Martha Bulloch Roosevelt
Martha Bulloch "Mittie" Roosevelt (born Martha Stewart Bulloch;[1] July 8, 1835 – February 14, 1884) was an American socialite. Roosevelt was also the mother of US President Theodore Roosevelt and the paternal grandmother of Eleanor Roosevelt. She was a great-granddaughter of Archibald Bulloch, grandniece of William Bellinger Bulloch, and granddaughter of General Daniel Stewart. A true Southern belle, Roosevelt is thought to have been one of the inspirations for Scarlett O'Hara.[2]
Martha Bulloch Roosevelt | |
|---|---|
 Bulloch in 1857 | |
| Born | Martha Stewart Bulloch July 8, 1835 Hartford, Connecticut, U.S. |
| Died | February 14, 1884 (aged 48) 6 West 57th Street New York City, U.S. |
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | Anna, Theodore Jr., Elliott, and Corinne |
| Parent(s) | James Stephens Bulloch Martha P. Stewart |
| Family | See Roosevelt family |
Childhood
Mittie was born in Hartford, Connecticut on July 8, 1835, to Major James Stephens Bulloch (1793–1849) and Martha "Patsy" Stewart (1799–1864). She had an elder sister, Anna Louisa Bulloch (1833–1893), and two younger brothers, Charles Irvine Bulloch (1838–1841) and Civil War Confederate veteran Irvine Stephens Bulloch (1842–1898).
Through her father's first marriage to Hester Amarintha "Hettie" Elliott (1797–1831), she had two elder half brothers:
- John Elliott Bulloch (1818–1821)
- James Dunwoody Bulloch (1823–1901), Civil War Confederate veteran
Through her mother's first marriage to Senator John Elliott (father of Hettie), she also had four elder half siblings:
- Susan Ann Elliott (1820–1905)
- Georgia Amanda Elliott (1822–1848)
- Charles William Elliott (1824–1827)
- Daniel Stewart "Stuart" Elliott (1826–1861), who died of tuberculosis while serving in the Confederate Army during the Civil War.[3]
When Mittie was four, Major Bulloch moved the family to Cobb County, Georgia and the new village that would become Roswell, Georgia. It lies just north of the Chattahoochee River and the city of Atlanta, Georgia, and Major Bulloch had gone there to become a partner in a new cotton mill with Roswell King, the town's founder. Bulloch had a mansion built, and soon after it was completed in 1839, the family moved into Bulloch Hall. As a significant antebellum structure, it has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The Bullochs were a wealthy planter family, members of the Georgia elite. In 1850, they held thirty-one negro slaves, most of whom worked in their cotton fields.[4] Others were assigned to such domestic tasks as cooking, sewing, and related work. Recent research in Bulloch records identified 33 slaves who were owned by the family. They have been commemorated on a plaque on the mansion grounds.[5]
Mittie, like all her siblings, was assigned a personal slave, or a "shadow," to act as companion. Mittie's companion, Lavinia, for example, went everywhere with her, stopping outside the classroom when Mittie went inside, and sleeping on a mat by her side at night. For the family, the emphasis was on the pleasure of the companionship rather than on the hostage implications in the arrangement.[6]
After Major Bulloch's death in 1849, the family's fortunes declined somewhat, but Mittie was given a grand wedding to Theodore Roosevelt Sr. in 1853. Later, as was expected of young southern gentlemen, Mittie's brothers Irvine and James fought in the Civil War as Confederate officers. They both lived in England after the war.[7] Her brother Dan also fought as a Confederate and was killed in action.
It is believed by some that the character of Scarlett O'Hara, in Margaret Mitchell's novel, Gone With the Wind, was based partly on Mittie.[2] (Another inspiration is said to have been Mitchell's own businesswoman grandmother.) Mittie was a true Southern belle, a beautiful and spirited woman at her best, not unlike the fictional Scarlett. Mitchell had, in fact, interviewed Mittie's closest childhood friend and bridesmaid, Evelyn King, for a story in the Atlanta Journal newspaper in the early 1920s.[8] In that interview, Mittie's beauty, charm, and fun-loving nature were described in detail.[2]
Marriage to Theodore Roosevelt Sr.
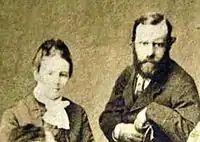
Mittie married Theodore "Thee" Roosevelt Sr. on December 22, 1853 at the Greek Revival-style family mansion Bulloch Hall in Roswell; they were wedded in front of the pocket doors in the formal dining room.
After their honeymoon, the couple moved into their new home at 28 East 20th Street, New York, a wedding present from C.V.S. Roosevelt. Each of C.V.S.'s elder sons lived near his own house at 14th Street and Broadway in Union Square. Shortly afterward, her mother, Patsy, and sister, Anna Bulloch, moved north to join Thee and Mittie in New York.
Mittie bore four children:
- Anna "Bamie/Bye" Roosevelt (1855–1931)
- Theodore "T.R." Roosevelt Jr. (1858–1919)
- Elliott Bulloch Roosevelt (1860–1893)
- Corinne Roosevelt (1861–1933)
Life after Roswell

During the war, Mittie was terrified for her brothers, Irvine and James. Irvine was the youngest officer on the CSS Alabama, firing the last gun before the ship sank in battle off the coast of Cherbourg, France while James was a Confederate agent in England, Scotland, and Wales. These emotional crises were mitigated somewhat by the maturity and management skills of Mittie's elder daughter, Bamie, who stepped into a leadership role at a young age, especially when her father, "Thee," was out of town in Washington, visiting Lincoln and lobbying Congress for programs to support the northern troops in the field and their families back home. Thee, a Northerner himself, left his conflicted home situation to serve for the Union cause, acting as an Allotment Commissioner for New York and traveling to persuade soldiers to send a percentage of their wages to their families.
During her children's education, the family traveled to Europe, predominantly spending time in England, France, Switzerland, Italy, Austria, and Germany from May 1869 to May 1870, then on a second trip, an extended boat trip down the Nile, a trip through the Holy Land, and on to Vienna, Germany and France from October 1872 to November 1873. On this second tour, Theodore Sr. returned to America to go back to work and oversee the building of the new family home at Number 6 West 57th Street. The three youngest children stayed in Dresden while Mittie and Bamie went to Paris and then the spa at Carlsbad so Mittie could restore her health.
Death
Mittie Roosevelt died of typhoid fever on February 14, 1884, aged forty-eight, on the same day and in the same house as her son Theodore's first wife, Alice Lee Roosevelt, who unexpectedly died of Bright's disease, and two days after the birth of her granddaughter Alice Roosevelt Longworth. She is buried at Green-Wood Cemetery located in Brooklyn, New York.
Mittie described in her son's autobiography
In his autobiography published in 1913, her elder son T.R. described his mother with these words, "My mother, Martha Bulloch, was a sweet, gracious, beautiful Southern woman, a delightful companion and beloved by everybody. She was entirely 'unreconstructed' [i.e., sympathetic to the Southern Confederate cause] to the day of her death."[9]
Gallery

 The fireplace mantle in the room where Theodore Roosevelt Sr. and Mittie Bulloch were married.
The fireplace mantle in the room where Theodore Roosevelt Sr. and Mittie Bulloch were married. Chapel at Green-Wood Cemetery, in Brooklyn, where Mittie is buried.
Chapel at Green-Wood Cemetery, in Brooklyn, where Mittie is buried.
Sources
Primary sources
- Roosevelt, Theodore. An Autobiography. (1913)
- Huddleston, Connie M. and Gwendolyn I. Koehler. "Mittie & Thee: An 1853 Roosevelt Romance." (nonfiction) (2015)
- Huddleston, Connie M. and Gwendolyn I. Koehler. "Between the Wedding & the War: The Bulloch/Roosevelt Letters 1854-1860) (2016)
Secondary sources
- Beale, Howard K. Theodore Roosevelt and the Rise of America to World Power (1956).
- Brands, H.W. Theodore Roosevelt (2001)
- Dalton, Kathleen. Theodore Roosevelt: A Strenuous Life. (2002)
- Harbaugh, William Henry. The Life and Times of Theodore Roosevelt. (1963)
- McCullouch, David. Mornings on Horseback, The Story of an Extraordinary Family, a Vanished Way of Life, and the Unique Child Who Became Theodore Roosevelt (2001)
- Morris, Edmund The Rise of Theodore Roosevelt (1979)
- Morris, Edmund Theodore Rex. (2001)
- Mowry, George. The era of Theodore Roosevelt and the birth of modern America, 1900–1912. (1954)
References
- "POTTS FAMILY SHORT STORY". heritech.com. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- McCullouch, p.47.
- Gary L. McKay; Walter E. Wilson (2012). James D. Bulloch: Secret Agent and Mastermind of the Confederate Navy. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company Inc.
- "RootsWeb.com Home Page". ftp.rootsweb.com. Retrieved April 16, 2018.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on June 4, 2008. Retrieved September 28, 2007.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Caroli, Betty Boyd (1998). The Roosevelt Women. New York City: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-07133-3.
- "Home – Theodore Roosevelt Association". www.theodoreroosevelt.org. Retrieved April 16, 2018.
- Mitchell, Peggy. – Atlanta Journal. – June 10, 1923
- "Roosevelt, Theodore. 1913. An Autobiography". www.bartleby.com. Retrieved April 16, 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Martha Bulloch Roosevelt. |

