Stanisława Walasiewicz
Stanisława Walasiewicz (3 April 1911 – 4 December 1980), also known as Stefania Walasiewicz,[2] and Stella Walsh,[3] was a Polish-American track and field athlete, who became a women's Olympic champion in the 100 metres. Born in Poland and raised in the United States, she became an American citizen in 1947. Upon her death, it was discovered that Walasiewicz had a Y chromosome and was intersex.[4]
 Stanisława Walasiewicz in 1938 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Born | 3 April 1911 Wierzchownia, Congress Poland, Russian Empire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | 4 December 1980 (aged 69) Cleveland, Ohio, United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 1.74 m (5 ft 9 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight | 60 kg (132 lb) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sport | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sport | Athletics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Event(s) | 100 m, 200 m, long jump | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Club | Warszawianka, Warszawa Legia Warszawa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achievements and titles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal best(s) | 100 yd – 10.5 (1944) 100 m – 11.6 (1937) 200 m – 23.6 (1935) long jump – 6.12 m (1939)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Medal record
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Background
Walasiewicz was born on 3 April 1911 in Wierzchownia (now Brodnica County), Congress Poland.[5] Her family emigrated to the United States when she was three months old. Her parents, Julian and Veronika Walasiewicz, settled in Cleveland, Ohio, where her father found a job as a steel mill worker.[6] Her family called her Stasia, a common Polish diminutive of her Christian name, which later gave birth to the American version of her name, Stella.[6]
Athletic career
Walasiewicz started her athletic career at South High School, a school located in the historic Slavic Village neighborhood on the east side of Cleveland, Ohio. In 1927, she qualified for a place on the American Olympic team started by the Cleveland Press newspaper. However, Walasiewicz was not an American citizen and could not obtain citizenship under the age of 21, so she could not compete.[6] The success of Halina Konopacka, a Polish athlete who won gold in the discus throw at the 1928 Summer Olympics, inspired Walasiewicz to join the local branch of Sokół, a Polish sports and patriotic organization active among the Polish diaspora. During the Pan-Slavic meeting of the Sokół movement in Poznań, she scored her first major international victories; she won five gold medals in the 60 metre, 100 metre, 200 metre and 400 metre races, as well as the long jump.[6] She was asked to stay in Poland and join the Polish national athletic team, and she continued to run in American challenges and games.
Walasiewicz continued to compete as an amateur, while also working as a clerk in Cleveland. In the period leading up to the 1932 Summer Olympics, she won American national championships in the 100-yard dash (1930), 220 yard dash (1930–1), and long jump (1930).[7] For her part in interstate athletic championships, the city of Cleveland awarded her a car.[6][8] She was offered American citizenship; however, just two days prior to taking her Oath of Citizenship, she changed her mind and instead adopted Polish citizenship, offered to her by the Polish consulate in New York.[6][9] In 1930, she was chosen the most popular Polish athlete by readers of the Przegląd Sportowy (Sports Review) daily.[10]
In the 1932 Summer Olympics, Walasiewicz represented Poland. In the 100 m dash, Walasiewicz equaled the current world record of 11.9 seconds and won the gold medal.[11] On the same day, she finished 6th out of 9 in the discus throw event.[12] Upon her return to Poland, she almost instantly became a well-known personality. She was welcomed by crowds in the port of Gdynia, and a few days later, she was awarded the Golden Cross of Merit for her achievements. She was again chosen the most popular Polish person in sports, and held that title for three years.[10]
In the spring of 1933, Walasiewicz appeared at the Championships of Warsaw, where she seized 9 gold medals in track and field, including 80 metres hurdling, 4 × 200 relay, and long jump.[13] On 17 September 1933, in Poznań, she beat two world records in one day: 7.4 seconds for the 60 m and 11.8 seconds for the 100 m. Her Olympic success also won her a scholarship at the Warsaw Institute of Physical Education, where she met some of the most notable Polish athletes of the time, including Jadwiga Wajs, Feliksa Schabińska, Maria Kwaśniewska, and Janusz Kusociński.
In the 1936 Olympics in Berlin, Walasiewicz attempted to defend her Olympic title for the 100 m dash, but Helen Stephens of the U.S. beat her by .02 second; Walasiewicz won the silver medal.[14] Ironically, in hindsight, Stephens was accused of being male and was forced to submit to a genital inspection to confirm her gender.[15]
After the Olympic Games, Walasiewicz moved to the U.S. and resumed her amateur career.[6] During and after World War II, she won American national championships in the 100 metres (1943, 1944 and 1948), the 200 metres (1939–40 and 1942–8), the discus throw (1941–2), and the long jump (1938–46, 1948 and 1951).[7][8]
In 1947, she accepted American citizenship, and she later married aviation draftsman Harry Olson in 1956.[16] Although the marriage did not last long, she continued to use the name Stella Walsh Olson for the rest of her life. She won her last U.S. title in 1951, at the age of forty.[8] and she was inducted into the U.S. Track and Field Hall of Fame in 1975.
Post-athletic career
After her retirement, she continued to be active in a variety of Polish sport associations in the U.S., where she organized championships and helped young athletes. She also funded a variety of awards for Polish sports people living in America. In 1974, Stella Walsh was inducted into the National Polish-American Sports Hall of Fame. Stella Walsh was a contestant on the 16 June 1954 episode of the radio quiz program You Bet Your Life, hosted by Groucho Marx.[17]
Death and controversy
Walsh was killed during an armed robbery in a parking lot in Cleveland, on 4 December 1980.[18][19] She was buying ribbons for a welcoming ceremony for visiting Polish basketball players.[20] An autopsy showed that she had no uterus, an abnormal urethra, and a non-functioning, underdeveloped penis, although some sources suggest she also displayed female characteristics.[21][22][23] Chromosome analysis revealed that most of her cells contained normal X and Y (male) chromosomes but some were X0 (containing only one X chromosome), resulting in XY gonadal dysgenesis.[4]
The controversy of her biological sex remains unresolved, and the situation is further complicated as many earlier documents, including her birth record, state that she was female; the Cuyahoga County coroner, Samuel Gerber, stated that Walasiewicz was "socially, culturally and legally" a woman.[6][4] There has also been controversy over whether her records and achievements should be erased.[24]
Legacy
In Cleveland, on Broadway Avenue, there is a city-owned recreational center named after Stella Walsh. It is attached to Cleveland South High School. She is buried in Calvary Cemetery in Cleveland, Ohio.[25]
Walasiewicz was discussed on BBC Radio 4's The Long View in April 2019 when the contentious issue was the "Gender in women's sport".[26]
See also
References
- "Stanisława Walasiewicz". Sports Reference. Archived from the original on 4 December 2009.
- "Stefania Walasiewicz". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Wallechinsky, David (2012). The Book of Olympic Lists. p. 19. ISBN 978-1845137731.
- "Ex-Olympian Stella Walsh legally a woman". Sarasota Journal. 12 February 1981. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- Some sources also cite 7 and 11 April
- Klaudia Snochowska-Gonzales; Tomasz Kuzia (14 August 2004). "Walasiewicz była kobietą" [Walasiewicz Was a Woman]. Gazeta Wyborcza (in Polish). 190. p. 8. Retrieved 31 May 2006.
- USA Track & Field – USA Outdoor Track & Field Champions. Usatf.org. Retrieved on 13 July 2015.
- "USA Outdoor Track & Field Champions—Women's Long Jump". USA Track & Field. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- At the time of Walasiewicz's birth, Poland was under partition, and she was officially a citizen of the Russian Empire, even though the state had ceased to exist as a result of the Russian Civil War.
- "Plebiscyt PS". ozarow.maz.pl. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- "Women's 100 meter run finals". The San Bernardino County Sun. 3 August 1932. Retrieved 23 August 2016 – via Newspapers.com.
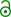
- Polish Olympic Committee (corporate author) (2005). "Los Angeles – 1932.08.02". Polski Portal Olimpijski PKOl. Polish Olympic Committee. Archived from the original on 3 February 2006. Retrieved 1 June 2006.
- Krzysztof Bazylow (25 October 2004). "1933 – STANISŁAWA WALASIEWICZ". sports.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 1 June 2006.
- Stuart Cameron (5 August 1936). "Bettered Olympic mark in broad jump; America leads by forty-five points now". Times Herald (New York). Retrieved 23 August 2016 – via Newspapers.com.
- "Helen Stephens is real girl". Harrisburg Telegraph. 6 August 1936. Retrieved 23 August 2016 – via Newspapers.com.
- Toby C. Rider (Pennsylvania State University, Berks, USA); Sarah Teetzel (University of Manitoba, Canada). "The Strange Tale of Stella Walsh's Olympic Eligibility" (PDF). Amateur Athletic Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2016.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "You Bet Your Life 35 Eps : Free Download & Streaming". Archive.org. 16 June 1954. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- "Olympic track star Stella Walsh dies". Wilmington Morning Star. 6 December 1980. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- "Stella Walsh Slain; Olympic Track Star". New York Times. 6 December 1980. p. 20. ProQuest 121246455
- Louise Mead Tricard (1 January 1996). American Women's Track and Field: A History, 1895 Through 1980. McFarland. p. 645. ISBN 978-0-7864-0219-9.
- Matt Tullis (27 June 2013). "Who was Stella Walsh?: The story of the intersex Olympian". SB Nation – via Associated Press (corporate author).
- "Coroner's report says Stella Walsh 'lived and died' a woman". United Press International. 23 January 1981. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- Renata Gorczyńska (15 November 2002). "Co ma wirus do płci" [What does the virus do to have sex]. Rzeczpospolita (in Polish). 266. Archived from the original on 24 July 2003. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- "Stella: Fontana woman recalls races vs. 'Polish Flyer'". The San Bernardino County Sun. 10 February 1981. p. 39. Retrieved 23 August 2016 – via Newspapers.com. (subscription required)
- Vigil, Vicki Blum (2007). Cemeteries of Northeast Ohio: Stones, Symbols & Stories. Cleveland, Ohio: Gray & Company. ISBN 978-1-59851-025-6.
- Presenter: Jonathan Freedland (30 April 2019). "Gender in women's sport". The Long View. BBC. BBC Radio 4. Retrieved 2 May 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stanisława Walasiewicz. |
- Stanislawa Walasiewicz at the International Olympic Committee
- Stanisława Walasiewicz at Find a Grave
- IAAF Official Website
- Stella Walsh: A Documentary
- Great Outings of History at the Wayback Machine (archived 27 September 2013)