Name of Poland
The ethnonyms for the Poles (people)[1] and Poland (their country)[2] include endonyms (the way Polish people refer to themselves and their country) and exonyms (the way other peoples refer to the Poles and their country). Endonyms and most exonyms for Poles and Poland are usually associated to derive from the name of the Lechitic tribe of Western Polans (Polanie), also stated by some sources has been the association in some languages for the exonyms for Poland to derive from the name of another tribe – the Lendians (Lędzianie).

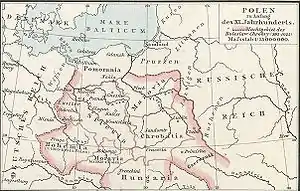


Endonyms
The Polish words for a Pole are Polak (masculine) and Polka (feminine), Polki being the plural form for two or more women and Polacy being the plural form for the rest. The adjective "Polish" translates to Polish as polski (masculine), polska (feminine) and polskie (neuter). The common Polish name for Poland is Polska. The latter Polish word is an adjectival form which has developed into a substantive noun, most probably originating in the phrase polska ziemia, meaning "Polish land".[3]
Rzeczpospolita
The full official name of the Polish state is Rzeczpospolita Polska which translates to "The Commonwealth of Poland". The word rzeczpospolita has been used in Poland since at least the 16th century, originally a generic term to denote any state with a republican or similar form of government. Today, however, the word is used almost solely in reference to the Polish State. Any other republic is referred to as republika in modern Polish.
Language roots
It is often assumed that all of the above names derive from the name of the Polans (Polanie), a West Slavic tribe which inhabited the territories of present-day Poland in the 9th-10th centuries. The origin of the name Polanie is theorized to be descendend ultimately from Proto-Slavic. It may derive from the word pole, Polish for "field".[4]
Many ancient tribes in Europe derived their names from the nature of the land they inhabited. Gervase of Tilbury wrote in his Otia imperialia ("Recreation for an Emperor", 1211): Inter Alpes Huniae et Oceanum est Polonia, sic dicta in eorum idiomate quasi Campania.(translation: "Between the Hunnic Alps and the Ocean there is Poland, thus called "Countryside" in their idiom.") Polans may have used Polska to describe their own territory in the Warta River basin. During the 10th century, they managed to subdue and unite the Slavic tribes between the rivers Oder and Bug River into a single feudal state and in the early 11th century, the name Polska was extended to the entire ethnically Polish territory. The lands originally inhabited by the Polans became known as Staropolska, or "Old Poland", and later as Wielkopolska, or "Greater Poland", while the lands conquered towards the end of the 10th century, home of the Vistulans (Wiślanie) and the Lendians, became known as Małopolska, or "Lesser Poland."
In Polish literature, Poland is sometimes referred to as Lechia, derived from Lech, the legendary founder of Poland. In the 17th-18th centuries, Sarmaci ("Sarmatians") was a popular name by which Polish nobles referred to themselves (see Sarmatism).
"Poland" in European literary sources
The earliest recorded mention of "Poland" is found in a Latin text written in 1003 A.D. and titled "Annales Hildesheimenses": "Heinricus Berthaldi comitis filius, et Bruno frater regis, et ambo Bolizavones, Polianicus vide licet ac Boemicus, a rege infideliter maiestatis rei deficient." In English: Henry, son of Berthold, and Bruno, brother of the king, and both Boleslaws, Polish and Czech, left the circle of friends of the Emperor.[5]
Exonyms
Variations of the country endonym Polska became exonyms in other languages.
In Slavic languages
Exonyms for Poland in Slavic languages. The West Slavic languages such as Czech and Slovak bear particular resemblance to the Polish endonym:
- Kashubian Pòlskô
- Czech Polsko
- Slovak Poľsko
- Serbo-Croatian: Пољска / Poljska
- Slovene Poljska
- Belarusian Польшча, Pol'shcha
- Ukrainian Польща, Pol'shcha
- Russian Польша, Pol'sha
- Bulgarian Полша, Polsha
- Macedonian Полска, Polska
In Romance languages
In Latin, which was the principal written language of the Middle Ages, the exonym for Poland became Polonia. It later became the basis for Poland's name in all Romance languages:
- Catalan Polònia
- Occitan Polonha
- French Pologne
- Italian, Galician, Romanian, Spanish Polonia
- Portuguese Polónia (European) / Polônia (Brazilian)
Many other languages (e.g. Albanian Polonia; Greek Πολωνία, Polōnía; Maltese Polonja) use a variation of the Latin name.
In Germanic languages
Germans, Poland's western neighbors, called it Polen. Other Germanic languages use related exonyms:
- Dutch, Danish, Swedish, Norwegian Polen
- English Poland
- Icelandic, Faroese Pólland
- Yiddish פױלן, Poyln
Non-Germanic languages which borrowed their word for Poland from Germanic include:
Other
The Lendians, a Proto-Polish tribe who lived around the confluence of the rivers Vistula and San (south-eastern Poland), have often misleadingly been associated as the source of another exonym, Lechia. The tribe's name likely comes from the Proto-Polish word lęda, or "scorched land".[3] Their name was borrowed to refer to Poland mainly by peoples who lived east or south of Poland:
- лях (lyakh) is used in East Slavic languages. It also appears in Polish literature as Lachy, a synonym for "Poles" and "Poland" used by East Slavic characters. Podlasie, a Polish region on the Belarusian border, derives its name from the same root. Lachy Sądeckie is the name of a small cultural group around Nowy Sącz in southern Lesser Poland.
- Lithuanian Lenkija
- Hungarian Lengyelország
- Persian لهستان, Lahestan. The word combines Lah with a common Persian suffix -stan, which means "The land of".
- Turkish Lehistan. It is now considered obsolete and replaced by Polonya.[6]
- Armenian Լեհաստան, Lehastan was also borrowed from Persian.
Related words
Some common English words, as well as scientific nomenclature, derive from exonyms of Poland in various languages.
- Alla polacca, like a polonaise (in musical notation); Italian for "Polish style"
- Polacca, a type of 17th-century sailing vessel
- Polka, a dance and genre of dance music originally from Bohemia; Czech (also Polish) "Pole" (feminine)
- Polonaise, several meanings including a dance of Polish origin; from French polonaise, "Polish" (feminine)
- 1112 Polonia, an asteroid; from Latin Polonia, "Poland"
- Polonium, a chemical element; from Latin Polonia
- Polska, a dance of Swedish origin; from Swedish polska, "Polish"
- Poulaines, a type of shoes popular in the 15th century in Europe; from Old French polain, "Polish"
- Polonia, the term to describe people of Polish origin living outside of Poland and in other countries.
See also
- Civitas Schinesghe
- Exonym and endonym
- Lechia
- List of country name etymologies
- Polish names
- Polish tribes
- Polonia (disambiguation)
- Polska Ludowa
References
- Polani by John Canaparius, Vita sancti Adalberti episcopi Pragensis, or Life of St. Adalbert of Prague, 999.
- Polenia by Thietmar of Merseburg Chronicle, 1002. (German: Polen)
- (in Polish) Wielka Encyklopedia Powszechna PWN
- "fr. pal, pele, altd. pal, pael, dn. pael, sw. pale, isl. pall, bre. pal, peul, it. polo, pole, pila, [in:] A dictionary of the Anglo-Saxon languages. Joseph Bosworth. S.275.; planus, plain, flat; from Indo-European pele, flat, to spread, also the root of words like plan, floor, and field. [in:] John Hejduk. Soundings. 1993. p. 399"; "the root pele is the source of the English words "field" and "floor". The root "plak" is the source of the English word "flake" [in:] Loren Edward Meierding. Ace the Verbal on the SAT. 2005. p. 82
- G.K. Walkowski (tr.) (2013), Vvitichindus, Res gestae Saxonicae. Annales Corbeienses. Annales Hildesheimenses, Bydgoszcz, ISBN 978-83-930932-9-8
- (in Turkish) Lehistan in Turkish Wikipedia
External links
| Look up Poland in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
