Museum Island
The Museum Island (German: Museumsinsel) is a museum complex on the northern part of the Spree Island in the historic heart of Berlin. It is one of the most visited sights of Germany's capital and one of the most important museum sites in Europe. Built from 1830 to 1930 by order of the Prussian Kings according to plans by five architects, the Museum Island was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999. It consists of the Altes Museum, the Neues Museum, the Alte Nationalgalerie, the Bode-Museum and the Pergamonmuseum.[1] Since the German reunification, the Museum Island has been rebuilt and extended according to a master plan.[2] In 2019, a new visitor center and art gallery, the "James-Simon-Galerie," was opened.
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 The Bode-Museum on Museum Island | |
| Location | Berlin, Germany |
| Criteria | Cultural: ii, iv |
| Reference | 896 |
| Inscription | 1999 (23rd session) |
| Area | 8.6 ha |
| Buffer zone | 22.5 ha |
| Coordinates | 52°31′17″N 13°23′44″E |
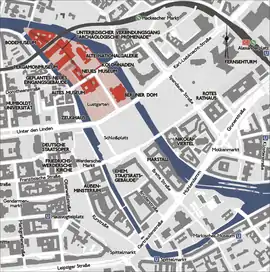 Map of Museum Island (in red) | |
 Location of Museum Island in Germany | |
Overview
The Museum Island is so-called for the complex of internationally significant museums, all part of the Berlin State Museums, that occupy the island's northern part:
- The Altes Museum (Old Museum) named as the Königliches Museum when it was built on August 3, 1830, until it was renamed in 1841. The museum was completed on the orders of Karl Friedrich Schinkel.
- The Neues Museum (New Museum) finished in 1859 according to plans by Friedrich August Stüler, a student of Schinkel. Destroyed in World War II, it was rebuilt under the direction of David Chipperfield for the Egyptian Museum of Berlin and re-opened in 2009.
- The Alte Nationalgalerie (Old National Gallery) completed in 1876, also according to designs by Friedrich August Stüler, to host a collection of 19th-century art donated by banker Joachim H. W. Wagener
- The Bode Museum on the island's northern tip, opened in 1904 and then called Kaiser-Friedrich-Museum. It exhibits the sculpture collections and late Antique and Byzantine art.
- The Pergamon Museum, constructed in 1930. It contains multiple reconstructed immense and historically significant buildings such as the Pergamon Altar and the Ishtar Gate of Babylon.
- The Humboldt Forum is scheduled to open in 2020 in the Berlin Palace opposite the Lustgarten park, and will incorporate the Ethnological Museum of Berlin and the Museum of Asian Art; both are successor institutions of the Ancient Prussian Art Chamber, which was also located in the Berlin Palace and which was established in the mid 16th century.
In 1999, the museum complex was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites.
History
A first exhibition hall was erected in 1797 at the suggestion of the archaeologist Aloys Hirt. In 1822, Schinkel designed the plans for the Altes Museum to house the royal Antikensammlung, the arrangement of the collection was overseen by Wilhelm von Humboldt. The island, originally a residential area, was dedicated to "art and science" by King Frederick William IV of Prussia in 1841. Further extended under succeeding Prussian kings, the museum's collections of art and archeology were turned into a public foundation after 1918. They are today maintained by the Berlin State Museums branch of the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation.

Museum Island further comprises the Lustgarten park and the Berlin Cathedral. Between the Bode and Pergamon Museums it is crossed by the Stadtbahn railway viaduct. The adjacent territory to the south is the site of the former royal and imperial Berlin Palace and the Palace of the Republic.
The Prussian collections became separated during the Cold War during the division of the city, but were reunited after German reunification, with the exception of some art and artifacts removed after World War II by Allied troops. These include the Priam's Treasure, also called the gold of Troy, excavated by Heinrich Schliemann in 1873, then smuggled out of Turkey to Berlin and smuggled out of Germany to Moscow. Today it is kept at the Pushkin Museum in Moscow.
As for the city's major museums, it took much of the 1990s for a consensus to emerge that Museum Island's buildings should be restored and modernized, with General Director Wolf-Dieter Dube's cautious plan for their use finally approved in January 1999. Then, six months later, Peter-Klaus Schuster took over and set in motion a far more ambitious program intended to turn Museum Island into a Louvre on the Spree.[3] The federal government pledged $20 million a year through 2010 for projects to enhance Berlin's prestige and Unesco declaring the island a World Heritage Site.[4]
The contents of the museums were decided on as follows: The Pergamon, with the Greek altar that gives it its name, retained much of its collection and was defined as a museum of ancient architecture. The Neues Museum presented archaeological objects as well as Egyptian and Etruscan sculptures, including the renowned bust of Queen Nefertiti. The Altes Museum, the oldest on the island, displayed Greek and Roman art objects on its first floor and hold exhibitions on its second floor. The Bode Museum's paintings went from Late Byzantine to 1800. And, as now, the Alte Nationalgalerie will cover the 19th century.[3] Once this process is completed, perhaps by 2020, the Gemäldegalerie’s painting collection will be transferred to the Bode, and a new annex, and Museum Island will present all art from the ancient civilizations to 1900.[5] The James Simon Gallery, a $94 million visitors’ center designed by the British architect David Chipperfield, is being built beside the Neues Museum. It will in turn be linked to the Neues, Altes, Pergamon and Bode Museums by an underground passageway decorated with archaeological objects.[5]
Once the Museum Island Master Plan is completed, the so-called Archaeological Promenade will connect four of the five museums in the Museum Island. The Promenade will begin at the Old Museum in the south, lead through the New Museum and the Pergamon Museum and end at the Bode Museum, located at the northern tip of the Island. Before World War II, these museums were connected by bridge passages above ground; they were destroyed due to the effects of the war. There have never been plans to rebuild them; instead, the central courts of individual museums will be lowered, which has already been done in the Bode Museum and in the New Museum. They will be connected by subterranean galleries. In a way, this archaeological promenade can be regarded as the sixth museum in the Island, because it is devised not only as a connecting corridor but also as a strung-out exhibition room for interdisciplinary presentations. The Archaeological Promenade may be characterized as a cross-total of the collections that are shown separately (in accordance with cultural regions, epochs, and art genres) in the individual museums of the Island. The Archaeological Promenade will address multi-focus topics that have occupied the human mind irrespective of time and cultural region, be it a question of life after death or issues of beauty and other topics.[6]
Museum Island is referenced in the song "On the Museum Island" by folk artist Emmy the Great.
The southern section of the island, south of Gertraudenstraße, is commonly referred to as Fischerinsel (Fisher Island) and is the site of a high-rise apartment development built when Mitte was part of East Berlin.
Photogallery




 Panorama with River Spree
Panorama with River Spree Tactile scale model of Museum Island
Tactile scale model of Museum Island
 Berlin Palace in July 2020
Berlin Palace in July 2020
See also
- Berlin State Museums
- List of museums in Berlin
References
- Museumsinsel (Museum Island), Berlin UNESCO World Heritage Centre
- Masterplan Museumsinsel
- Alan Riding (March 12, 2002), Berlin, Banking on Its Museums; Seeking a New Identity, the City Shakes Up Its Art Legacy New York Times.
- Desmond Butler (December 2, 2001), Berlin Museum's Revival Bolsters German Identity New York Times.
- Alan Riding (November 27, 2006), German Museums Move Closer to Reunification New York Times.
- Hermann Parzinger (December 17, 2015), Museum Island and Humboldt-Forum: A New Centre for Art and Culture in Berlin SCIENCE First Hand.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Museumsinsel. |
- Museumsinsel (Museum Island), Berlin UNESCO official website
- Official Museum Island website (in English)
- Masterplan The future of the Museum Island
- Museum Island — Interactive 360° panorama during the Festival of Lights
- A Remarkable Success Story – the Museum Island in Berlin, article on the website of the Goethe-Institut, February 2010 (in English)