Demographics of Myanmar
The following is an overview of the demographics of Myanmar (also known as Burma), including statistics such as population, ethnicity, language, education level and religious affiliation.
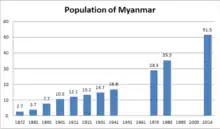
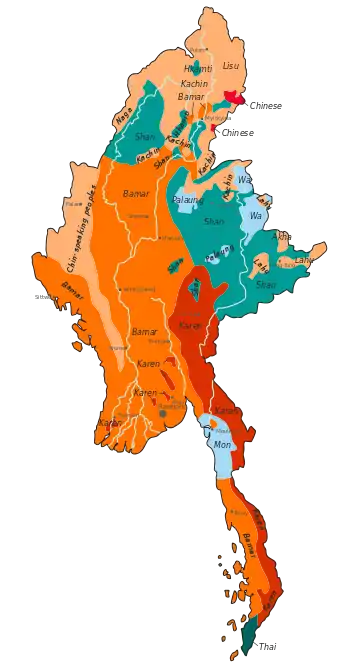
Population
1983 census
At the time of the 1983 census in Burma, as of 31 March 1983, the population was 35,442,972. As of July 2012, this was estimated by the CIA World Factbook to have increased to 60,584,650. Other estimates put place the total population at around 60 million. China's People's Daily reported that Burma had a census in 2007, and at the end of 2009 has 59.2 million people, and growing at 2% annually.[1] with exception for Cyclone Nargis in 2008. Most of these estimates have indeed overlooked the demographic changes that were at work since the 1970s in the country.[2][3][4]
Britain-based human rights agencies place the population as high as 70 million. Estimates for the country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS. This can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected.
No trustworthy census has occurred since the 1930s. In the 1940s, the detailed census results were destroyed during the Japanese invasion of 1942. Census results after that time have been flawed by civil wars and a series of military governments. The census in 1983 occurred at a time when parts of the country were controlled by insurgent groups and inaccessible to the government.
2014 census
The Provisional results of the 2014 census show that the total population of Myanmar is 51,419,420—a population well below the official estimates of more than 60 million.[3][4] This total population includes 50,213,067 persons counted during the census and an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern Rakhine State, Kachin State and Kayin State who were not counted. More females (51.8%) were counted than males (48.2%). People who were out of the country at the time of the census are not included in these figures.
The provisional census results indicated that there were 10,889,348 households in Myanmar. On average, 4.4 people lived in each household in the country. The average household size was highest in Kachin State and Chin State at 5.1. The lowest household sizes were observed in Ayeyawady Region, Bago Region, Magway Region and Naypyidaw Union Territory, each at 4.1.[5]
Vital statistics
Burma has a low fertility rate (2.23 in 2011), slightly above replacement level, especially as compared to other Southeast Asian countries of similar economic standing, like Cambodia (3.18) and Laos (4.41), representing a significant decline from 4.7 in 1983 to 2.4 in 2001, despite the absence of any national population policy.[2][4][6][7]
The fertility rate is much pronouncedly lower in urban areas. This is attributed to extreme delays in marriage (almost unparalleled in the region, with the exception of developed countries), the prevalence of illegal abortions, and the high proportion of single, unmarried women of reproductive age (with 25.9% of women aged 30–34 and 33.1% of men and women aged 25–34 single).[7][8]
These patterns stem from several cultural and economic dynamics. The first is economic hardship, which results in the delay of marriage and family-building (the average age of marriage in Burma is 27.5 for men, 26.4 for women).[7][8] The second is the social acceptability of celibacy among the Burmese, who are predominantly Buddhist and value celibacy as a means of spiritual development.[6][9]
Births and deaths [10]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR1 | CDR1 | NC1 | TFR1 | IMR1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 856,000 | 515,000 | 341,000 | 47.5 | 28.6 | 18.9 | 6.00 | 212.8 |
| 1955–1960 | 885,000 | 466,000 | 419,000 | 44.4 | 23.4 | 21.0 | 6.00 | 175.2 |
| 1960–1965 | 928,000 | 454,000 | 475,000 | 41.9 | 20.5 | 21.4 | 6.10 | 155.7 |
| 1965–1970 | 993,000 | 426,000 | 567,000 | 40.1 | 17.2 | 22.9 | 6.10 | 131.1 |
| 1970–1975 | 1,092,000 | 418,000 | 674,000 | 39.2 | 15.0 | 24.2 | 5.90 | 112.7 |
| 1975–1980 | 1,068,000 | 402,000 | 666,000 | 34.2 | 12.9 | 21.4 | 4.90 | 97.5 |
| 1980–1985 | 1,085,000 | 421,000 | 664,000 | 31.5 | 12.2 | 19.2 | 4.30 | 93.0 |
| 1985–1990 | 1,100,000 | 445,000 | 656,000 | 29.2 | 11.8 | 17.4 | 3.80 | 89.7 |
| 1990–1995 | 1,017,000 | 418,000 | 598,000 | 25.0 | 10.3 | 14.7 | 3.10 | 76.1 |
| 1995–2000 | 969,000 | 405,000 | 564,000 | 22.3 | 9.3 | 13.0 | 2.95 | 65.4 |
| 2000–2005 | 24.0 | 9.7 | 14.3 | 2.80 | 59.8 | |||
| 2005–2010 | 21.2 | 9.2 | 12.0 | 2.50 | 55.0 | |||
| 2010–2015 | 18.6 | 8.5 | 10.1 | 2.25 | ||||
| 2015–2020 | 17.7 | 8.2 | 9.5 | 2.17 | ||||
| 2020–2025 | 16.8 | 8.4 | 8.4 | 2.07 | ||||
| 2025–2030 | 16.0 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 1.99 | ||||
| 2030–2035 | 15.1 | 9.4 | 5.7 | 1.92 | ||||
| 2035–2040 | 14.1 | 10.0 | 4.1 | 1.86 | ||||
| 1 CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||
Births and deaths [11]
| Year | Population | Live births | Deaths | Natural increase | Crude birth rate | Crude death rate | Rate of natural increase | TFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 948,106 | 325,343 | 622,763 | 2.040 | ||||
| 2010 | 965,937 | 346,205 | 619,732 | 2.030 | ||||
| 2011 | 1,007,039 | 342,420 | 664,619 | 2.010 | ||||
| 2012 | 856,279 | 250,874 | 605,405 | 2.010 | ||||
| 2013 | 835,595 | 257,216 | 578,379 | |||||
| 2014 | 51,419,000 | 836,961 | 278,533 | 558,428 | 2.5 | |||
| 2015 | 739,152 | 225,526 | 513,626 | 2.5 | ||||
| 2016 | 765,844 | 213,187 | 552,657 | 2.5 | ||||
| 2017 | 787,172 | 231,210 | 555,962 | 11.0 | 2.4 |
Fertility and births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[12]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015–2016 | 18 | 2.3 (2.0) | 16 | 1.9 (1.7) | 18.8 | 2.4 (2.1) |
Crude Birth Rate (CBR), Total Fertility Rate (TFR), and Total Marital Fertility Rate (TMFR) by region (2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census):[13]
| Region | Crude Birth Rate (CBR) | Total Fertility Rate (TFR) | Total Marital Fertility Rate (TMFR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (Myanmar) | 18.8 | 2.3 | 4.0 |
| Urban | 15.8 | 1.8 | 3.6 |
| Rural | 20.1 | 2.5 | 4.2 |
| Kachin | 22.0 | 2.8 | 5.1 |
| Kayah | 26.1 | 3.3 | 5.7 |
| Kayin | 23.8 | 3.4 | 5.4 |
| Chin | 29.9 | 4.4 | 6.9 |
| Sagaing | 19.4 | 2.3 | 4.4 |
| Tanintharyi | 21.9 | 3.0 | 5.0 |
| Bago | 17.6 | 2.2 | 3.6 |
| Magway | 17.6 | 2.1 | 3.8 |
| Mandalay | 16.9 | 1.9 | 3.7 |
| Mon | 18.1 | 2.4 | 4.2 |
| Rakhine | 18.0 | 2.2 | 3.5 |
| Yangon | 15.5 | 1.7 | 3.3 |
| Shan | 21.2 | 2.7 | 4.3 |
| Ayeyawady | 20.2 | 2.6 | 4.1 |
| Naypyitaw | 18.7 | 2.1 | 3.4 |
Structure of the population [14][15]
Structure of the population (01.10.2012) (Estimates) :
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 30 139 447 | 30 836 546 | 60 975 993 | 100 |
| 0-4 | 2 892 346 | 2 843 804 | 5 736 150 | 9.41 |
| 5-9 | 3 019 538 | 2 933 751 | 5 953 054 | 9.76 |
| 10-14 | 3 061 725 | 2 939 751 | 6 001 476 | 9.84 |
| 15-19 | 2 939 176 | 2 830 830 | 5 770 006 | 9.46 |
| 20-24 | 2 804 028 | 2 729 466 | 5 533 494 | 9.07 |
| 25-29 | 2 608 652 | 2 578 175 | 5 186 827 | 8.51 |
| 30-34 | 2 378 395 | 2 414 221 | 4 792 616 | 7.86 |
| 35-39 | 2 134 820 | 2 212 315 | 4 347 135 | 7.13 |
| 40-44 | 1 868 709 | 1 984 907 | 3 853 616 | 6.32 |
| 45-49 | 1 604 910 | 1 737 570 | 3 342 480 | 5.48 |
| 50-54 | 1 325 584 | 1 459 978 | 2 785 562 | 4.57 |
| 55-59 | 1 081 479 | 1 213 529 | 2 295 008 | 3.76 |
| 60-64 | 838 871 | 962 728 | 1 801 599 | 2.95 |
| 65-69 | 647 286 | 766 066 | 1 413 352 | 2.32 |
| 70-74 | 477 948 | 593 666 | 1 071 614 | 1.76 |
| 75-79 | 335 405 | 449 974 | 785 379 | 1.29 |
| 80+ | 120 575 | 186 050 | 306 625 | 0.50 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-14 | 8 973 609 | 8 717 306 | 17 690 915 | 29,01 |
| 15-64 | 19 584 624 | 20 123 484 | 39 708 108 | 65,12 |
| 65+ | 1 581 214 | 1 995 756 | 3 576 970 | 5,87 |
Structure of the population (2014) (Census) Population - 51 486 253, enumerated - 50 279 900 :
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 24 228 714 | 26 051 186 | 50 279 900 | 100 |
| 0-4 | 2 262 783 | 2 209 347 | 4 472 130 | 8.89 |
| 5-9 | 2 438 372 | 2 380 705 | 4 819 077 | 9.58 |
| 10-14 | 2 595 759 | 2 512 613 | 5 108 362 | 10.16 |
| 15-19 | 2 290 998 | 2 334 991 | 4 625 989 | 9.20 |
| 20-24 | 2 091 525 | 2 239 544 | 4 331 069 | 8.61 |
| 25-29 | 1 995 465 | 2 150 669 | 4 146 134 | 8.25 |
| 30-34 | 1 884 549 | 2 014 312 | 3 898 861 | 7.75 |
| 35-39 | 1 705 630 | 1 857 850 | 3 563 480 | 7.09 |
| 40-44 | 1 548 942 | 1 734 131 | 3 283 073 | 6.53 |
| 45-49 | 1 375 041 | 1 571 107 | 2 946 148 | 5.86 |
| 50-54 | 1 182 341 | 1 376 891 | 2 559 232 | 5.09 |
| 55-59 | 935 979 | 1 115 958 | 2 051 937 | 4.08 |
| 60-64 | 712 040 | 864 805 | 1 576 845 | 3.14 |
| 65-69 | 466 618 | 597 875 | 1 064 493 | 2.12 |
| 70-74 | 301 679 | 411 491 | 713 170 | 1.42 |
| 75-79 | 228 315 | 324 983 | 553 298 | 1.10 |
| 80-84 | 130 875 | 204 701 | 335 576 | 0.67 |
| 85-89 | 56 979 | 101 090 | 158 069 | 0.31 |
| 90+ | 24 834 | 48 123 | 72 957 | 0.15 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-14 | 7 296 904 | 7 102 665 | 14 399 569 | 28.64 |
| 15-64 | 15 722 510 | 17 260 258 | 32 982 768 | 65.60 |
| 65+ | 1 209 300 | 1 688 263 | 2 897 563 | 5.76 |
Life expectancy
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 36.1 | 1985–1990 | 57.8 |
| 1955–1960 | 41.3 | 1990–1995 | 59.6 |
| 1960–1965 | 44.2 | 1995–2000 | 61.3 |
| 1965–1970 | 49.6 | 2000–2005 | 62.9 |
| 1970–1975 | 51.9 | 2005–2010 | 64.3 |
| 1975–1980 | 54.0 | 2010–2015 | 66.0 |
| 1980–1985 | 56.0 |
Source: UN World Population Prospects[16]
Ethnic groups
Government classifications
The Burmese government identifies eight major national ethnic races (which comprise 135 "distinct" ethnic groups), which include the Bamar (68%), Shan (9%), Kayin (7%), Rakhine (4%), Mon (2%), Kayah, and Kachin. However, the government classification system is flawed, because it groups ethnic groups by geography, rather than by linguistic or genetic similarity (e.g. the Kokang are under the Shan ethnicity, although they are a Han-Chinese sub-group).
Unrecognised ethnic groups include Burmese Han-Chinese and Burmese Indians, who form 3% and 2% of the population respectively. The remaining 5% of the population belong to small ethnic groups such as the remnants of the Anglo-Burmese and Anglo-Indian communities, as well as the Lisu, Rawang, Naga, Padaung, Moken, and many minorities across Shan State.
Language
The official language and primary medium of instruction of Burma is Burmese (65%). Multiple languages are spoken in Burma, and include Shan (6.4%), Karen (5.2%), Kachin (1.8%), Chin (1.6%), Mon (1.5%), and Rakhine (1.5%). English is also spoken, particularly by the educated urban elite, and is the secondary language learnt in government schools. Recent years, the education of Chinese language has been recovered, after long-term limitation from the government of Myanmar.
Religious affiliation
| Religious group |
Population % 1973[17] |
Population % 1983[17] |
Population % 2014[17][note 1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buddhism | 88.8% | 89.4% | 87.9% |
| Christianity | 4.6% | 4.9% | 6.2% |
| Islam | 3.9% | 3.9% | 4.3% |
| Hinduism | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.5% |
| Tribal religions | 2.2% | 1.2% | 0.8% |
| Other religions | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Not religious | n/a | n/a | 0.1% |
| Faith | % (2008 est.) |
|---|---|
| Total Buddhism | 89% |
| Theravada Buddhism | 89% |
| Mahayana Buddhism | <1% |
| Total Christianity | 4% |
| Baptist | 3% |
| Roman Catholicism | 1% |
| Total Islam | 4% |
| Sunni Islam | 2.65% |
| Shia Islam | 1.35% |
| Total other religions | <1% |
| Animism | 1% |
| Other (inc. Hinduism) | 2% |
Buddhist Sangha
Below are statistics regarding the Buddhist monastic community in Myanmar, compiled by the State Sangha Maha Nayaka Committee.[18]
| Division | Samanera members | % | Bhikkhu members | % | Sangha members | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kachin State | 3,121 | 1.2% | 4,845 | 1.7% | 7,966 | 1.5% |
| Kayah State | 1,300 | 0.5% | 760 | 0.3% | 2,060 | 0.4% |
| Kayin State | 5,967 | 2.4% | 8,113 | 2.9% | 14,080 | 2.6% |
| Chin State | 157 | 0.1% | 300 | 0.1% | 457 | 0.1% |
| Sagaing Region | 25,050 | 9.9% | 29,991 | 10.6% | 55,041 | 10.3% |
| Tanintharyi Region | 3,009 | 1.2% | 6,086 | 2.2% | 9,095 | 1.7% |
| Naypyidaw Union Territory | 5,713 | 2.3% | 5,243 | 1.9% | 10,956 | 2% |
| Bago Region | 18,032 | 7.1% | 32,166 | 11.4% | 50,198 | 9.4% |
| Magway Region | 13,654 | 5.4% | 17,695 | 6.3% | 31,349 | 5.9% |
| Mandalay Region | 47,217 | 18.7% | 52,747 | 18.7% | 99,964 | 18.7% |
| Mon State | 13,466 | 5.3% | 19,303 | 6.8% | 32,769 | 6.1% |
| Rakhine State | 6,395 | 2.5% | 6,548 | 2.3% | 12,943 | 2.4% |
| Yangon Region | 36,654 | 14.5% | 51,788 | 18.3% | 88,442 | 16.5% |
| Shan State | 57,850 | 22.9% | 19,663 | 7% | 77,513 | 14.5% |
| Ayeyawady Region | 15,377 | 6.1% | 27,117 | 9.6% | 42,494 | 7.9% |
| Subtotal | 252,962 | 100% | 282,365 | 100% | 535,227 | 100% |
| Division | Thilashin members | % |
|---|---|---|
| Kachin State | 1,103 | 1.8% |
| Kayah State | 303 | 0.5% |
| Kayin State | 1,000 | 1.7% |
| Chin State | 43 | 0.1% |
| Sagaing Region | 9,915 | 16.4% |
| Tanintharyi Region | 978 | 1.6% |
| Naypyidaw Union Territory | 923 | 1.5% |
| Bago Region | 5,100 | 8.4% |
| Magway Region | 2,473 | 4.1% |
| Mandalay Region | 8,174 | 13.5% |
| Mon State | 3,550 | 5.9% |
| Rakhine State | 534 | 0.9% |
| Yangon Region | 16,960 | 28.1% |
| Shan State | 3,814 | 6.3% |
| Ayeyawady Region | 5,520 | 9.1% |
| Subtotal | 60,390 | 100% |
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Age structure
- 0–14 years: 26.85% (male 7,567,976/female 7,233,577)
- 15-24 years: 17.75% (male 4,917,290/female 4,865,264)
- 25-54 years: 42.36% (male 11,426,913/female 11,922,728)
- 55-64 years: 7.52% (male 1,930,253/female 2,213,263)
- 65 years and over: 5.53% (male 1,327,811/female 1,718,739) (2017 est.)
Median age
- total: 28.2 years (2017 est.)
Population growth rate
0.91% (2017 est.)
Urbanisation
- urban population: 29.6% of total population (2014 census)
- rate of urbanisation: 2.9% of annual rate of change (2010–15 est.)
Human sex ratios
- at birth: 1.06 males/female
- under 15 years: 1.03 males/female
- 15–64 years: 0.98 male/female
- 65 years and over: 0.75 male/female (2009 est.)
- total population: 0.93 male/female (2014 census)
Life expectancy
- total population: 68.2 years
- male: 66.6 years
- female: 69.9 years (2017 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
- 5.8% (2016)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
- 18.9% (2016)
Literacy
(age 15 and over can read and write, official statistics)
- total population: 75.6%
- male: 80%
- female: 71.8% (2016 est.)
Education expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2011)
Notes
- Based on the estimated overall population, including both the enumerated and non-enumerated population (51,486,253), and on the assumption that the non-enumerated population in Rakhine State affiliate with the Islamic faith.
References
- "Myanmar population hits over 59 mln in 2009". People's Daily. Xinhua. 1 July 2010. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2013). "Demographic changes in Myanmar since 1983: An examination of official data". Population and Development Review. 39 (2): 309–324. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2013.00593.x.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2015). "Provisional results of the 2014 census of Myanmar: The surprise that wasn't". Asian Population Studies. 11 (1): 4–6. doi:10.1080/17441730.2014.972084. S2CID 154114929.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2015). "Myanmar's first census in more than 30 years: A radical revision of the official population count" (PDF). Population & Societies. No. 527 (November): 1–4.
- Summary of the Provisional Results (PDF). Ministry of Immigration and Population. August 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- Jones, Gavin W. (2007). "Delayed Marriage and Very Low Fertility in Pacific Asia" (PDF). Population and Development Review. 33 (3): 453–478. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2007.00180.x.
- Myat Mon (2008). "The Economic Position of Women in Burma". Asian Studies Review. 24 (2): 243–255. doi:10.1111/1467-8403.00076 (inactive 10 January 2021).CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2021 (link)
- United Nations, Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs (30 June 2000). "WorldMarriage Patterns 2000" (PDF). Retrieved 28 August 2017.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Nyi Nyi (2005). "V: Conclusion and Recommendation" (PDF). The Determinants of Age at First Marriage in Myanmar (Master's thesis). Mahidol University. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision
- "United Nations Statistics Division - Demographic and Social Statistics". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "Myanmar Demographic and Health Survey 2015-16" (PDF). 15 March 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "The Union Report : Census Report Volume 2" (PDF). 10 April 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "United Nations Statistics Division - Demographic and Social Statistics". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". Archived from the original on 19 September 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
- Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population MYANMAR (July 2016). The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census Census Report Volume 2-C. Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population MYANMAR. pp. 12–15.
- "၁၃၈၁(၂၀၁၉) ခုနှစ်၊ ဝါဆိုသံဃာနှင့်သီလရှင်စာရင်း". နိုင်ငံတော် သံဃာ့မဟာနာယကအဖွဲ့ (in Burmese). 2016. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- Population Projections for Myanmar, 1983-2013 Asia Pacific Population Journal, Vol. 6, No. 2 (PDF document)
 This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.