List of shipwrecks in 1889
The list of shipwrecks in 1889 includes ships sunk, foundered, grounded, or otherwise lost during 1889.
| 1889 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr |
| May | Jun | Jul | Aug |
| Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| Unknown date | |||
| References | |||
January
5 January
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Paris C. Brown | The steamer struck a snag and sank in the Mississippi River at Hermitage, Louisiana with part of her superstructure above water. One passenger and six crew killed.[1][2] |
17 January
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Advance | The schooner was wrecked on rocks at the southwest corner of the Pensacola Navy Yard, Pensacola.[3] | |
| Urbano | The bark was lost off Pensacola, Florida.[3] |
21 January
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| H. F. Morse | The Tug was wrecked on Harding Ledge in Massachusetts Bay. One crewman killed.[4] | |
| Unknown and unknown | The 2 Barges were wrecked when their Tug H. F. Morse was wrecked on Harding Ledge in Massachusetts Bay. Five crewmen killed between the two crews.[5] |
February
7 February
9 February
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Annie | The 41.73-ton, 57-foot (17.4 m) schooner departed San Francisco, California bound for Unalaska on Unalaska Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands and was never seen or heard from again. Her entire crew of 11 was lost.[7] | |
| Harvest Home | The schooner ran aground at Cardigan. Her four crew were rescued by Lizzie & Charles Leigh Clare ( |
17 February
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HMS Cumberland | The training ship – a former ship-of-the-line – burned on the River Clyde in Scotland.[9] |
March
1 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| No. 102 | The 35-metre type torpedo boat suddenly capsized and foundered during manoeuvres off Toulon, France. Six of her crew were killed.[10] |
2 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Otter | The 73.75-ton, 81-foot (24.7 m) schooner departed San Francisco, California, bound for the Shumagin Islands in the eastern Aleutian Islands and was never seen or heard from again. Her entire crew of 23 men was lost.[11] |
3 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| James A. Hamilton | The 77.8-ton, 81.5-foot (24.8 m) whaling schooner departed San Francisco, California bound for Unalaska on Unalaska Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands and was never seen or heard from again. Her entire crew of 18 men and all three men aboard her as passengers were lost.[7][12] |
7 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Duke of Buccleugh | The Eastern Steamship Company 3,099 GRT sail and steam cargo ship was wrecked following a collision with the 1,478-ton sailing ship Vandalia ( |
8 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Vega | The steamship was driven ashore and wrecked near Langton Matravers, Dorset. All 29 people on board were rescued.[14] |
13 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kangaroo | The Steamer sank while laying at Spottsville, Kentucky. The Captain/Owner and his nephew killed.[15] |
16 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SMS Adler |  SMS Adler | |
| SMS Eber |  Wrecked ships in Apia Harbor, Upolu, Samoa soon after the storm. The view looks northwestward, with the shattered bow of the German gunboat Eber on the beach in the foreground. The stern of USS Trenton is at right, with the sunken USS Vandalia alongside. The German gunboat Adler is on her side in the center distance. USS Trenton's starboard quarter gallery has been largely ripped away. | |
| USS Nipsic |  The wreck of USS Nipsic is at left; the wreck of USS Trenton is at center, with the wreck of USS Vandalia alongside in the center. | |
| SMS Olga |  The wreck of SMS Olga at right; the wreck of USS Trenton is at left, with the wreck of USS Vandalia alongside. | |
| USS Trenton |  The wreck of USS Trenton is at left, with the wreck of USS Vandalia alongside. The wreck of SMS Olga at right. | |
| USS Vandalia |  The wreck of USS Vandalia, seen from the wreck of USS Trenton. |
19 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kate & Anna | The 30.7-gross register ton, 45-foot (13.7 m) steam sealing schooner was blown ashore and wrecked on the southwestern shore of Morzovia Bay, later called Morzovhoi Bay (55°N 163°W), on the Alaska Peninsula on the coast of the Territory of Alaska after her anchor line parted in a gale. Her crew of six survived.[16] |
28 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ruth Darling | The Schooner was run into and sunk by Wyanoke ( |
30 March
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Stella | On her way from Southampton, England, to Guernsey and Jersey in the Channel Islands in thick fog, the steamer ran at full speed onto Les Casquets reef near Alderney in the Channel Islands and sank within minutes with the loss of over 80 lives.[18] |
April
6 April
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Danmark | The passenger steamer foundered in the North Atlantic after her propellor shaft snapped. A total of 721 passengers and crew saved by the cargo steamer Missouri ( |
18 April
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Everett | The Steamer was sunk in a wind storm in the Mississippi River near Burlington, Iowa. Five killed.[19] |
22 April
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lizzie Williams | During a voyage from San Francisco, California, to Kodiak Island, Territory of Alaska, carrying 82 passengers – 75 of them Chinese cannery workers – and a crew of 14, as well as an 1,100-ton cannery fit and supplies as cargo, the 790-ton, 159.4-foot (48.6 m) bark was wrecked without loss of life on a shoal off Tugidak Island in the Kodiak Archipelago. The steamers Al-Ki and Elsie (both |
May
12 May
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Alaskan |  Painting of Alaskan sinking. |
22 May
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ohio | The 363.8-ton 110.9-foot (33.8 m) whaling bark became unmanageable after her hull was stove in by ice and was blown ashore and wrecked on Nunivak Island in the Bering Sea. Her crew survived and was rescued from the island by the bark Ocean ( |
24 May
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Steelfield | The full-rigged ship was sighted on this date whilst on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Callao, Peru. No further trace, presumed foundered with the loss of all hands.[23] |
June
1 June
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kangaroo | The Steamer was lost off, or in, the Brisbane River. Scrapped in place.[24] |
25 June
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Jessie W. Knight | The Schooner was sunk in a collision by Wm. R. McCabe ( |
28 June
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Edward S. Webster | The 83-foot (25.3 m) schooner sank after striking a submerged rock at the entrance to Coal Harbor (55°20′30″N 160°39′30″W) on Unga Island in the Shumagin Islands off the south coast of the Territory of Alaska′s Alaska Peninsula. Her crew of 12 survived. She later was condemned, sold, and refloated.[26] |
30 June
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| William Armstrong | The Ferry sank in the St. Lawrence River between Morristown, New York and Brockville, Ontario. One passenger killed.[27] |
July
5 July
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kenilworth | The Barque was wrecked entering the North East Channel to the Torres Strait from Bramble Bay, Australia.[28] |
16 July
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lorenzo D. Baker | The steamer was destroyed by fire in the Atlantic Ocean in the vicinity of (38°15′N 69°49′W). Survivors rescued by Whaling Schooner Franklin ( |
21 July
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Eduardo | The steamer was wrecked in dense fog on Old Man Island 2 miles south of Cutler, Maine. All 40 crew rescued.[31][32] |
August
4 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bloomer | The schooner capsized in a squall 55 miles (89 km) east southeast of Pensacola, Florida.[3] |
9 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wildwood | While departing Nushagak on Bristol Bay in the Territory of Alaska carrying the summer's catch from the cannery at Nushagak, the 1,056.09-ton, 198.8-foot (60.6 m) bark was wrecked in the Nushagak River 2 nautical miles (3.7 km; 2.3 mi) south of Harkanock. Her entire crew of 21 survived.[33] |
17 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A.E. Vickery | The wooden three-masted schooner sank after striking a shoal while entering the American Narrows in the St. Lawrence River near Alexandria Bay, New York. |
20 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Torpedo boat No. 10 | The torpedo boat capsized in the Øresund and subsequently sank whilst under tow for Copenhagen. She was salvaged, repaired and returned to service.[34] |
25 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lame Duck | The steamer was sunk in a collision with "Commonwealth" ( |
28 August
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ancon | The 1,208.05-ton sidewheel paddle steamer was stranded on a rock projecting from a reef in Naha Bay (55°36′12″N 131°38′00″W) in Southeast Alaska as she was departing the wharf at Loring, Territory of Alaska. Her back broke as the tide receded, and she became a total loss. All on board – 119 passengers and 72 crewmen – survived.[7] |
September
4 September
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lucretia | The 350-ton whaling bark was wrecked on an uncharted reef in the Chukchi Sea off the coast of Siberia 7 nautical miles (13 km; 8.1 mi) west of Herald Island. The steam bark Abram Barker ( |
5 September
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Earnmoor | The tramp steamer sank in a hurricane in the Atlantic Ocean northeast of the Greater Antilles with the loss of 17 lives. The seven survivors floated in an open lifeboat for 21 days before the schooner Mosquito ( |
15 September
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Island Belle | The 19-ton, 43.5-foot (13.3 m) schooner was wrecked on the southern shore of Delarof Harbor (55°10′30″N 160°30′00″W) on the coast of Unga Island in the Shumagin Islands in the Territory of Alaska. Her crew of four survived.[36] |
16 September
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Leo | The Naptha Launch burned between Loraine, Ohio and Cleveland, Ohio. Lost with all hands.[37] | |
| HMS Lily | The Arab-class gunvessel was wrecked off Point Amour Lighthouse, Labrador, in thick fog with the loss of seven lives. | |
| Torpedo boat No. 9 | The torpedo boat ran aground in the Øresund. She was refloated on 18 September, subsequently returned to service.[34] |
24 September
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C. M. Gifford | The tow steamer, towing Chas. E. Wyman ( |
Unknown date
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha | After losing ropes, a canoe, and her portside bulwarks and stanchions overboard in a gale 5 nautical miles (9.3 km; 5.8 mi) east of Cape Fairweather (58.8056°N 137.9442°W) in Southeast Alaska, the 26.28-ton schooner was beached at Yakutat, Territory of Alaska, sometime soon after the revenue cutter USRC Rush ( |
October
2 October
3 October
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| "Corona" | The steamer was destroyed by a boiler explosion in the Mississippi River near Prophet's Island. 35 died.[40] |
16 October
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Thesis | The cargo steamer struck a reef at the south end of the Sound of Mull between the Isle of Mull and Scotland off Inninmore Point and sank four hours later. Her crew of 11 abandoned ship safely. |
21 October
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Carl D. Lathrop | The schooner sprung a leak and capsized 10 miles (16 km) south southwest of the Cape St. George Lighthouse, Florida.[41] |
30 October
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cheseborough | 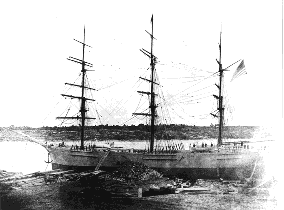 The wreck of Cheseborough |
Unknown date
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Llandaff | The Welsh collier was wrecked at Land's End, Cornwall. She was repaired and returned to service.[42] | |
| Malta | The steamer was wrecked at Botallack Head, St Just in Penwith, Cornwall, United Kingdom; vessel was a complete loss but no lives were lost.[43] |
November
16 November
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fearless | The Tug ran aground on the north spit of the Umpqua River and went to pieces. Lost with everyone on board, one passenger and seven crew.[44] |
20 November
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| "Manhattan" | The cargo-liner was sunk in a collision with Schooner Agnes Manning ( |
December
22 December
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Adonis | The wooden brigantine was wrecked approximately 15 miles (24 km) south of Crowdy Head, New South Wales, Australia, when she sprang a leak while carrying a cargo of coal between Wollongong and the Richmond River in New South Wales. |
25 December
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wide West | The screw steamer was wrecked on Destruction Island off Washington, United States, after losing her propeller and auxiliary sailing rig in high winds and heavy seas. Her crew abandoned ship safely. |
26 December
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clan McKenzie | The steamer was sunk in a collision in snow with Oregon ( | |
| Oregon | The steamer was damaged in a collision with Clan McKenzie ( |
Unknown date
| Ship | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Herald of the Morning | The hulk of the square-rigged sailing ship, severely damaged by fire in Hobsons Bay, New South Wales, Australia, on 15 November 1859 and never repaired, was scuttled ca. 1889. | |
| Queensmore | The cargo ship caught fire in the Atlantic Ocean whilst on the return leg of her maiden voyage. An attempt was made to beach her in Dunmanus Bay but she struck the Bullig Reef and sank.[51] |
References
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Hermitage, La steamer Paris C. Brown wreck, Jan 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- Singer, Stephen D. (1998) [1992]. Shipwrecks of Florida: A Comprehensive Listing (Second ed.). Sarasota, Florida: Pineapple Press. p. 31. ISBN 1-56164-163-4.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "SS Princesse Josephine (+1889)". wrecksite.eu. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (A)
- "Cardigan & District Shipwrecks and Lifeboat Service". Glen Johnson. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- britainsnavy.co.uk HMS Cumberland (1842) (8th) 3rd Rate 70-gun
- "The Loss of French Torpedo Boats". The Marine Engineer. April 1889. pp. 30–31.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (O)
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (J)
- "Loss of Duke of Buccleugh". Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- "Historical List of Shipwrecks at Chesil Beach & from Bridport to Lyme Regis". Burton Bradstock Online. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (K)
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "SS Stella (1889)". www.wrecksite.eu. Retrieved 26 Aug 2015.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (L)
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- "Alaskan (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- "Steelfield". The Yard. Retrieved 18 February 2017.
- "Kangaroo (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (E)
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "Kenilworth (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Portland Daily Press, July 23, 1889". chroniclingamerica.loc.gov. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Eduardo (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Portland Daily Press, July 23, 1889". chroniclingamerica.loc.gov. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (W)
- "Sea Accidents and Losses". Danish Naval History. Retrieved 24 December 2019.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- alaskashipwreck.com Alaska Shipwrecks (I)
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- "SS Geographique (+1889)". wrecksite.eu. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- Singer, Stephen D. (1998) [1992]. Shipwrecks of Florida: A Comprehensive Listing (Second ed.). Sarasota, Florida: Pineapple Press. p. 32. ISBN 1-56164-163-4.
- Noall, C. (1969?) Cornish Shipwrecks Illustrated. Truro: Tor Mark Press; p. 31
- Noall, C. (1969?) Cornish Shipwrecks Illustrated. Truro: Tor Mark Press; p. 23
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- "Manhattan (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
- "SV Nominoé (+1889)". Wrecksite. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- "Annual report of the Supervising Inspector-general Steamboat-inspection Service, Year ending June 30, 1890". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Sacramento Daily Record, December 28, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Sacramento Daily Record, December 28, 1889". Columbia University. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- "Queensmore". The Yard. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
| Ship events in 1889 | |||||||||||
| Ship launches: | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 | 1894 |
| Ship commissionings: | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 | 1894 |
| Ship decommissionings: | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 | 1894 |
| Shipwrecks: | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 | 1894 |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.