Oxaceprol
Oxaceprol is an anti-inflammatory drug used in the treatment of osteoarthritis.[1] It is derived from L-proline, a DNA-encoded amino acid. The active effect of Oxaceprol is to inhibit the adhesion and migration of white blood cells.[2]
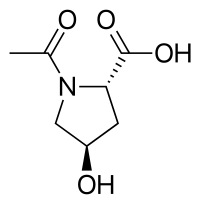 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | (2S,4R)-1-acetyl-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.058 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H11NO4 |
| Molar mass | 173.168 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Herrmann G, Steeger D, Klasser M, Wirbitzky J, Fürst M, Venbrocks R, et al. (2000). "Oxaceprol is a well-tolerated therapy for osteoarthritis with efficacy equivalent to diclofenac". Clinical Rheumatology. 19 (2): 99–104. doi:10.1007/s100670050025. PMID 10791619. S2CID 25654850.
- Clayton JJ (August 2007). "Nutraceuticals in the management of osteoarthritis". Orthopedics. 30 (8): 624–9, quiz 630-1. doi:10.3928/01477447-20070801-13. PMID 17727018. Retrieved 2013-06-08.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
