south-east of Kendal on the A65. The parish had a population of 1,771 recorded in the 2001 census,[1] increasing to 1,843 at the 2011 Census (including Middleton).[2] Notable buildings include St Mary's Church, a Norman building with fine carved columns. The view of the River Lune from the churchyard is known as Ruskin's View after John Ruskin, who called it "one of the loveliest views in England". It was painted by J. M. W. Turner.
| Kirkby Lonsdale | |
|---|---|
 Ruskin's View | |
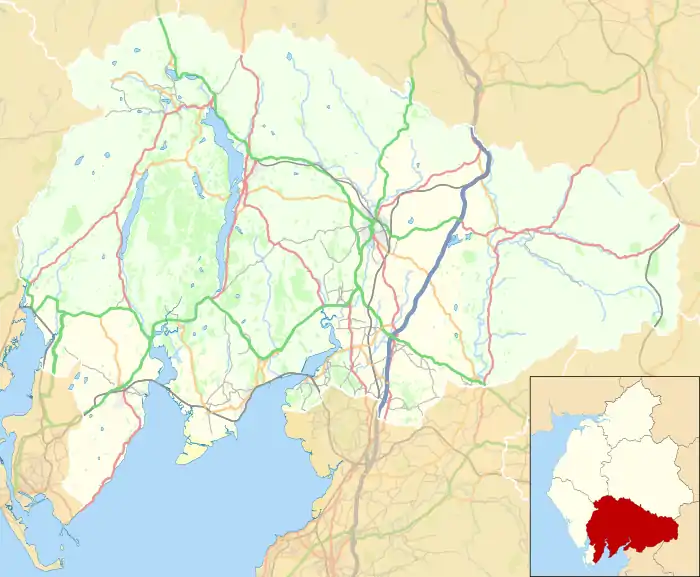 Kirkby Lonsdale Location in South Lakeland 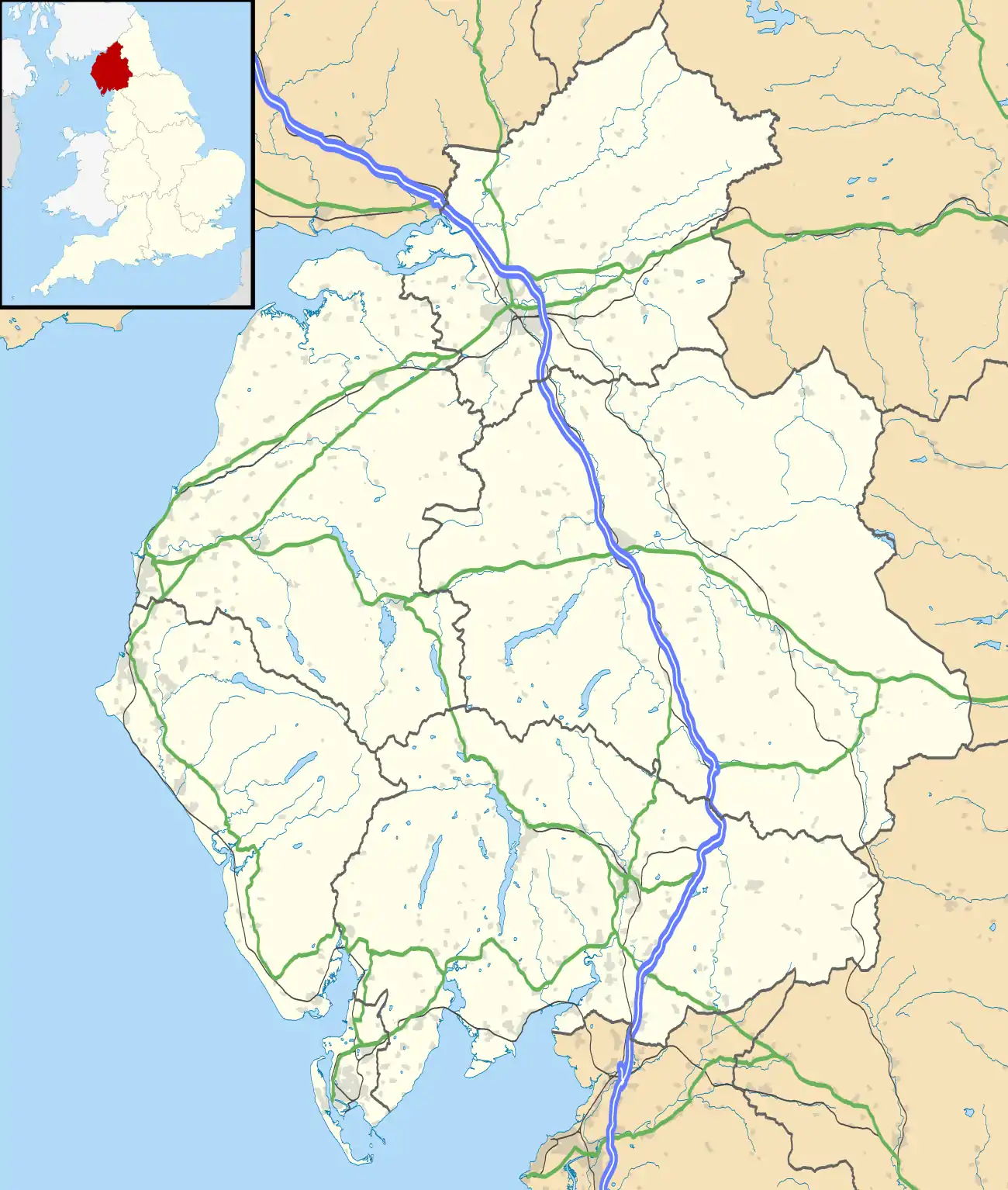 Kirkby Lonsdale Location within Cumbria | |
| Population | 1,843 (2011 Census) |
| OS grid reference | SD6178 |
| Civil parish |
|
| District | |
| Shire county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | CARNFORTH |
| Postcode district | LA6 |
| Dialling code | 015242 |
| Police | Cumbria |
| Fire | Cumbria |
| Ambulance | North West |
| UK Parliament | |
Governance
Kirkby Lonsdale is part of the Westmorland and Lonsdale parliamentary constituency, of which Tim Farron is the current MP representing the Liberal Democrats.[3]
For Local Government purposes, it is in the Kirkby Lonsdale Ward of South Lakeland District Council and the Sedbergh & Kirkby Lonsdale Division of Cumbria County Council.
Kirkby Lonsdale has its own parish council; Kirkby Lonsdale Town Council.[4]
Early history
Early signs of occupation in the area are a Neolithic stone circle on Casterton Fell and remains of Celtic settlements at Barbon, Middleton and Hutton Roof.
During the Roman occupation, a Roman road followed the River Lune, linking forts at Low Borrow Bridge (near Tebay) and Over Burrow (south of Kirkby Lonsdale). A Roman milestone unearthed in 1836 and described as "the best in the country" was re-erected on a hill near Hawkin Hall (SD 623 859), close to where it was found.

Kirkby Lonsdale developed at a crossing over the River Lune, where drovers' and pack-horse routes converged. It is one of few Cumbrian towns mentioned in the Domesday Book, where it is called Cherchibi (village with a church). The earlier church was rebuilt by the Normans, who erected an artificial mound or motte on nearby glebe land. A wooden tower or keep is thought to have surmounted the stronghold as a base for control over the surrounding area.
In later years, the mound was used for cockfighting, hence the current name of Cockpit Hill. In 1093, Ivo de Taillebois (Baron of Kendal) granted the church at Kirkby Lonsdale to St Mary's Abbey in York, which held it until the Dissolution. Thereafter the Abbey and all its possessions, including St Mary's Church at Kirkby Lonsdale, were passed to Trinity College, Cambridge, which retains patronage to this day.
In 1227, the town gained a market charter and the right to hold an annual fair every September. Each week stallholders would gather in Market Street to sell their wares, as did horse traders in the Horsemarket and pig sellers in Swinemarket. Thursdays were, as now, the scene of great activity.
19th century onwards
The weekly market and daily throughput of drovers and pack-horse carriers created a bustling town, with a total of 29 inns and alehouses, of which eight still serve that purpose. By the early 19th century, the old market area was becoming too congested for its volume of trade and a new market place was built in 1822.

The steep incline of Mill Brow with its fast-flowing (now culverted) stream was the industrial heart of Kirkby Lonsdale, with several mills using water power for grinding corn, bark and bone, carding wool, manufacturing snuff, making bobbins, fulling cloth and sawing timber.
The Keighley and Kendal Turnpike of 1753 passed through Kirkby Lonsdale and met there with a turnpike from Milnthorpe on the coast. In 1818, the two trusts were amalgamated.[5] Kirkby Lonsdale railway station, 2 miles (3 km) away in Lancashire, opened in 1861 and closed to passengers in 1954.
Today, Kirkby Lonsdale remains a busy town with a market. The centre is a mix of elegant 18th-century buildings and stone cottages huddled around cobbled courtyards and narrow alleyways, with names such as Salt Pie Lane and Jingling Lane.
St Mary's Church is an active Anglican parish church in the deanery of Kendal, the archdeaconry of Westmorland and Furness, and the diocese of Carlisle. Its benefice is united with those of six local churches to form the Kirkby Lonsdale Team Ministry.[6] It contains Norman architecture and is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building.[7]
Kirkby Lonsdale's secondary school, Queen Elizabeth School,[8] specialises in the performing arts, sports and languages. It is situated on Biggins Road, it takes pupils aged 11–18.
A two-day Victorian fair used to be hosted in the town each September. The streets were closed to traffic and filled with traders' stalls, craft demonstrations and entertainment, while visitors were encouraged to wear Victorian dress.
Motorbike enthusiasts meet every Sunday at Devil's Bridge.
Devil's Bridge

The town is noted for the Devil's Bridge (54.199°N 2.590°W) which at one time carried the Skipton to Kendal road over the River Lune. It dates from around 1370 and is constructed of fine gritstone ashlar. It has three spans, the western two measuring 54.75 feet (16.69 m) each and the eastern one 29 feet (8.8 m), or 45 feet (14 m) from river to parapet. The piers are hexagonal, measuring 60 feet (18 m) around and extend upwards to provide pedestrian refuges. At the eastern end is a sundial in the form of a square block on an octagonal column.[9] The bridge was probably built by monks of St Mary's Abbey, York.
In common with many bridges of the same name, legend holds that the Devil appeared to an old woman, promising to build a bridge in exchange for the first soul to cross over it. When the bridge was finished, the woman threw bread over the bridge and her dog chased after it, thereby outwitting the Devil. Several large stones in the surrounding area, including the Great Stone of Fourstones, are ascribed to the Devil's purse strings bursting open as he ferried masonry to build it. It was repaired in 1705 and repointed in 1829 using Roman-style cement. The eastern arch was repaired in around 1869.
The roadway on the bridge is only 12 feet (3.7 m) wide, insufficient for modern traffic. As vehicle numbers increased the bridge was closed to vehicular traffic in 1932.[10] Traffic instead crosses the river by the Stanley Bridge, 490 feet (150 m) to the south, which was built in the 1930s. Devil's Bridge is a grade I listed structure and a Scheduled Ancient Monument.[9]
The river beneath Devil's Bridge is popular with scuba divers due to relatively easy access and egress, deep rock pools (about 16 ft in a low swell) and good visibility. The bridge also witnesses illegal "tombstoning" (bridge diving), which has caused at least one death, of a 22-year-old man in 2012.[11]
See also
- Listed buildings in Kirkby Lonsdale
- Lonsdale, South Australia, named after Kirkby Lonsdale
References
- "Parish headcount" (PDF). Cumbria County Council. Retrieved 13 January 2009.
- "Town population 2011". Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- "Tim Farron". theyworkforyou.com. Archived from the original on 1 June 2013.
- "Kirkby Lonsdale Town Council".
- "Introduction To The Main Roads of Kendale". British Historyac.uk. p. 18. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- St Mary the Virgin, Kirkby Lonsdale, Church of England, retrieved 16 August 2012
- Historic England, "Church of St Mary, Kirkby Lonsdale (1145774)", National Heritage List for England, retrieved 16 August 2012
- Queen Elizabeth School.
- Historic England. "Devils Bridge (that part in Casterton CP) (1086899)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
- "Devil's Bridge, Kirkby Lonsdale". Engineering Timelines. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
- "Warning as Devil's Bridge 'tombstoning' continues despite death". BBC. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kirkby Lonsdale. |
- Cumbria County History Trust: Kirkby Lonsdale (nb: provisional research only - see Talk page)
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Kirkby Lonsdale. |