Timeline of Vladivostok
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Vladivostok, Primorsky Krai, Russia.
19th century
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Russia | ||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||
|
Prehistory • Antiquity • Early Slavs
Feudal Rus' (1097–1547) Novgorod Republic • Vladimir-Suzdal Mongol conquest • Grand Duchy of Moscow
Russian Revolution (1917–1923) February Revolution • Provisional Government
|
||||||||||||||
|
Timeline 860–1721 • 1721–1796 • 1796–18551855–1892 • 1892–1917 • 1917–1927 1927–1953 • 1953–1964 • 1964–1982 1982–1991 • 1991–present |
||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
- 1858 - Territory ceded to Russia by China per Treaty of Aigun.
- 1860 - June: Russian ship Manchzhur arrives; military barracks constructed under command of Nikolay Vasilyevich Komarov.
- 1864 - Kunst & Albers in business.[1]
- 1865 - Vladivostok designated a free port.[2]
- 1871
- Okhotsk Military Flotilla based in Vladivostok.
- Japan-Vladivostok telegraph cable installed.
- Amerikanskaya Street laid out.
- 1877 - Maritime navigation light established.[3]
- 1880
- Vladivostok designated a city.[4]
- Population: 7,300.
- 1881 - Vladivostok Police directorate formed.
- 1883
- 1884 - Society for the Study of the Amur Region established.[6]
- 1887 - Public reading-hall opens.
- 1888 - Oblast governor's residence related to Vladivostok from Khabarovsk.
- 1890 - Amurskiy Regional Museum opens.[7][8]
- 1891 - May: Nicholas II visits city.[9]
- 1892 - Far East newspaper begins publication.[6]
- 1894 - State Bank branch opens.[6]
- 1897 - Population: 28,896.
- 1898 - Russo-Chinese Bank branch opens.[6]
- 1899
- Oriental Institute opens.[10]
- Advertiser newspaper begins publication.[6]
20th century
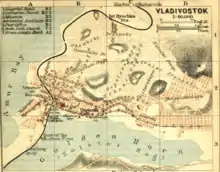
Map of Vladivostok, 1914
- 1902 - Vladivostok Sea School of Far Navigation founded.[11]
- 1903 - Trans-Siberian Railway begins operating.
- 1906 - January: Armed revolt.
- 1907
- Siberian Bank branch opens.[12]
- October: Armed revolt.
- Winter: After a multitude of alleged paranormal incidents and multiple crew deaths, the Ivan Vassili is burned by drunken sailors.[13]
- 1908 - Tram begins operating.
- 1909 - Population: 90,100.[14]
- 1912
- Train station built.[8]
- Theater and Music begins publication.
- 1917 - December: Japanese military occupies railroad.[15]
- 1918
- Vladivostok Fortress constructed.
- April 4: Three Japanese killed.[16]
- April 5: United States,[4] Japanese, and British military stationed in city.
- 1920 - April: United States military withdraws from city.[16]
- 1922 - October 25: Red Army in power.
- 1930s - Transit prisons established.
- 1930
- Far Eastern Politechnical Institute established.
- Moscow-Vladivostok automotive rally conducted.[17]
- 1931 - Maxim Gorky Academic Theater founded.
- 1932 - Airfield begins operating.
- 1942 - A Doolittle Raid B-25 makes an emergency landing in Valdivostok.
- 1954 - Krushchev visits city.[18]
- 1957 - Dynamo Stadium opens.
- 1958
- Vladivostok designated a closed city.[18]
- Vladivostok State Medical Institute established.
- Football Club Luch formed.
- 1960 - Centennial Prospect (street) laid out.
- 1965 - Population: 367,000.[19]
- 1967 - Far Eastern Technological Institute founded.[20]
- 1974 - November: USA-USSR arms control summit held.
- 1985 - Population: 600,000.[21]
- 1988 - City opens to Soviet citizens.[4]
- 1990 - Vladimir Yefremov becomes mayor.
- 1991
- Sister city relationship established with San Diego, USA.[22]
- Vladivostok's closed city status ends.[18]
- 1992
- 1993 - Viktor Cherepkov becomes mayor.
- 1994 - Tolstoshein Konstantin Borisovich becomes mayor.
- 1996
- September 21: VladiROCKstok music festival held.
- Viktor Cherepkov becomes mayor again.
- 1998 - Youry Kopylov becomes mayor.
- 1999 - Spartak Primorye basketball club formed.
- 2000 - City becomes part of the Far Eastern Federal District.
21st century
- 2003 - Pacific Meridian film festival begins.
- 2004 - Vladimir Nikolayev elected mayor.[25]
- 2005 - Czechoslovak Legions Graveyard renovated.
- 2006 - Vladivostok Times news site begins publication.
- 2008
- Igor Poushkharyov becomes mayor.
- December: Protest.[26]
- 2009 - Protests.[27]
- 2010
- 2011 - Sakhalin–Khabarovsk–Vladivostok pipeline opens.
- 2012
- Zolotoy Rog Bridge and Russky Bridge built.
- September: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit held on Russky Island.[30]
- 2020 - Vladivostok dispute between China and Russia
See also
- History of Vladivostok
- Pacific Fleet (Russia)
- List of mayors of Vladivostok
- Other names of Vladivostok
- List of cities and towns in the Russian Far East
References
- "Zwölf Deutsche, die in Russland Karriere machten". Russland Heute (in German). 2011. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05.
- Britannica 1910.
- Findlay (1879). Description and list of the lighthouses of the world (19th ed.). London: Laurie.
- Hudgins 2004.
- "WorldCat". USA: Online Computer Library Center. Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- Ministry of Ways of Communication 1900.
- "Russianmuseums.info". Russian Cultural Heritage Network. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- "Vladivostok". Russia. Lonely Planet. Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- "Сколько "Царских ворот" на Дальнем Востоке? Память о путешествии Николая II" [How many "king's gates" in the Far East? The memory of the journey of Nicholas II]. Школа Жизни (Shkolazhizni.ru) (in Russian). St. Petersburg: Ройбер (Roiber). 2009.
- Baedeker 1914.
- "Maritime State University". Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- Lester Maynard (1909). "Russia in Asia". Commercial Relations of the United States with Foreign Countries.
- Nautical Nightmares | Part 1 | For Those In Peril
- Madrolle 1912.
- "Japanese Occupy Vladivostok Terminal; Foil Bolshevist Plan to Seize Supplies". New York Times. December 12, 1917. Missing or empty
|url=(help) - Paul E. Dunscomb (2006). "'A Great Disobedience against the People': Popular Press Criticism of Japan's Siberian Intervention, 1918-22". Journal of Japanese Studies. 32.
- Lewis H. Siegelbaum (2008), Cars for comrades: the life of the Soviet automobile, Ithaca, USA: Cornell University Press, ISBN 9780801446382, 0801446384
- Brunn 2008.
- "Population of capital cities and cities of 100,000 and more inhabitants". Demographic Yearbook 1965. New York: Statistical Office of the United Nations. 1966.
- "Vladivostok State University Economics and Service". Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Statistical Office (1987). "Population of capital cities and cities of 100,000 and more inhabitants". 1985 Demographic Yearbook. New York. pp. 247–289.
- "Sister Cities". USA: City of San Diego. Retrieved December 1, 2015.
- Christoffersen 1994.
- "Shaman and the Epic Theatre". New Theatre Quarterly. Cambridge University Press. 2004.
- "Vladivostok mayor stripped of power amid corruption investigation". New York Times. March 1, 2007.
- "Car duty protests challenge Russia's Putin". Reuters. December 16, 2008.
- "Protests against Putin sweep Russia as factories go broke". The Guardian. UK. June 6, 2009.
- "International Youth Tiger Summit opens in Vladivostok". Xinhuanet. Xinhua News Agency. November 19, 2010.
- "Population of capital cities and cities of 100,000 or more inhabitants". Demographic Yearbook 2011. United Nations Statistics Division. 2012.
- "APEC Russia 2012". Retrieved March 2, 2013.
This article incorporates information from the Russian Wikipedia and German Wikipedia.
Bibliography
- Published in 19th century
- Edmond Cotteau (1885), "De Vladivostok a Nagasaki", De Paris au Japon a travers la Siberie: voyage exécuté du 6 mai au 7 aout 1881 (in French) (2nd ed.), Paris: Librairie Hachette
- Isabella Lucy Bird (1898). "Nagasaki-Wladivostock". Korea and her neighbors: a narrative of travel, with an account of the recent vicissitudes and the present position of the country. London: John Murray.
- "Ussuri Railway: Vladivostok". Guide to the Great Siberian Railway. St. Petersburg: Ministry of Ways of Communication. 1900.
- Published in 20th century
- "(Vladivostok)", Asiatic Pilot: East coast of Siberia, Sakhalin Island and Korea, Washington, DC: United States Navy. Hydrographic Office., 1909
- "Vladivostok", Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.), New York, 1910, OCLC 14782424 – via Internet Archive
- Claudius Madrolle (1912), "Vladivostok", Northern China, Paris: Hachette & Company, OCLC 8741409
- "Vladivostok", Russia with Teheran, Port Arthur, and Peking, Leipzig: Karl Baedeker, 1914, OCLC 1328163
- "Siberia: Vladivostok". Pacific Ports Manual (7th ed.). Los Angeles, USA: Terminal Publishing Company. 1921.
- Gaye Christoffersen (1994–1995). "The Greater Vladivostok Project: Transnational Linkages in Regional Economic Planning". Pacific Affairs. 67.
- William Richardson (1995). "Vladivostok: City of three eras". Planning Perspectives. International Planning History Society. 10.
- Published in 21st century
- Sharon Hudgins (2004), "Vladivostok: Capital of Russia's Wild East", Other Side of Russia: A Slice of Life In Siberia and the Russian Far East, USA: Texas A&M University Press, ISBN 9781585444045
- Stanley D. Brunn; et al., eds. (2008). "Vladivostock". Cities Of The World: World Regional Urban Development (4th ed.). USA: Rowman & Littlefield.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vladivostok. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.