Tourism in Myanmar
Tourism in Myanmar (also known as Burma) is a developing sector. Although Myanmar possesses great tourist potential and attractions in many respects, much of the industry remains to be developed. The number of visitors to Burma is small compared to her neighbours, outpaced by even Laos. This is primarily due to its political situation. However, after the junta transferred power to the civilian government, the tourism sector saw an increase in tourism arrivals, and in 2012, tourist arrivals surpassed the one million mark for the first time. In 2013, the Tourism Master Plan was created, targeting 7.5 million arrivals by 2020.[1]
.jpg.webp)
Tourism has been developed mainly by Myanmar's government, which has encouraged tourism since 1992. Private enterprises also exist, catering to a wide range of tourists.
In 2010, 791,505 foreign tourists visited Myanmar, with 295,174 foreign tourists entering the country via Yangon International Airport.[2] By 2012, more than 1 million foreign tourists visited Myanmar. In 2013, the number of foreign arrivals reached more than 2.04 million, counting both air and overland arrivals.[1]
Tourism has been promoted by advocacy groups as a method of providing economic benefit to Burmese civilians, and to avoid isolating the country from the rest of the world. Voices for Burma, a pro-democracy advocate group, states, "We believe that small-scale, responsible tourism can create more benefits than harm. So long as tourists are fully aware of the situation and take steps to maximise their positive impact and minimise the negatives, we feel their visit can be beneficial overall. Responsible tourists can help Burma primarily by bringing money to local communities and small businesses, and by raising awareness of the situation worldwide."[3]
A former Burmese tourism minister estimated that 12% of the government revenues are derived from tourism, with the tourism industry contributing $182 million USD (2007) to the government's annual budget.[4]
Statistics
In the 2010-2011 fiscal year, tourists comprised 73.84% (313,127 arrivals) of overseas visitors, primarily entering the country by air, representing 69.26% of arrivals, followed by land and sea, which represented 29.97% and 0.77% of arrivals respectively.[5] An additional 110,914 visitors arrived through other visa types and represented an additional 26.16% of the total.[5] In 2012, revenues from tourism jumped to over $534 million in 2012, up from $315 million in 2011.[6]
General trends
Tourist arrivals to Yangon Entry Point, Mandalay & Bagan Gateways, Nay Pyi Taw Gateway and Border Tourism.
| Year | Tourist arrivals | % Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 4,364,101 | +23%[7] |
| 2018 | 3,551,592 | +3.15%[8] |
| 2017 | 3,443,133 | +18.00%[9] |
| 2016 | 2,907,207 | -37.89%[10] |
| 2015 | 4,681,020 | +51.91% |
| 2014 | 3,081,412 | +50.73% |
| 2013 | 2,044,307 | +93.04% |
| 2012 | 1,058,995 | +29.72% |
| 2011 | 816,369 | +3.14% |
| 2010 | 791,505 | +3.79% |
| 2009 | 762,547 | +4.28% |
| 2008 | 731,230 | +2.06% |
Tourists by nationality
The governmental statistics body, the Central Statistical Organization, reported more than 3,000,000 travellers flocked to Myanmar in 2014, compared with approximately 816,000 visitors in 2011. Among these, 1,022,081 tourist arrivals (excluding visitors under special entry visas such as social or business visas) were via Yangon International Airport.[11][12]
Most visitors arriving to Myanmar on short term basis were from the following countries of nationality:[13]
| Rank | Country | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 333,085 | 212,642 | 183,886 | 147,977 | 125,609 | 90,550 | 70,805 | 62,018 | |
| 2 | 291,231 | 273,889 | 243,443 | 204,539 | 198,229 | 139,770 | 94,342 | 61,696 | |
| 3 | 104,376 | 101,484 | 100,084 | 90,312 | 83,434 | 68,671 | 47,690 | 21,321 | |
| 4 | 72,852 | 65,829 | 64,397 | 63,715 | 58,472 | 54,934 | 34,805 | 22,524 | |
| 5 | 65,057 | 73,085 | 76,502 | 69,015 | 62,631 | 53,653 | 37,589 | 21,680 | |
| 6 | 58,657 | 61,859 | 50,198 | 45,125 | 47,692 | 39,140 | 26,296 | 15,391 | |
| 7 | 53,329 | 58,919 | 48,869 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 8 | 47,632 | 47,010 | 43,931 | 40,852 | 46,534 | 39,758 | 30,499 | 23,287 | |
| 9 | 43,281 | 41,623 | 38,537 | 34,638 | 32,306 | 21,042 | 16,868 | 12,318 | |
| 10 | 43,218 | 58,369 | 52,304 | 47,235 | 41,453 | 35,462 | 30,064 | 19,414 | |
| 11 | 36,609 | 47,717 | 51,051 | 45,120 | 40,921 | 33,203 | 24,296 | 11,056 | |
| 12 | 28,838 | 39,952 | 39,044 | 35,727 | 32,265 | 27,712 | 23,063 | 14,006 | |
| 13 | 27,962 | 32,628 | 34,010 | 30,820 | 29,175 | 11,728 | 18,261 | 10,415 | |
| 14 | 16,855 | 18,242 | 17,969 | 14,821 | 12,613 | 11,728 | 10,830 | 9,710 | |
| 15 | 16,748 | 18,143 | 16,421 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 16 | 11,315 | 13,558 | 12,765 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 17 | 11,065 | 14,068 | 15,024 | 14,051 | 12,268 | 8,975 | 6,485 | 3,685 | |
| 18 | 10,019 | 13,558 | 13,694 | 13,897 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 19 | 9,428 | 13,950 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 20 | 7,183 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Tourist attractions
The most popular available tourist destinations in Myanmar include big cities such as Yangon and Mandalay; religious sites in Mon State, Pindaya, Bago and Hpa-An; nature trails in Inle Lake, Kalaw, Kengtung, Putao, Pyin Oo Lwin; ancient cities such as Bagan and Mrauk-U; as well as beaches in Nabule Ngapali, Maungmagan Ngwe-Saung, Mergui.[14]
Yangon
Mandalay
Mon State
- Kyaiktiyo Pagoda
- Mudon (the world's largest reclining Buddha)
- Mawlamyine
- Thanbyuzayat (WWII Death Railway)
Rakhine State
- Mrauk U
- Ngapali Beach
- Mahamuni Buddha Image Casted at the Buddha's lifetime in Kyauk Taw
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Myanmar
| Site | Image | Location | Criteria | Area ha (acre) |
Year | Description | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyu city-states | .jpg.webp)   |
Myanmar| |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
5,809 ha (proper); 6,790 ha (buffer zone) | 2014 | The site includes three of the six main Pyu city-states, namely Halin, Beikthano and Sri Ksetra. | [21] |
| Bagan |  |
Mandalay Region | Cultural | 2018 | The site includes all of the monuments throughout the ancient capital of the Pagan kingdom. | [22] | |
Tentative list to be added
| Site | Image | Location | Proposed criteria | Year Listed as Tentative Site | Description | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wooden Monasteries of Konbaung Period: Ohn Don, Sala, Pakhangyi, Pakhannge, Legaing, Sagu, Shwe-Kyaung (Mandalay) |  |
Multiple locations | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes seven wooden monasteries, nameyly, Ohn Don, Sala, Pakhangyi, Pakhannge, Legaing, Sagu, and Shwe-Kyaung (Mandalay). | [23] |
| Badah-lin and associated caves |  |
Shan State | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes various caves used as workshop and rock painting sites in the Paleolithic to Neolithic periods. | [24] |
| Ancient cities of Upper Myanmar: Innwa, Amarapura, Sagaing, Mingun, Mandalay |      |
Multiple locations | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes the historic cities of Innwa, Amarapura, Sagaing, Mingun, Mandalay | [25] |
| Myauk-U Archaeological Area and Monuments |  |
Rakhine State | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes all monuments built by the Arakanese kingdom's capital between the 15th to 16th centuries. | [26] |
| Inle Lake |  |
Shan State | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes the mountain lake and its preserved cultural landscape. | [27] |
| Mon cities: Bago, Hanthawaddy | .JPG.webp) |
Bago Region | Cultural | 1996 | The site includes all monuments in Bago, formerly called Hanthawaddy. | [28] |
| Ayeyawady River Corridor |  |
Multiple locations | Natural | 2014 | The site includes three main segments, namely Mingun to Kyauk Maung segment, Moda Section,Takaung to Shwegu segment, and Shwegu to Bhamo segment. | [29] |
| Hkakabo Razi Landscape | Kachin State | Natural | 2014 | The site includes Hkakabo Razi National Park and Hponkan Razi Wildlife Sanctuary, along with a proposed Southern Extension of Hkakabo Razi National Park. | [30] | |
| Indawgyi Lake Wildlife Sanctuary |  |
Kachin State | Natural | 2014 | The site includes the entire Indawgyi lake. | [31] |
| Natma Taung National Park |  |
Chin State | Natural | 2014 | The site includes Nat Ma Taung, the highest point in Chin State. | [32] |
| Myeik Archipelago | 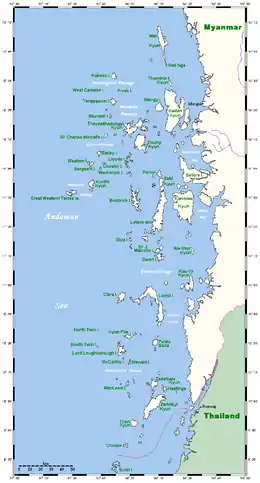 |
Tanintharyi Region | Natural | 2014 | The site includes more than 800 islands of primarily limestone and granite. The archipelago is home to the Moken people. | [33] |
| Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary |  |
Kachin State | Natural | 2014 | The site is highly significant in the conservation of Indochinese tigers. | [34] |
| Taninthayi Forest Corridor |  |
Taninthayi Region | Natural | 2014 | The site is an important mixed deciduous forest with bamboo clumps as well as grassland and is a thriving site for the endangered Gurney's pitta. | [35] |
Historical Politics
In May 2011, Aung San Suu Kyi and her party National League for Democracy expressed the opinion that responsible tourism to Burma should be encouraged. Other pro-democracy activists, such as Ma Thanegi, advocated small scale tourism, and careful spending. Tourists are welcome to Burma provided they are "keen to promote the welfare of the common people and the conservation of the environment and to acquire an insight into the cultural, political and social life of the country while enjoying a happy and fulfilling holiday in Burma."[36][37] In their official statement they request not only the development of the people's livelihood but also the promotion of "self respect and self-reliance in the people."[38]
References
- "Amid Burma Tourism Boom, Calls for Govt to Aid Development". Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- Feng, Yingqiu (1 June 2011). "Myanmar continues efforts in developing tourism". Xinhua. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- Voices For Burma's tourism policy http://www.voicesforburma.org/
- "Report on Tourism in Burma" (PDF). Info Birmanie. March 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2011. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Table 29.OVERSEAS VISITORS". Central Statistical Organization. Ministry of National Planning and Economic Development. Archived from the original on 7 October 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- "Tourist income surges 70% in Myanmar". Investvine.com. 25 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- "Tourism of Myanmar".
- "Tourism of Myanmar". telegraph. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- "Tourism of Myanmar" (PDF). telegraph. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- http://tourism.gov.mm/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Myanmar-Tourism-Statistics-2016-1.pdf
- "Myanmar Tourism Statistics 2014" (PDF). Central Statistical Organization. Ministry of National Planning and Economic Development. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 January 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Myanmar Tourism Statistics". Ministry of Hotels and Tourism.
- "Myanmar Travel Agency". birma.com. p. Tourist Destinations. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- Planet, Lonely. "Kalaw travel | Myanmar (Burma)". Lonely Planet. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- "THE 5 BEST Things to Do in Kalaw - 2019 (with Photos) - TripAdvisor". www.tripadvisor.com. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- "Kalaw information". Go-Myanmar.com. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- "Shan State – Ministry of Hotels & Tourism Myanmar". Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- Dunham, Jillian (16 December 2015). "A Three-Day Trek in the Highlands of Myanmar". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- "TripAdvisor: Read Reviews, Compare Prices & Book". TripAdvisor. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- "Chitwan National Park". UNESCO. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1588
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/821/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/822/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/823/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/824/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/825/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/826/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5870/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5871/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5872/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5873/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5874/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5875/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5876/
- Michael Kerr (12 April 2012). "Burma: how can holidaymakers visit ethically?". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- Charlie Norton (14 August 2009). "Burma opposition leader Suu Kyi: 'Tourism might help'". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- "NLD statement No 10/05/11 released on 20th May 2011 regarding tourism in Burma". National League for Democracy. 20 May 2011. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Myanmar. |