London Borough of Merton
The London Borough of Merton (/ˈmɜːtən/ (![]() listen)) is a borough in south-west London, England.
listen)) is a borough in south-west London, England.
London Borough of Merton | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms  Council logo | |
 Merton shown within Greater London | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | Civic Centre Morden |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Merton London Borough Council |
| • Leadership | Stephen Alambritis (Labour) |
| • Mayor | Sally Kenny |
| • London Assembly | Leonie Cooper (Lab) AM for Merton and Wandsworth |
| • MPs | Stephen Hammond (Conservative) Siobhain McDonagh (Lab) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 14.52 sq mi (37.61 km2) |
| Area rank | 287th (of 317) |
| Population (mid-2019 est.) | |
| • Total | 206,548 |
| • Rank | 90th (of 317) |
| • Density | 14,000/sq mi (5,500/km2) |
| • Ethnicity[1] | 48.4% White British 2.2% White Irish 0.1% White Gypsy or Irish Traveller 14.2% Other White 1.3% White & Black Caribbean 0.6% White & Black African 1.4% White & Asian 1.3% Other Mixed 4.1% Indian 3.7% Pakistani 1.1% Bangladeshi 1.3% Chinese 7.9% Other Asian 5.2% Black African 4.1% Black Caribbean 1.1% Other Black 0.7% Arab 1.2% Other |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code(s) | 020 |
| ONS code | 00BA |
| GSS code | E09000024 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | http://www.merton.gov.uk |
The borough was formed under the London Government Act 1963 in 1965 by the merger of the Municipal Borough of Mitcham, the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon and the Merton and Morden Urban District, all formerly within Surrey. The main commercial centres in Merton are Mitcham, Morden and Wimbledon, of which Wimbledon is the largest. Other smaller centres include Raynes Park, Colliers Wood, South Wimbledon, Wimbledon Park and Pollards Hill. The borough is the host of the Wimbledon tournament, one of tennis's Grand Slam competitions.
The borough derives its name from the historic parish of Merton which was centred on the area now known as South Wimbledon. Merton was chosen as an acceptable compromise, following a dispute between Wimbledon and Mitcham over the new borough's name. The local authority is Merton London Borough Council, which is based in Morden.
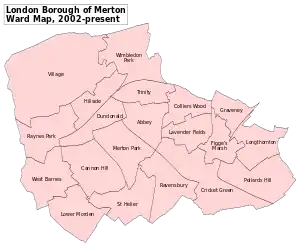
Districts
- Bushey Mead
- Colliers Wood
- Copse Hill
- Cottenham Park
- Crooked Billet
- Lower Morden
- Merton Park
- Mitcham
- Mitcham Common
- Morden
- Morden Park
- Motspur Park (also partly Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames)
- New Malden (also partly Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames)
- Norbury (also partly in London Borough of Croydon and London Borough of Lambeth)
- Pollards Hill (also partly in London Borough of Croydon)
- Raynes Park
- St. Helier (also partly in the London Borough of Sutton)
- South Wimbledon
- Summerstown (also partly in the London Borough of Wandsworth)
- Wimbledon
- Wimbledon Park
History of the Borough
Merton Borough Council
The May 2014 local government elections saw the Labour Party win an overall majority, following the gain of seven seats from the Conservative Party, and one from UKIP. This followed four years as a minority administration. The current council has a Labour majority and its composition is:
- Labour: 34
- Conservatives: 17
- Liberal Democrats: 6
- Merton Park Residents: 3
Mayors
At the Annual Council Meeting, a ceremonial mayor is elected to serve for a year. At the same time, it elects a deputy mayor to serve alongside the mayor. Since 1978, each Mayor must also be an elected councillor. Cllr Sally Kenny who is a Labour councillor for Lower Morden ward is currently the Mayor and Cllr John Dehaney who is a Labour councillor for Graveney ward is her deputy.[2]
Media
A lot of filming for former ITV police drama The Bill took place in Merton, particularly in the districts of Mitcham and Colliers Wood. The set of Sun Hill police station was also located in the Borough. Ray Austin, born at 9 Abbey Rd Merton on the 5 December 1932, is an English television and film director, television writer, novelist and former stunt performer and actor who worked in both the United Kingdom and the United States. He filmed episodes of The Avengers and The Saint in and around Merton. He served as director on episodes of some 150 programs between 1968 and 2010.
The main local newspaper in Merton is the Wimbledon Times (recently changed name from Wimbledon Guardian). This newspaper was founded in 1977 by a former Conservative councillor on Merton Council, but since then the paper has been sold on and it is now widely published in different editions across South London. The newspaper is available free, though there is a charge if bought from a newsagent. It is published each Friday.
Economy
Notable businesses with their headquarters in Merton including:
- Eidos Interactive, a subsidiary of Square Enix, located in Wimbledon Bridge House in Wimbledon.[3]
- Lenstore, an online optical retailer, located in Wimbledon Park
- Square Enix Europe: located in Wimbledon Bridge House in Wimbledon.[3]
- Lidl head offices, located in Wimbledon.
Education
London's Poverty Profile (a 2017 report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute) found that 40% of Merton's 19-year-olds lack level 3 qualifications. This is the 5th worst figure out of 32 London boroughs.[4]
Transport
Merton is served by a wide range of National Rail stations across the borough, as well as the southern tip of London Underground's Northern line and the District line on the Wimbledon branch. The borough is also served by several Tramlink stops from Wimbledon, that goes to Croydon, New Addington, Elmers End and Beckenham. It is the only London Borough which has tube, rail and tram services.
London Underground stations
Tramlink stops
- Wimbledon
- Dundonald Road
- Merton Park
- Morden Road
- Phipps Bridge
- Belgrave Walk
- Mitcham
- Mitcham Junction
National Rail stations
- Tooting
- Haydons Road
- Wimbledon
- Wimbledon Chase
- South Merton
- Morden South
- St Helier
- Mitcham Junction
- Mitcham Eastfields
- Raynes Park
- Motspur Park
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: driving a car or van, 19.2% of all residents aged 16–74; underground, metro, light rail, tram, 13.0%; train, 13.0%; bus, minibus or coach, 7.5%; on foot, 5.0%; work mainly at or from home, 3.4%; bicycle, 2.4%.[5]
Demographics and social conditions
In 2001, the census recorded that 25% of the population of the borough was from an ethnic minority. The highest ethnic populations were recorded in wards in the east of the borough in Mitcham, Eastfields and Pollards Hill. The percentage of population from ethnic minorities is predicted to rise across the borough within the next decade.
A 2017 report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute found that Merton has a poverty rate of 20%, which is the 7th lowest rate in London. It also found that the level of pay inequality in Merton is lower than in any other borough, except neighbouring Croydon.[4]
According to the council's comparative assessment of wards made in 2004, the most deprived wards within the borough were in the south and east where unemployment rates, educational attainment and the quality of health were worst. The most affluent wards were in the north and west of the borough.
Comparative crime rates appear to be unrelated to the deprivation ranking of wards. The wards containing Mitcham town centre and the St Helier Estate are ranked highest for crime within Merton with the wards containing the commercial shopping centres of Colliers Wood and Wimbledon also featuring high in the ranking.
The constituency area of Wimbledon is an affluent area of London with a high proportion of city workers, while Mitcham and Morden is relatively deprived by comparison, which explains the geographical split of political representation of the borough at both national and local elections.
Merton currently operates a Police Cadet scheme under the Metropolitan Police Service.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 4,831 | — |
| 1811 | 5,656 | +17.1% |
| 1821 | 6,433 | +13.7% |
| 1831 | 6,652 | +3.4% |
| 1841 | 7,364 | +10.7% |
| 1851 | 7,334 | −0.4% |
| 1861 | 14,118 | +92.5% |
| 1871 | 20,901 | +48.0% |
| 1881 | 27,684 | +32.5% |
| 1891 | 41,318 | +49.2% |
| 1901 | 63,273 | +53.1% |
| 1911 | 96,895 | +53.1% |
| 1921 | 122,245 | +26.2% |
| 1931 | 154,267 | +26.2% |
| 1941 | 174,151 | +12.9% |
| 1951 | 196,599 | +12.9% |
| 1961 | 187,074 | −4.8% |
| 1971 | 178,023 | −4.8% |
| 1981 | 165,098 | −7.3% |
| 1991 | 171,808 | +4.1% |
| 2001 | 187,908 | +9.4% |
| 2011 | 199,693 | +6.3% |
| Note:[6] | ||
Ethnicity
| Ethnic Group | 2001[7] | 2011[8] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: British | 120,378 | 64.1% | 96,658 | 48.4% |
| White: Irish | 5,464 | % | 4,417 | 2.2% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | 216 | 0.1% | ||
| White: Other | 15,041 | 8.0% | 28,315 | 14.1% |
| White: Total | 140,883 | 74.97% | 129,606 | 64.8% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | 8,043 | % | 8,106 | 4.0% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | 4,504 | % | 7,337 | 3.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | 1,702 | % | 2,216 | 1.1% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | 2,485 | % | 2,618 | 1.3% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | 6,558 | % | 15,866 | 7.9% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | 23,292 | 12.4% | 36,143 | 17.9% |
| Black or Black British: African | 6,976 | % | 10,442 | 5.2% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | 6,438 | % | 8,126 | 4.0% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | 1,212 | % | 2,243 | 1.1% |
| Black or Black British: Total | 14,626 | 7.7% | 20,811 | 10.6% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | 1,630 | % | 2,579 | 1.2% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | 734 | % | 1,279 | 0.6% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | 1,918 | % | 2,829 | 1.4% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | 1,587 | % | 2,647 | 1.3% |
| Mixed: Total | 5,869 | 3.1% | 9,334 | 4.5% |
| Other: Arab | 1,413 | 0.7% | ||
| Other: Any other ethnic group | 3,238 | % | 2,386 | 1.1% |
| Other: Total | 3,238 | % | 3,799 | 1.8% |
| Black, Asian, and minority ethnic: Total | 47,025 | 25.0% | 70,033 | 35.2% |
| Total | 187,908 | 100.00% | 199,693 | 100.00% |
Features of interest
Wimbledon tennis tournament
Each year The Championships, Wimbledon, better known as simply Wimbledon, one of the four tennis Grand Slam tournaments (along with the US, French and Australian Opens) is held at the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club in Church Road Wimbledon. The event takes place over a fortnight at the end of June and beginning of July and is the largest annual sporting event to take place in the United Kingdom with over 200,000 visitors during the Wimbledon fortnight.
Football
The borough gained a football team in 1889 when Wimbledon Old Centrals were founded, and were soon a member of the local football leagues.[9] The club later adopted the title Wimbledon FC and moved into a new stadium at Plough Lane in 1912, where it would spend the next 79 years. As the 20th century wore on, the club enjoyed considerable success in non-league football.[10] The club was elected to the Football League in 1977[11] and enjoyed a great run of success when began in 1983 with the Fourth Division title, and saw them reach the First Division in 1986 – a mere nine years after joining the Football League. They quickly established themselves in the highest division of English football, and as clear underdogs, pulled off a shock win in the 1988 FA Cup Final against Liverpool, England's most successful and dominant club side in Europe during that era.[12] They were founder members of the FA Premier League in 1992[13] and survived at that level until 2000, before relocating to Milton Keynes, some 70 miles away in Buckinghamshire, in a controversial move in 2003, being rebranded as Milton Keynes Dons in 2004. The club had left its Plough Lane stadium in 1991 to ground-share with Crystal Palace at Selhurst Park, with numerous plans to build a new stadium in a number of different locations (including back in London and even in Dublin or Cardiff) being considered over the following decade before the club's owners chose Milton Keynes as their destination.
However, a new Wimbledon club – AFC Wimbledon – was formed to represent the local area in 2002 by fans of the original club after the move to Milton Keynes was given the go-ahead. The new Wimbledon club's progress was rapid, and after just nine years in existence they won promotion to the Football League in 2011.[14] The club currently plays at Kingsmeadow Stadium, the home of Kingstonian F.C., but in 2016 it gained permission to build a new stadium back on Plough Lane, using the former Greyhound Stadium around a hundred yards from its old stadium site and still within in the London Borough of Merton. In 2018 the final agreements were signed off and demolition work started on the site (for both stadium and 600 flats) in April 2018. Building is expected to be completed for the 2020–21 season.[15][16][17]
The borough also has five non-League football clubs: Colliers Wood United F.C. who play at Wibbandune Sports Ground; Raynes Park Vale F.C. who play at Prince George's Fields; Tooting & Mitcham United F.C. who play at Imperial Fields, Morden; and Merton Forest F.C who also play at Prince George's Fields and a Celebrity Fundraising Football team – Celeb FC who play all over the UK without charge for small UK charities.
Baitul Futuh mosque

In 2003, the largest mosque in western Europe was opened in Morden. The Baitul Futuh mosque can accommodate 10,000 people and was built at a cost of £5.5 million entirely donated voluntarily by the Ahmadiyya Community. The mosque has been voted in the top 50 in the world by Spectator Magazine.[18] It is also acting as the centre for the 'Loyalty, Freedom and Peace' campaign in order to improve the integration of Muslims and non-Muslims alike.[19]
Television
The Talkback Thames television studio on Deer Park Road was used as Sun Hill Police Station in the ITV police drama The Bill from its inception in 1984 until it was axed in 2010.[20]
Sister cities
Freedom of the Borough
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the Borough of Merton:
Individuals
- Andy Murray OBE: 20 July 2014.[22]
- Angela Mortimer: 27 June 2014.[23][24]
- Ann Haydon-Jones CBE: 27 July 2014.[23][24]
- Virginia Wade OBE: 27 July 2014.[23][24]
References
- 2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales, Office for National Statistics (2012). See Classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom for the full descriptions used in the 2011 Census.
- "The Mayor of Merton". Merton London Borough Council.
- "About us". Square Enix Europe.
- "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16–74 including those not in employment. Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey’s longest part by distance.
- "Merton: Total Population". A Vision of Britain Through Time. Great Britain Historical GIS Project. Retrieved 6 September 2011.
- "KS006 – Ethnic group". NOMIS. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- "Ethnic Group by measures". NOMIS. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- "1889 to 1899". Memories of The Dons. historicaldons.com. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012.
- "Plough Lane – Wimbledon". Wayback Machine. Old Football Grounds.
- "1970 to 1979". Memories of The Dons. historicaldons.com. Archived from the original on 19 February 2012.
- "1980 to 1989". Memories of The Dons. historicaldons.com. Archived from the original on 30 September 2011.
- "The second coming of Wimbledon". BBC Sport – Football. 25 November 2010.
- "AFC Wimbledon 0-0 Luton Town (4-3 on pens)". BBC Sport – Football. 21 May 2011.
- "New stadium update featured on the agenda".
- "New stadium update".
- "Home Sweet Home". AFC Wimbledon. 8 July 2019. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- Baitul Futuh mosque – top 50 buildings in the world Spectator magazine
- "Muslim's for 'Loyalty, Freedom & Peace' Campaign".
- "Talkback Thames". IMDb.
- "Interactive City Directory". Sister Cities International. Archived from the original on 12 March 2014. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- "Andy Murray given Freedom of Merton | Merton Council News Room". News.merton.gov.uk. 20 June 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- "Freedom of The Borough". London Borough of Merton. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- "Former Wimbledon Champions awarded Freedom of Merton". YouTube. 31 July 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2020.