Saskatchewan Glacier
The Saskatchewan Glacier is located in Banff National Park, Alberta, Canada, approximately 120 km (75 mi) northwest of the town of Banff, and can be accessed from the Icefields Parkway. Saskatchewan Glacier is the largest outflow glacier from the Columbia Icefield, which rests along the Continental Divide. The glacier is a primary water source for the North Saskatchewan River. The glacier is approximately 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) long and covers an area of 30 km2 (11.5 mi2) and was measured in 1960 to be over 400 metres (1,300 ft) thick at a distance of 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) from the terminal snout. Between the years 1893 and 1953, Saskatchewan Glacier had retreated a distance of 1,364 metres (4,475 ft), with the rate of retreat between the years 1948 and 1953 averaging 55 metres (180 ft) per year. The glacier, which flows northeast, exhibits a prominent medial morraine. [1]
| Saskatchewan Glacier | |
|---|---|
 Saskatchewan Glacier in Alberta, Canada seen from Parker Ridge | |
  | |
| Coordinates | 52.138546°N 117.193222°W |
| Area | 30 square kilometres (12 sq mi) |
| Length | 13 kilometres (8 mi) |
| Status | Receding |
See also
References
- Ommanney, C. Simon L. "Glaciers of the Canadian Rockies" (pdf). Satellite Image Atlas of Glaciers of the World. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2006-07-04.
Gallery
 Saskatchewan Glacier with Castleguard Mountain from Parker Ridge
Saskatchewan Glacier with Castleguard Mountain from Parker Ridge Saskatchewan Glacier & Parker Ridge from glacier's toe
Saskatchewan Glacier & Parker Ridge from glacier's toe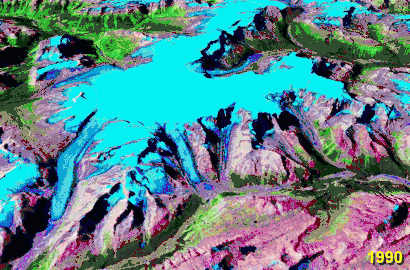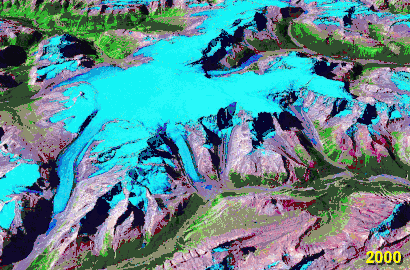 In this animated gif of the Columbia Icefield, glaciated areas in 1990 are compared to 2000. The Saskatchewan Glacier is the large tongue shaped glacier on the left, which has both retreated and thinned along most of its length during the period.
In this animated gif of the Columbia Icefield, glaciated areas in 1990 are compared to 2000. The Saskatchewan Glacier is the large tongue shaped glacier on the left, which has both retreated and thinned along most of its length during the period.
References
- Smith, D.G. (1987). Landforms of Alberta interpreted from airphotos and satellite imagery. Edmonton, Alberta: Alberta Remote Sensing Centre, Alberta Environment. p. 35. ISBN 0-919975-10-0.