Sela Pass
The Sela Pass (more appropriately called Se La, as La means Pass) is a high-altitude mountain pass located on the border between the Tawang and West Kameng Districts of Arunachal Pradesh state in India. It has an elevation of 4170 m (13,700 ft) and connects the Indian Buddhist town of Tawang to Dirang and Guwahati. The pass carries the National Highway 13 (previously NH 229), connecting Tawang with the rest of India. The pass supports scarce amounts of vegetation and is usually snow-covered to some extent throughout the year. Sela Lake, near the summit of the pass, is one of approximately 101 lakes in the area that are sacred in Tibetan Buddhism. While Sela Pass does get heavy snowfall in winters, it is usually open throughout the year unless landslides or snow require the pass to be shut down temporarily.
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
| Sela Pass | |
|---|---|
| Se La | |
 Sela pass Gate in April 2015 | |
| Elevation | 4,170 metres (13,680 ft) |
| Location | Arunachal Pradesh, India |
| Range | Himalaya |
| Coordinates | 27°30′17″N 92°06′17″E |
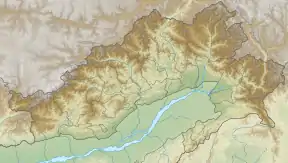  | |
Geography
Sela Pass crosses a subrange of the Himalayas that separates Tawang District from the rest of India.[1] The pass is 4170 m (13,700 ft) high[2][3] and is situated at a distance of 78 km from Tawang town and 340 km from Guwahati.[4] While the Border Roads Organization (BRO) of India works to keep the pass is open throughout the year, it may shut down temporarily after landslides and during heavy snow. Summers at Sela Pass are not very cold but temperature in winter can dip down to -10 degree Celsius.[5] Sela lake is a large lake located on the north side of the pass at an elevation of 4,160 metres (13,650 ft).[6] This lake often freezes during the winter and is drained Nuranang River, a tributary of the Tawang River. Limited vegetation grows around the lake which is used as a grazing site for yaks during the summer.[3]
Tunnel
Sela Tunnel, Government of India announced the funding for construction of all weather road transport tunnel in 2018-19 budget.[7] Construction will start in January 2019. [8] The under-construction Bhalukpong-Tawang railway, expected to be completed by December 2022, will also pass through here.
Religion
Sela Pass is a sacred site in Tibetan Buddhism. Buddhists believe that there are about 101 sacred lakes in and around the pass.[1][2]
Legend
*During the Sino-Indian War in 1962, Brigadier Hoshiar Singh Rathee was in charge of the defence of Sela Pass of this region with a brigade of Indian Army consisting of soldiers from battalions of various regiments, including 1 SIKH, 2 Sikh LI, 4 Sikh LI and also soldiers from Garhwal Rifles.
Brig. Hoshiar Singh was killed in action fighting for the Indian Army in the NEFA region in 1962 when his party was ambushed by invading Chinese soldiers while commanding the defence of the Sela Pass.
By the afternoon of 23 November 1962 ( 2 days after ceasefire) Chinese troops belonging to No.2 Company of 154 Regiment (419 Unit) massacred brigade commander, three officers and twenty nine other ranks while the rest were wounded or captured at Phudung near Phitang Bridge, southwest of Bomdilla.
Brig. Hoshiar Singh's body was preserved in Phudung by the local Monpas. Much later, Indian army officers returned to Phudung and cremated the courageous soldier with his eldest son performing the last rites.
*According to legend, a sepoy of the Indian Army named Jaswant Singh Rawat fought alone against the Chinese soldiers near the pass during the 1962 Sino-Indian War. A tribal woman named Sela who had brought food and water to him is said to have killed herself upon seeing the dead body of Jaswant Singh Rawat. Singh was posthumously awarded the Maha Vir Chakra for his courage and devotion to duty.[1][3]
Gallery
 Sela Pass Gate
Sela Pass Gate Clouds moving into the pass
Clouds moving into the pass Sela Pass
Sela Pass.jpg.webp) Jainath Bridge, Sela Pass
Jainath Bridge, Sela Pass View of Jaswant Garh
View of Jaswant Garh Sela Pass, Arunachal Pradesh, India
Sela Pass, Arunachal Pradesh, India.jpg.webp) Sela Pass is prone heavy landslides
Sela Pass is prone heavy landslides.jpg.webp) A village in the middle of Sela Pass
A village in the middle of Sela Pass
See also
- Tourism in North East India
- Tawang Town
- Tawang Monastery
- Bhalukpong-Tawang railway, under-construction
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sela Pass. |
- "Sela Pass". Pan India Internet Private Limited (PIIPL). arunachalonline.in. Retrieved 19 April 2013.
- "High Altitude Sela Pass–Backbone of Tawang District". Sankara Subramanian C (www.beontheroad.com). beontheroad.com. 21 January 2011. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- "Sela Passmountain pass". travelomy.com. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- "How To Reach Sela Pass". Travelomy. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- "Sela Pass". Travelomy. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- "Other Important Attractions of Tawang District". National Informatics Centre, Tawang (Arunachal Pradesh). Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- Sela pass tunnel, Economic Times, 1 Feb 2018.
- "Work for construction of Sela tunnel to start soon: DGBR". Business Standard. Press Trust of India. 21 November 2018. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
.jpg.webp)