Shuozhou
Shuozhou is a prefecture-level city in northern Shanxi province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest. It is situated along the upper reaches of the Fen River. The prefecture as a whole has an area of about 5,737 km2 (2,215 sq mi) and, in 2010, a population of about 1.71 million.[2]
Shuozhou
朔州市 | |
|---|---|
 The Pagoda of Fogong Temple, Ying County, built in 1056. | |
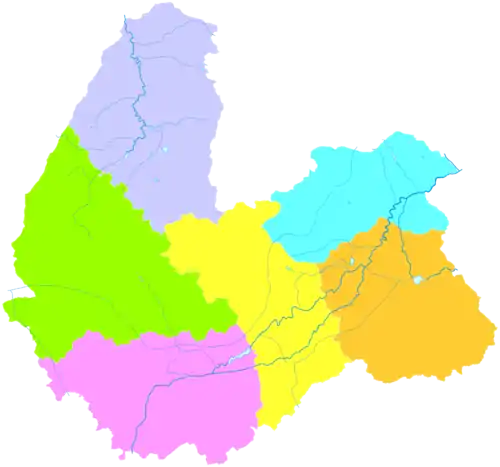
.png.webp) Location of Shuozhou City jurisdiction in Shanxi | |
 Shuozhou Shuozhou city center in Shanxi | |
| Coordinates (Shuozhou municipal government): 39°19′54″N 112°25′58″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shanxi |
| County-level divisions | 6 |
| Municipal seat | Shuocheng District |
| Government | |
| • Type | Prefecture-level city |
| • CPC Shuozhou Secretary | Wang Maoshe (王茂设) |
| • Mayor | LI Zhengyin (李正印) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 10,662 km2 (4,117 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 176.00 km2 (67.95 sq mi) |
| • Districts[1] | 4,093.7 km2 (1,580.6 sq mi) |
| Population (2010)[2] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 1,714,857 |
| • Density | 160/km2 (420/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 433,700 |
| • Districts[1] | 745,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 036000 |
| Area code(s) | 0349 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-SX-06 |
| Licence plates | 晋F |
| Administrative division code | 140600 |
| Website | www |
| Shuozhou | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 朔州 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Seat of Shuo Prefecture | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Former names | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mayi | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 馬邑 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 马邑 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Horse Town | ||||||||
| |||||||||
History
The site of Shuozhou was the ancient Chinese frontier town of Mayi,[3] which was used as a trading post between China and the Xiongnu nomads of the eastern Eurasian steppe.
In 201 BC, the founder of the Han dynasty Liu Bang (posthumously known as Emperor Gaozu or the "High Ancestor") moved Han Xin from his fief around Yuzhou in Henan to Mayi, where he was attacked by the Xiongnu. Finding himself distrusted by the Han emperor, Han Xin allied with the Xiongnu instead and joined them on their raids against China until his death in battle in 196 BC. Mayi was subsequently the capital of Dai Prefecture and the scene of an attempted ambush of the Xiongnu by Chinese troops in 133 BC.
During the chaos between the fall of the Sui and rise of the Tang, Mayi was the base of the would-be emperor Liu Wuzhou.
Administrative divisions
The seat of government is in Shuocheng District, the urban core of the city.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2003 est.) |
Area (km²) | Density (/km²) |
| Shuocheng District | 朔城区 | Shuòchéng Qū | 380,000 | 1,793 | 212 |
| Pinglu District | 平鲁区 | Pínglǔ Qū | 190,000 | 2,314 | 82 |
| Shanyin County | 山阴县 | Shānyīn Xiàn | 220,000 | 1,652 | 133 |
| Ying County | 应县 | Yìng Xiàn | 270,000 | 1,708 | 158 |
| Youyu County | 右玉县 | Yòuyù Xiàn | 100,000 | 1,965 | 51 |
| Huairen city | 怀仁市 | Huáirén Shì | 250,000 | 1,230 | 203 |
Climate
Shuozhou has a continental, monsoon-influenced semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk),[4] with cold, very dry, and somewhat long winters, and warm, somewhat humid summers. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −9.8 °C (14.4 °F) in January to 21.9 °C (71.4 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 7.42 °C (45.4 °F). Typifying the influence of the East Asian Monsoon, over three-fourths of the annual 399 millimetres (15.7 in) of precipitation occurs from June to September.
| Climate data for Shuozhou (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −1.4 (29.5) |
2.8 (37.0) |
9.1 (48.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.2 (82.8) |
26.4 (79.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
7.4 (45.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.8 (14.4) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
1.3 (34.3) |
9.8 (49.6) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.9 (71.4) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.7 (58.5) |
8.0 (46.4) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −16.8 (1.8) |
−12.9 (8.8) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
8.4 (47.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
13.8 (56.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
0.4 (32.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1.6 (0.06) |
2.6 (0.10) |
10.2 (0.40) |
17.8 (0.70) |
33.4 (1.31) |
57.0 (2.24) |
101.0 (3.98) |
90.0 (3.54) |
56.0 (2.20) |
21.1 (0.83) |
6.1 (0.24) |
1.7 (0.07) |
398.5 (15.67) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 52 | 47 | 44 | 39 | 42 | 52 | 68 | 73 | 66 | 58 | 53 | 53 | 54 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[5] | |||||||||||||
Economy
It is a centre of industry, and its notable industries are primarily mining of coal and other ores such as iron, bauxite, mica, manganese, and graphite. Other economic sectors include agriculture, chemical industry, ceramics, and fishing.
Education
- North University of China, Shuozhou http://neuc.nuc.edu.cn/
Tourism
Western tourists rarely come to this area of China, but there are some attractions. The Yingxian Tower, built in 1056 during the Liao Dynasty, is one of the main sites of the region. It was built entirely of wood, without using nails, and serves as a museum of calligraphy. There are also some paleolithic ruins, and ancient gravesites from the Dongyi people.
Transportation
The Dayun Expressway (Datong—Yuncheng) passes through it, and it has 5 specialized train lines.
References
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 46. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- 朔州市2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报(Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China). National Bureau of Statistics of China. Retrieved 30 August 2012.
- Anecdotes about Spirits and Immortals, Vol. II, Waiwen Chubanshe, 2004, p. 749. (in Chinese) & (in English)
- Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., and McMahon, T. A.: Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 11, 1633-1644, doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007, 2007.
- 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data. China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
External links
- Official website (in Chinese)