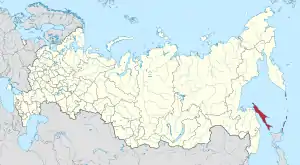
Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast (Russian: Сахали́нская о́бласть, tr. Sahalínskaya óblast', IPA: [səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ]) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian Far East. The oblast has an area of 87,100 square kilometers (33,600 sq mi). Its administrative center and largest city is Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast has a population of 497,973.[6] Besides people from other parts of the former Soviet Union and the Korean Peninsula, the oblast is home to Nivkhs and Ainu, with the latter having lost their language in Sakhalin recently. Sakhalin is rich in natural gas and oil, and is Russia's fourth wealthiest federal subject and wealthiest oblast.[10] It borders Khabarovsk Krai to the west and Kamchatka Krai to the north, along with Hokkaido, Japan to the south.
Sakhalin Oblast | |
|---|---|
| Сахалинская область | |
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 50°33′N 142°36′E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal district | Far Eastern[1] |
| Economic region | Far Eastern[2] |
| Established | October 20, 1932[3] |
| Administrative center | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk |
| Government | |
| • Body | Oblast Duma |
| • Governor | Valery Limarenko[4] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 87,100 km2 (33,600 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 37th |
| Population (2010 Census)[6] | |
| • Total | 497,973 |
| • Estimate (2018)[7] | 490,181 (−1.6%) |
| • Rank | 72nd |
| • Density | 5.7/km2 (15/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 79.7% |
| • Rural | 20.3% |
| Time zone | UTC+11 (MSK+8 |
| ISO 3166 code | RU-SAK |
| License plates | 65 |
| OKTMO ID | 64000000 |
| Official languages | Russian[9] |
| Website | http://www.adm.sakhalin.ru |
Demographics
Population: 497,973 (2010 Census);[6] 546,695 (2002 Census);[11] 709,629 (1989 Census).[12]
- Vital statistics for 2012
- Births: 6,316 (12.8 per 1,000)
- Deaths: 6,841 (13.8 per 1,000)[13]
Total fertility rate:[14]
| Year | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | 1.59 | 1.56 | 1.57 | 1.71 | 1.81 | 1.96 | 2.02 | 2.16(e) |
Ethnic groups:[6] 409,786 ethnic Russians are the largest group, followed by 24,993 Koreans (see Sakhalin Koreans), 12,136 Ukrainians and a host of less numerous ethnic groups, including 219 Japanese and Ainu (0.05%), who were native to the region and opposed the Soviet acquisition of the territory following World War II. The ethnic composition of the oblast in 2010 by percentages was as follows:
- Russians: 86.5%
- Koreans (Sakhalin Koreans): 5.3%
- Ukrainians: 2.6%
- Tatars: 1%
- Belarusians: 0.6%
- Japanese or Ainu: 0.05%
- 24,035 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[15]
Religion
According to a 2012 survey[16] 21.6% of the population of Sakhalin Oblast adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 4% are unaffiliated generic Christians, 2% adheres to other Orthodox churches or is an Orthodox believer without belonging to any church, 1% of the population adheres to the Slavic native faith (Rodnovery) or to local Siberian native faiths, 1% adheres to forms of Protestantism. In addition, 37% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 15% is atheist, and 18.4% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.[16]
History
The etymology of Sakhalin can be traced back to the Manchu word for black river (Amur river, Heilongjiang river). Sakhalin shares this etymology with the Chinese province of Heilongjiang (Chinese for black river).
The indigenous people of Sakhalin are the Nivkhs, Oroki, and Ainu minorities.
The first Europeans to explore the waters around Sakhalin Island were Ivan Moskvitin and Martin Gerritz de Vries in the mid-1600s, Jean-François de La Pérouse in 1787 and Adam Johann von Krusenstern in 1805. Early maps of Sakhalin reflect the uncertainty of the age as to whether or not the land mass was attached to the Asian continent. The fact that it is not connected was conclusively established by Mamiya Rinzō, who explored and mapped Sakhalin in 1809 and definitively recorded by Russian navigator Gennady Nevelskoy in 1849.
Japanese settlement on Sakhalin dates to at least the Edo period. Ōtomari was supposedly established in 1679, and cartographers of the Matsumae domain mapped the island, and named it “Kita-Ezo”. During the Ming and Qing dynasties China considered the island part of its empire, and included the Sakhalin peoples in its "system for subjugated peoples". At no time though was any attempt ever made to establish an Imperial military presence on the island. Japan, concerned about Russian expansion in northeast Asia, unilaterally proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island in 1845. Russian settlers ignored this claim (and the similar claim of China) however, and beginning in the 1850s, established coal mines, administration facilities, schools, prisons and churches on the island.

In 1855, Russia and Japan signed the Treaty of Shimoda, which declared that both nationals could inhabit the island: Russians in the north, and Japanese in the south, without a clear boundary between. Russia also agreed to dismantle its military base at Ōtomari. Following the Second Opium War, Russia forced the Qing to sign the Treaty of Aigun and Convention of Peking, under which China lost all territories north of Heilongjiang (Amur) and east of Ussuri, including Sakhalin, to Russia. A Czarist penal colony was established in 1857, but the southern part of the island was held by the Japanese until the 1875 Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875), when they ceded it to Russia in exchange for the Kuril islands. After the Russo-Japanese War, Russia and Japan signed the Treaty of Portsmouth of 1905, which resulted in the southern part of the island below 50° N passing to Japan; the Russians retained the other three-fifths of the area. South Sakhalin was administrated by Japan as Karafuto-chō (樺太庁), with the capital Toyohara, now known as Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk.

After the Russian Revolution and subsequent civil war northern Sakhalin ultimately became governed by the Russian SFSR as a part of Far Eastern Oblast (1922-1926), Far Eastern Krai (1926-1938) and Khabarovsk Krai (included Russian-administered territories of Sakhalin in 1938-1947). Sakhalin Oblast was established on 20 October 1932 as a part of Far Eastern Krai, and became part of Khabarovsk Krai upon the latter foundation in 1938.
In August 1945, the Soviet Union took over the control of entire Sakhalin and Kuril Islands. The Soviet attack on South Sakhalin started on August 11, 1945, about a month before the Surrender of Japan in World War II. The 56th Rifle Corps consisting of the 79th Rifle Division, the 2nd Rifle Brigade, the 5th Rifle Brigade and the 214th Tank Brigade attacked the Japanese 88th Division. Although the Red Army outnumbered the Japanese by three times, they could not advance due to strong Japanese resistance. It was not until the 113th Rifle Brigade and the 365th Independent Naval Infantry Rifle Battalion from Sovietskaya Gavan (Советская Гавань) landed on Tōrō (塔路), a seashore village of western Sakhalin on August 16 that the Soviets broke the Japanese defense line. Japanese resistance grew weaker after this landing. Actual fighting continued until August 21. However, this was relatively limited in scope. From August 22 to August 23, most of the remaining Japanese units announced truce. The Soviets completed the conquest of Sakhalin on August 25, 1945 by occupying the capital of Sakhalin, then known as Toyohara. Japanese sources claim that 20,000 civilians were killed during the invasion.


Post-war
Soviet-conquered areas of South Sakhalin and Kuril Islands were declared a South Sakhalin Oblast by the Soviet authorities in a decree issued on 2 February 1946.[18] Almost a year later, on January 2, 1947 the South Sakhalin Oblast was disbanded and included into Sakhalin Oblast, forming present-day boundary of the latter. On the same day Sakhalin Oblast was excluded from Khabarovsk Krai.[19] The Japanese who had been living there before mostly repatriated to Japan, but at least one-third of Koreans were refused repatriation; stuck on the island, they and their descendants became known as the Sakhalin Koreans.
The status of the southern Kuril Islands remains disputed. The issue remains a major strain on Japanese-Russian relations. Even now, no official peace treaty has been signed between the two nations.[20]
Japan renounced its claims of sovereignty over southern Sakhalin in the Treaty of San Francisco (1952), having already abolished Karafuto Prefecture as a legal entity on June 1, 1949. However, that treaty did not explicitly approve Russian sovereignty over southern Sakhalin. From Japan's official position, Sakhalin's attribution has not yet been determined, and it is marked as No Man's Land on Japanese maps. Nevertheless, Japan currently has a Consulate-General in Sakhalin's capital city.
On September 1, 1983, the Soviets downed Korean Air Lines Flight 007, carrying 269 occupants, including U.S. Congressman Larry McDonald, west of Sakhalin Island near the smaller Moneron Island.
In 1995 the 7.0 Mw Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt. On 24 April 1996 Sakhalin Oblast, alongside Rostov Oblast, signed a power-sharing agreement with the federal government, granting it autonomy.[21] This agreement would be abolished on 4 March 2002.[22]
Ainu
As of the 2002 census, 333 residents of the oblast still identified themselves as ethnic Japanese. Data on Ainu population is not available; "Ainu" may have been either included in the "Other" category or the Ainus may have identified themselves as "Russians" during the census. Many locals are ethnically Ainu or have Ainu ancestry but identify as Russian and only speak the Russian language today, often not knowing about their Ainu ancestry.
Most of the 888 Japanese people living in Russia (2010 Census) are also of mixed Japanese-Ainu ancestry, although they do not acknowledge it (full Japanese ancestry gives them the right of visa-free entry to Japan).[23]
Post-war population
According to the first post World War II Soviet Census in 1959, the population of the oblast numbered 649,405. That figure dropped slightly to 615,652 in 1970 before rising to 661,778 in 1979 and peaking at 710,242 in 1989. Throughout this time period, the Russian population increased slightly in percentage from 77.7% in 1959 to 81.6% in 1989. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the population of the oblast has declined sharply. Compared with the Soviet 1989 Census, the population of the Oblast according to the Russian 2002 Census had declined by 163,547 or 23.0%, to 546,695. The 2010 population of 497,973 recorded in 2010 is the lowest on record since the oblast was created, although the decline was less (8.9%) than during the 1990s.
Law and government
The governor Alexander Khoroshavin was appointed on August 9, 2007.[25] He was succeeded by Oleg Kozhemyako on March 25, 2015.
Administrative divisions
Tourism
Due to restrictions, the entire Sakhalin Oblast and its internal and territorial waters except for Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk are considered to be a border zone, which means that the freedom of movement for foreigners is dramatically restricted and any movement outside of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk requires registration to the Federal Security Service (FSB) and the Border Guard. Scuba diving and recreation on the seacoast is permitted only in places defined by the Border Guard.[26]
References
- Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", No. 20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- Постановление ВЦИК от 20.10.1932 "О реорганизации системы административно-территориального деления Дальневосточного края" Archived September 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- Щербина стала исполняющим обязанности врио главы Сахалинской области
- Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (May 21, 2004). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved November 1, 2011.
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- https://mrd.gks.ru/folder/27963
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек" [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров" [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- "Естественное движение населения в разрезе субъектов Российской Федерации". www.gks.ru. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Каталог публикаций::Федеральная служба государственной статистики". www.gks.ru. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Перепись-2010: русских становится больше". Perepis-2010.ru. December 19, 2011. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- "Arena: Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia". Sreda, 2012.
- 2012 Arena Atlas Religion Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017. Archived.
- Указ Президиума ВС СССР от 02.02.1946 "Об образовании Южно-Сахалинской области в составе Хабаровского края РСФСР" (in Russian)
- Указ Президиума Верховного Совета СССР от 2 января 1947 года "О ликвидации Южно-Сахалинской области и включении ее территории в состав Сахалинской области" (in Russian)
- Hindell, Juliet (April 18, 1998). "Russia and Japan's island row". BBC News. Retrieved January 18, 2009.
- "Newsline - May 30, 1996 Rostov, Sakhalin Oblasts Sign Power-Sharing Agreements". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. May 30, 1996. Retrieved May 2, 2019.
- Chuman, Mizuki. "The Rise and Fall of Power-Sharing Treaties Between Center and Regions in Post-Soviet Russia" (PDF). Demokratizatsiya: 146.
- "В России снова появились айны - самый загадочный народ Дальнего востока". 5-tv.ru. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- "ExxonMobil Announces Drilling of World-Record Well on Sakhalin Island, Eastern Russia". OilVoice. April 25, 2007. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- Legislators in Sakhalin appoint Khoroshavin as governor, RIA, 09/ 08/ 2007
- "sakhalinindependent.com". sakhalinindependent.com. Retrieved March 18, 2018.
- "Hokkaido-AB.pdf" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 4, 2010. Retrieved May 30, 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sakhalin Oblast. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Sakhalin Oblast. |
- (in Russian) Official website of Sakhalin Oblast
- (in English) Official website of Sakhalin Oblast
- Sakhalin (oblast) at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- Steam and the Railways of Sakhalin