List of leaders of North Korea
The Supreme leader of North Korea is the de facto top leader of North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK). The holder of the office serves as the leader of the Workers' Party of Korea (currently General Secretary) , chief of the state (currently Chairman of the State Affairs Commission) and the Supreme Commander of the Korean People's Army as well as the holder of the highest office of North Korea.
| Supreme Leader of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea
조선민주주의인민공화국의 최고령도자 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Status | Supreme leader |
| Residence | Ryongsong Residence[1] |
| Appointer | Hereditary succession (de facto) |
| Term length | Life tenure |
| Inaugural holder | Kim Il-sung |
| Formation | 9 September 1948 |
| List of leaders of North Korea | |
| Hangul | |
|---|---|
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Joseon Minjujuui Inmin Gonghwagukui Choegoryeong Doja |
| McCune–Reischauer | Chosŏn Minjujuŭi Inmin Konghwagugŭi Ch'oegoryŏng Toja |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of North Korea |
|
|
At the end of World War II, the Soviet Union occupied the northern half of Korea and in 1946 established the Provisional People's Committee for North Korea chaired by Kim Il-sung. On 9 September 1948, the DPRK was proclaimed, also led by Kim Il-sung.
The leaders of the DPRK have been Kim Il-sung, his son Kim Jong-il, and his grandson Kim Jong-un. In this role they have not held consistent titles, though they were each leaders of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK)—titled as Chairman from 1948 to 1966, General Secretary from 1966 to 2011, First Secretary from 2011 to 2016, Chairman again from 2016 to 2021, and finally General Secretary again since 2021—for almost all of their period in power. Even though they have the appearance of a dynasty, succession is informal.
From 1948 to 1972, the nominal head of state was the Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly (SPA). In 1972, the constitution was amended to create an executive presidency. Kim Il-sung, who had served as Premier of North Korea since the DPRK's inception, was unanimously elected President of North Korea by the Supreme People's Assembly on December 28. He held this office until his death on 8 July 1994 when he was proclaimed the "eternal President of the Republic". Practical functions of the head of state were then exercised by the President of the Presidium of the Supreme People's Assembly, before being transferred to the Chairman of the State Affairs Commission.
After the death of Kim Il-sung, his son Kim Jong-il was understood to have inherited his father's near-absolute control over the country.[2][3][4] Although he had been his father's designated successor since at least 1991, it took him three years to fully consolidate his power. He was elected general secretary of the party in 1997, and was reelected Chairman of the National Defence Commission (NDC) in 1998. During his rule he was given a range of titles. He ruled the country until his death on 17 December 2011. He was succeeded by his son, Kim Jong-un, who was revealed to be in charge of the country since his father's death by the Rodong Sinmun and finally publicly acknowledged as "Supreme Leader" at the military review ending Kim Jong-il's funeral on 29 December 2011. Who would succeed Kim Jong-un is uncertain and has been speculated upon after health concerns arose in April of 2020.[5]
The government is headed by the Premier of the Cabinet, formerly called Premier of the Administration Council.
Other important institutions include the SPA, whose sessions are chaired by the Chairman of the Supreme People's Assembly, and, since 1993, the Chairman of the NDC–since 2016, known as the State Affairs Commission–which holds supreme command of the DPRK's armed forces.
While two other parties, the Korean Social Democratic Party and the Chondoist Chongu Party, nominally exist, only the WPK holds any power at the national level. The other parties, and indeed all other mass organizations in the country, are completely subservient to the WPK. Almost nothing is mentioned about the minor parties except the names of their current leaders.[6]
Since 1997, the SPA chairman, premier and NDC/SAC chairman have officially formed a triumvirate heading the executive branch, with powers equivalent to one-third of a president's powers in other presidential systems. The SPA chairman conducts foreign affairs and receives the credentials of ambassadors, the premier handles domestic policy and the NDC/SAC chairman commands the armed forces. In practice, however, the real power is vested in the SAC chairman (who has also been leader of the WPK), an office constitutionally defined as the "highest post in the state”.
Currently, General Secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea is the first priority political position of the Supreme Leader.[7]
Supreme leader of North Korea
All supreme leaders of North Korea hold the positions of leader of the Workers' Party of Korea and supreme commander of the Korean People's Army. The Constitution of North Korea has officially recognized the title "Supreme Leader" since 2009, when the chairman of the National Defence Commission (and as of 2016 when it was replaced by chairman of the State Affairs Commission) was formally designated as the "supreme leader of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea" (Korean: 조선민주주의인민공화국의 최고 령도자).[8][9][10]
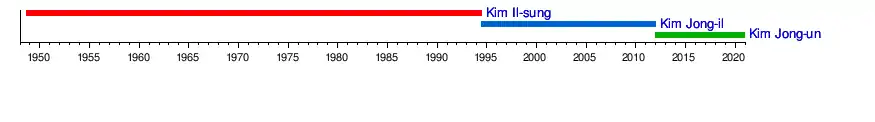
Generations of leadership
First generation Second generation Third generation
- Bold offices refer to the highest positions in North Korea
| Picture | Name | Offices held | Period | Ideology | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Kim Il-sung 김일성 (1912–1994) | ||||
| Premier of the Cabinet of the DPRK | 9 September 1948 – 28 December 1972 | 9 September 1948 ↓ 8 July 1994 † (45 years, 302 days) |
Juche (Ten Principles) | ||
| Chairman of the Central Committee of the WPK | 30 June 1949 – 11 October 1966 | ||||
| Chairman of the Central Military Commission of the WPK | 26 June 1950 – 8 July 1994 | ||||
| Supreme Commander of the KPA | 4 July 1950 – 24 December 1991 | ||||
| General Secretary of the Central Committee of the WPK | 11 October 1966 – 8 July 1994 | ||||
| President of the DPRK | 28 December 1972 – 8 July 1994 | ||||
| Chairman of the National Defence Commission of the DPRK | 28 December 1972 – 9 April 1993 | ||||
| Eternal President of the DPRK | 5 September 1998 – present | ||||
 |
Kim Jong-il 김정일 (1941–2011) | ||||
| Supreme Commander of the KPA | 24 December 1991 – 17 December 2011 | 8 July 1994 ↓ 17 December 2011 † (17 years, 162 days) |
Juche Songun (Ten Principles) | ||
| Chairman of the National Defence Commission of the DPRK | 9 April 1993 – 17 December 2011 | ||||
| General Secretary of the WPK | 8 October 1997 – 17 December 2011 | ||||
| Chairman of the Central Military Commission of the WPK | |||||
| Eternal General Secretary of the WPK | 11 April 2012 – present | ||||
| Eternal Chairman of the National Defence Commission of the DPRK | 13 April 2012 – present | ||||
 |
Kim Jong-un 김정은 (born 1983) | ||||
| Supreme Commander of the KPA | 30 December 2011 – present | 17 December 2011 ↓ Incumbent (9 years, 52 days) | |||
| First Secretary of the WPK | 11 April 2012 – 9 May 2016 | ||||
| Chairman of the Central Military Commission of the WPK | 11 April 2012 – present | ||||
| First Chairman of the National Defence Commission of the DPRK | 13 April 2012 – 29 June 2016 | ||||
| Chairman of the WPK | 9 May 2016 – 10 January 2021 | ||||
| Chairman of the State Affairs Commission | 29 June 2016 – present | ||||
| Supreme Representative of the Korean People[11] | April 2019 – present | ||||
| General Secretary of the WPK | 10 January 2021 – present | ||||
Leaders of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK)

| No. | Portrait | Name | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman | |||||||
| 1 | Kim Tu-bong (1889–1958) | 28 August 1946 | 30 June 1949 | 2 years, 306 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Chairman of the Central Committee | |||||||
| 2 | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) | 30 June 1949 | 11 October 1966 | 17 years, 103 days | Workers' Party | ||
| General Secretary of the Central Committee | |||||||
| (2) | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) | 11 October 1966 | 8 July 1994 † | 27 years, 270 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Vacant (8 July 1994–8 October 1997) | |||||||
| General Secretary of the Party | |||||||
| 3 | Kim Jong-il (1941–2011) [lower-alpha 1] | 8 October 1997 | 17 December 2011 † | 23 years, 122 days | Workers' Party | ||
| First Secretary of the Party | |||||||
| 4 | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 11 April 2012 | 9 May 2016 | 4 years, 28 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Chairman of the Party | |||||||
| (4) | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 9 May 2016 | 10 January 2021 | 4 years, 246 days | Workers' Party | ||
| General Secretary of the Party | |||||||
| (4) | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 10 January 2021 | Incumbent | 28 days | Workers' Party | ||
Heads of state
| No. | Portrait | Name | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly | |||||||
| 1 | Kim Tu-bong (1889–1958) | 9 September 1948 | 20 September 1957 | 9 years, 11 days | Workers' Party (WPNK until 1949) | ||
| 2 | Choe Yong-gon (1900–1976) | 20 September 1957 | 28 December 1972 | 15 years, 99 days | Workers' Party | ||
| President of the Republic | |||||||
| 3 | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) [lower-alpha 2] | 28 December 1972 | 8 July 1994 † | 21 years, 192 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Vacant (8 July 1994–5 September 1998) | |||||||
| President of the Presidium of the Supreme People's Assembly | |||||||
| 4 | Kim Yong-nam (born 1928) | 5 September 1998 | 11 April 2019 | 20 years, 218 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 5 | Choe Ryong-hae (born 1950) | 11 April 2019 | Incumbent | 1 year, 302 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Supreme Leader of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea | |||||||
| — | Kim Jong-il (1941–2011) | 9 April 2009 | 17 December 2011 † | 2 years, 252 days | Workers' Party | ||
| — | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 8 March 2012 | Incumbent | 8 years, 336 days | Workers' Party | ||
Heads of government
| No. | Portrait | Name | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premier of the Cabinet | |||||||
| 1 | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) | 9 September 1948 | 28 December 1972 | 24 years, 110 days | Workers' Party (WPNK until 1949) | ||
| Premier of the Administration Council | |||||||
| 2 | Kim Il (1910–1984) | 28 December 1972 | 19 April 1976 | 3 years, 113 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 3 | Pak Song-chol (1913–2008) | 19 April 1976 | 16 December 1977 | 1 year, 241 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 4 | Ri Jong-ok (1916–1999) | 16 December 1977 | 27 January 1984 | 6 years, 42 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 5 | Kang Song-san (1931–2007) | 27 January 1984 | 29 December 1986 | 2 years, 336 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 6 | Ri Kun-mo (1926–2001) | 29 December 1986 | 12 December 1988 | 1 year, 349 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 7 | Yon Hyong-muk (1931–2005) | 12 December 1988 | 11 December 1992 | 3 years, 365 days | Workers' Party | ||
| (5) | Kang Song-san (1931–2007) | 11 December 1992 | 21 February 1997 | 4 years, 72 days | Workers' Party | ||
| – | Hong Song-nam (1929–2009) Acting | 21 February 1997 | 5 September 1998 | 1 year, 196 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Premier of the Cabinet | |||||||
| 8 | Hong Song-nam (1929–2009) | 5 September 1998 | 3 September 2003 | 4 years, 363 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 9 | Pak Pong-ju (born 1939) | 3 September 2003 | 11 April 2007 | 3 years, 220 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 10 | Kim Yong-il (born 1944) | 11 April 2007 | 7 June 2010 | 3 years, 57 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 11 | Choe Yong-rim (born 1930) | 7 June 2010 | 1 April 2013 | 2 years, 298 days | Workers' Party | ||
| (9) | Pak Pong-ju (born 1939) | 1 April 2013 | 12 April 2019 | 6 years, 11 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 12 | Kim Jae-ryong | 12 April 2019 | 13 August 2020 | 1 year, 123 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 13 | Kim Tok-hun (born 1962) | 13 August 2020 | Incumbent | 178 days | Workers' Party | ||
Heads of parliament
| No. | Portrait | Name | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman of the Standing Committee of the Supreme People's Assembly | |||||||
| 1 | Kim Tu-bong (1889–1958) | 9 September 1948 | 20 September 1957 | 9 years, 11 days | Workers' Party (WPNK until 1949) | ||
| 2 | Choe Yong-gon (1900–1976) | 20 September 1957 | 28 December 1972 | 15 years, 99 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 3 | Hwang Jang-yop (1923–2010) | 28 December 1972 | 7 April 1983 | 10 years, 100 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 4 | Yang Hyong-sop (born 1925) | 7 April 1983 | 5 September 1998 | 15 years, 151 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Chairman of the Supreme People's Assembly | |||||||
| 5 | Choe Thae-bok (born 1930) | 5 September 1998 | 11 April 2019 | 20 years, 218 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 6 | Pak Thae-song (born 1955) | 11 April 2019 | Incumbent | 1 year, 302 days | Workers' Party | ||
Heads of the military

| No. | Portrait | Name | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman of the Central Military Commission of the Workers' Party of Korea | |||||||
| 1 | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) | 26 June 1950 | 28 December 1972 | 22 years, 185 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Chairman of the National Defence Commission | |||||||
| (1) | Kim Il-sung (1912–1994) | 28 December 1972 | 9 April 1993 | 20 years, 102 days | Workers' Party | ||
| 2 | Kim Jong-il (1941–2011) [lower-alpha 3] | 9 April 1993 | 17 December 2011 † | 18 years, 252 days | Workers' Party | ||
| First Chairman of the National Defence Commission | |||||||
| 3 | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 13 April 2012 | 29 June 2016 | 4 years, 77 days | Workers' Party | ||
| Chairman of the State Affairs Commission | |||||||
| (3) | Kim Jong-un (born 1983) | 29 June 2016 | Incumbent | 4 years, 223 days | Workers' Party | ||
See also
Notes
- Kim Jong-il died on 17 December 2011, but was posthumously named the "Eternal General Secretary" on 11 April 2012. Thus his son and successor as leader, Kim Jong-un, was not given the title of General Secretary.
- Kim Il-sung died on 8 July 1994, but was posthumously named the "Eternal President of the Republic" on 5 September 1998. Thus his son and successor as leader, the late Kim Jong-il, did not assume the post of head of state until April 2009 and the President of the Presidium of the Supreme People's Assembly became recognised as the de facto head of state.
- Kim Jong-il died on 17 December 2011, but was posthumously named the "Eternal Chairman of the National Defence Commission" on 13 April 2012. Thus his son and successor as leader, Kim Jong-un, was given the title of "First Chairman".
References
- "Kim Jong-il's 'Mt. Ryongnam Range' is succeeded by Kim Jong-un's 'Mt. Ami Range'". Leonid Petrov’s Korea Vision. Retrieved December 12, 2012.
- Barry Turner (2013). The Statesman's Yearbook 2014: The Politics, Cultures and Economies of the World. Springer. p. 746. ISBN 978-1-349-59643-0.
However, it is widely understood that Kim, like his late father, yields absolute power over the state, party and army.
- Korea Focus on Current Topics. Korea Foundation. 2000. pp. 109–110.
Kim Jong-il exercises near absolute power based on juche thought and respect for his revolutionary legacy.
- Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia (1999). Japan and Russia in Northeast Asia: Partners in the 21st Century. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-275-96382-8.
On February 14, 1974, Kim Il Sung announced the ten major principles to the party leadership, thus forcing power rivals to accept his "divinity, absolutism, and unconditionality" as was articulated in the principles. As a result, one may consider Kim Jong Il's control over North Korea, at least for the time being, as absolute, because he has made it almost impossible to openly advocate ideas directed against his father or express discontent with the system.
- "Kim Jong-un: Who might lead N Korea without Kim?". BBC.
- Savada, Andrea Matles. "Mass Organizations." North Korea: A country study. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1993.
- "Supreme Leader Kim Jong Un Cuts Tape for Completion of Sunchon Phosphatic Fertilizer Factory". Kim Il-sung University. Korean Central News Agency (KCNA). 2020-05-02. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
Kim Jong Un, chairman of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK), chairman of the State Affairs Commission of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and supreme commander of the armed forces of the DPRK, attended the ceremony.
- Petrov, Leonid (12 October 2009). "DPRK has quietly amended its Constitution". Leonid Petrov's KOREA VISION. Retrieved 12 September 2015.
- Isozaki, Atsuhito. "North Korea Revamps Its Constitution". thediplomat.com. DIPLOMAT MEDIA INC. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- "Article 100". Socialist Constitution of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (PDF). Amended and supplemented on April 1, Juche 102 (2013), at the Seventh Session of the Twelfth Supreme People's Assembly. Pyongyang: Foreign Languages Publishing House. 2014. p. 22. ISBN 978-9946-0-1099-1.CS1 maint: others (link)
- Josh Doyle (16 April 2019). "Is Kim Jong Un 'supreme representative of all the Korean people'?". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
.jpg.webp)