Wanamaker's
John Wanamaker Department Store was one of the first department stores in the United States. Founded by John Wanamaker in Philadelphia, it was influential in the development of the retail industry including as the first store to use price tags. At its zenith in the early 20th century, Wanamaker's also had a store in New York City at Broadway and Ninth Street. Both employed extremely large staffs. By the end of the 20th century, there were 16 Wanamaker's outlets, but after years of change the chain was bought by Albert Taubman,[3] and added to his previous purchase of Woodward & Lothrop, the Washington, D.C., department store. In 1994, Woodies, as it was known, filed for bankruptcy. The assets of Woodies were purchased by the May Company Department Stores and JCPenney. In 1995, Wanamaker's transitioned to Hecht's, one of the May Company brands.[4] In 2006, Macy's Center City became the occupant of the former Philadelphia Wanamaker's Department Store, which is now a National Historic Landmark.

John Wanamaker Store | |
 The Grand Court | |
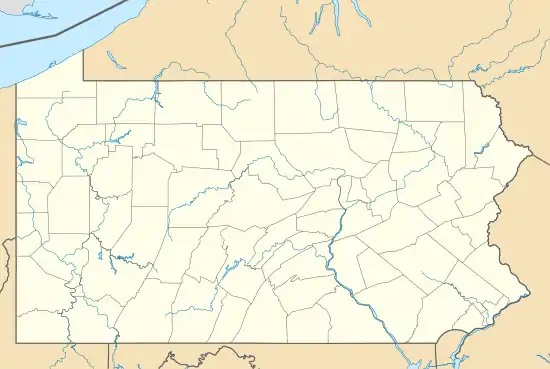  | |
| Location | 1300 Market St, Philadelphia, PA 19107 |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 39°57′5.98″N 75°9′43.81″W |
| Built | 1876 |
| Architect | Thompson, Starrett Co.; Daniel Burnham |
| Architectural style | Renaissance |
| NRHP reference No. | 78002459[1] |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | June 2, 1978[2] |
| Designated NHL | June 2, 1978 |
History
Beginnings

John Wanamaker was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1838. Due to a persistent cough, he was unable to join the U.S. Army to fight in the American Civil War, so instead started a career in business. In 1861, he and his brother-in-law Nathan Brown founded a men's clothing store in Philadelphia called Oak Hall. Wanamaker carried on the business alone after Brown's death in 1868. Eight years later, Wanamaker purchased the abandoned Pennsylvania Railroad station for use as a new, larger retail location. The concept was to renovate the terminal into a "Grand Depot" similar to London's Royal Exchange or Paris's Les Halles—two central markets, and forerunners of the modern department store, that were well known in Europe at that time.

The Wanamaker's Grand Depot opened in time to service the public visiting Philadelphia for the American Centennial Exposition of 1876, and in fact resembled one of the many pavilions at that world's fair because of its fanciful new Moorish facade. In 1877 the interior of Wanamaker's was refurbished and expanded to include not only men's clothing, but women's clothing and dry goods as well. This was Philadelphia's first modern-day department store, and one of the earliest founded in America. A circular counter was placed at the center of the building, and concentric circles radiated around it with 129 counters of goods. The store also accepted mail orders, though it was not a large business until the early twentieth century.[5][6]
Enlightened retailing
_(14780590225).jpg.webp)
Wanamaker first thought of how he would run a store on new principles when, as a youth, a merchant refused his request to exchange a purchase. A practicing Christian, he chose not to advertise on Sundays. Before he opened his Grand Depot for retail business, he let evangelist Dwight L. Moody use its facilities as a meeting place, while Wanamaker provided 300 ushers from his store personnel. His retail advertisements—the first to be copyrighted beginning in 1874—were factual, and promises made in them were kept.

Wanamaker guaranteed the quality of his merchandise in print, allowed his customers to return purchases for a cash refund and offered the first restaurant to be located inside a department store. Wanamaker also invented the price tag.[7]
His employees were to be treated respectfully by management (including not being scolded in public), and John Wanamaker & Company offered its employees access to the John Wanamaker Commercial Institute, as well as free medical care, recreational facilities, profit sharing plans, and pensions—long before these types of benefits were considered standard in corporate employment.


Innovation and "firsts" marked Wanamaker's. The store was the first department store with electrical illumination (1878), first store with a telephone (1879), and the first store to install pneumatic tubes to transport cash and documents (1880).
Wanamaker's commissioned a Philadelphia/New Jersey artist, George Washington Nicholson (1832–1912), to paint a large landscape mural, "The Old Homestead", which was finished in March 1892. The 7-by-14-foot (2.1 by 4.3 m) mural was still owned by Wanamaker's in 1950, but has since passed into a private collection.
In 1910, Wanamaker replaced his Grand Depot in stages, and constructed a new, purpose-built structure on the same site in Center City Philadelphia. The new store, built in the Florentine style with granite walls by Chicago architect Daniel H. Burnham, had 12 floors (nine for retail), numerous galleries and two lower levels totaling nearly two million square feet. The palatial emporium featured the Wanamaker Organ, the former St. Louis World's Fair pipe organ, at the time one of the world's largest organs. The organ was installed in the store's marble-clad central atrium known as the Grand Court. Another item from the St. Louis Fair in the Grand Court is the large bronze eagle, which quickly became the symbol of the store and a favorite meeting place for shoppers. All one had to say was "Meet You at The Eagle" and everyone knew where to go. The store was dedicated by President William Howard Taft on December 13, 1911.
Despite its size, the organ was deemed insufficient to fill the Grand Court with its music. Wanamaker's responded by assembling its own staff of organ builders and expanding the organ several times over a period of years. The "Wanamaker Organ" is the largest fully operational pipe organ in the world, with some 28,750 pipes. It is famed for the delicate, orchestra-like beauty of its tone as well as its incredible power. The organ still stands in place in the store today and free recitals are held twice every day except Sunday. Visitors are also invited to tour the organ's console area and meet with staff after recitals.[8] Once a year, usually in June, "Wanamaker Organ Day" is held, which is a free recital which lasts most of the day.
News of the Titanic's sinking was transmitted to Wanamaker's wireless station in New York City, and given to anxious crowds waiting outside—yet another first for an American retail store. Public Christmas Caroling in the store's Grand Court began in 1918.
In 1919, El Mundo, a Spanish newspaper said of its New York store that it was 100 special departments all under one roof, including El Departamento de Latino-Americano de Servicio Personal (The Department of Personal Service for Latin-Americans).[9]
Other innovations included employing buyers to travel overseas to Europe each year for the latest fashions, the first White sale (1878) and other themed sales such as the February "Opportunity Sales" to keep prices as low as possible while keeping volume high. The store also broadcast its organ concerts on the Wanamaker-owned radio station WOO beginning in 1922. Under the leadership of James Bayard Woodford, Wanamaker's opened piano stores in Philadelphia and New York that did a huge business with an innovative fixed-price system of sales. Salons in period decor were used to sell the higher-price items. Wanamaker also tried selling small organs built by the Austin Organ Company for a time.
Slow decline
After John Wanamaker's death in 1922, the business carried on under Wanamaker family ownership. Rodman Wanamaker, John's son, enhanced the reputation of the stores as artistic centers and temples of the beautiful, offering imported luxuries from around the world. After his death in 1928, the stores (managed for the family by a trust) continued to thrive for a time. The men's clothing and accessories department was expanded into its own separate store on the lower floors of the Lincoln-Liberty Building, two doors down on Chestnut Street, in 1932. This building, which also had a private apartment for the Wanamaker family on its top floor, was sold to Philadelphia National Bank in 1952; the initials on the building's crown read "PNB" until November 2014, even though the bank no longer existed[10] (PNB was acquired by CoreStates, which was then acquired by First Union, which was rebranded as Wachovia Bank after acquiring Wachovia Corporation, and later acquired by Wells Fargo & Co.). Over time, Wanamaker's lost business to other retail chains, including Bloomingdale's and Macy's, in the Philadelphia market. The Wanamaker Family Trust finally sold John Wanamaker and Company, with its underpatronized stores, to Los Angeles, California-based Carter Hawley Hale Stores for US$60 million cash in 1978. Carter Hawley Hale poured another $80 million into renovating the stores, but to no avail—customers had gone elsewhere in the intervening decades and did not come back.
Later Innovations

Finally, in 1986, the now 15-store chain was sold to Woodward & Lothrop, owned by Detroit shopping-mall magnate A. Alfred Taubman. Taubman reorganized the business with a shortened corporate name (Wanamaker's Inc.), and poured millions more into store renovations and public relations campaigns. This too was no help, as Taubman's retail interests were heavily in debt and the stores' combined sales were a disappointment. Believing that the Wanamaker Building space was more valuable than portions of the historic Wanamaker store, the Philadelphia flagship store was reduced to its first five stories, the Juniper Street side became the lobby of an office building for the upper stories, and the former basement budget "Downstairs Store" became a parking garage. The Crystal Tea Room restaurant was closed and eventually leased to the Marriott Corporation for use as a ballroom. Personal effects of Mr. Wanamaker from his until-then preserved office on the eighth floor, and the store archives, were donated to the Historical Society of Pennsylvania. Beloved huge Easter paintings of the trial and Passion of the Christ by Mihály Munkácsy that had been personal favorites of Mr. Wanamaker and were displayed every year in the Grand Court during Lent were unceremoniously sold at auction.
Woodward & Lothrop collapsed in bankruptcy, filing for Chapter 11 on January 17, 1994, and with it the Wanamaker stores, which were sold to May Department Stores Company on June 21, 1995. Wanamaker's Inc. was formally dissolved, and operations were consolidated with May's Hecht's division in Arlington, Virginia. After 133 consecutive years, the Wanamaker's name was removed from all stores and replaced with Hecht's. In 1997, May acquired Wanamaker's historic rival Strawbridge & Clothier and re-branded all Philadelphia-area Hecht's locations with the Strawbridge's name. The Center City Hecht's (temporarily named Strawbridge's) was closed for a lengthy renovation and refurbishment that saw the former Wanamaker retail space reduced in size again to three floors, and the former selling floors on the upper floors further subdivided into commercial office space. This was to prepare the way, in 1997, for New York-based Lord & Taylor, another division of May Department Stores, to open in the former Wanamaker's flagship in Center City Philadelphia. In August 2006 the store was converted to Macy's, operated by the Macy's East Division of Federated Department Stores Inc., (now Macy's Inc.), which acquired May in late 2005. The New York Wanamaker's store on Broadway was replaced by Kmart by 1996.
The store was not immune to the major change in retailing away from regional chains to national chains. The uniformity of brand offerings and the cost savings available to national chains all worked against the viability of the store as an independent personality, although customers generally had a major say in determining store offerings and the magnificence of its commercial space did tend to cause it to be stocked with better offerings. Other retailers had also learned to offer goods with much smaller staff rosters. The ability of retailers to "go national" in opposition to regional tastes is still an experiment-in-progress with mixed results.
The Wanamaker's flagship store, with its famous organ and eagle from the St. Louis World's Fair, was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1978. Retailers continue to reap significant monetary returns from the elegance of this unparalleled retail space. In 1992, a nonprofit group, the Friends of the Wanamaker Organ, was founded to promote the preservation, restoration and presentation of the famous pipe organ.[11]
As a retail site, the Philadelphia flagship store has proved quite profitable for later tenants Lord & Taylor and now Macy's. With a long tradition of parades and fireworks displays, Macy's has taken a prominent civic role in fostering historic Wanamaker traditions, especially the Wanamaker Organ and the Holiday Pageant of Lights Christmas Show. In 2008, Macy's celebrated its 150th birthday in the Philadelphia flagship store with a concert featuring the Wanamaker Organ and the Philadelphia Orchestra that attracted a capacity audience.
Christmas Light Show


In 1956, the Philadelphia Wanamaker's premiered a Christmas Light Show, a large musical and blinking light display several stories high, viewable from several levels of the building, but with the best viewing on the central ground floor. Its popularity with Philadelphia parents and children, as well as tourists, ensured a continuous run, even after the building was sold to different business interests.
For decades until 1994, the melodic baritone "voice", or narrator, of the show was John Facenda, known to Philadelphians for decades reporting the news on radio and television, as well as nationally known as the voice of NFL Films. NFL Films' Ed Sabol referred to Facenda as "The Voice of God" (Facenda is in the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton, Ohio). His wordsmithing and dramatic baritone delivery were highlights of the shows and did much to boost Facenda's stock and mystique. Various announcers narrated the show between 1995 and 2005. Beginning in 2006, under Macy's, Julie Andrews became the show's narrator. Also in 2006, the Santa Express Train at the top of the Grand Court returned.
In 2007, the entire Christmas Light Show was completely modernized and rebuilt by Macy's Parade Studio on new trusses with lighter materials and LED lighting. In 2008, a new and bigger Magic Christmas Tree with LED lights debuted. However, due to safety concerns and logistical issues, the dancing water fountains were retired and will not return.[12]

Floor setup
- Ground floor: 2,500-pound "Durana" bronze eagle statue in the Grand Court, made by German sculptor August Gaul for the 1904 Louisiana Purchase Exhibition and purchased by John Wanamaker; for many decades, Philadelphians would agree to "meet me at the eagle" (at Wanamaker's).[13]
- 3rd floor: Egyptian Hall auditorium behind the executive offices, also a Greek Hall auditorium. The architecture of Egyptian Hall is presently (2008) obscured by the Executive Offices and Dickens Christmas Village.
- 8th floor: Toy department had a Rocket Express monorail (from 1946 to 1984) for the kids that traveled around the entire department, camera dept, piano and organ dept. The monorail car is a feature at Philadelphia's Please Touch Museum.[14]
- 9th floor: Crystal Tea Room
- 10th floor: In-house physician and nurses
- 12th floor: Wanamaker Organ Shop, where the Wanamaker Organ was enlarged by an in-house expert staff
- Sub-floors: The Downstairs Store, post office, lost and found, shoe repair, the Dairy Bar restaurant. This area became a parking garage.
- Radio broadcasting station
- Model house on the furniture floor
- Home of the world's largest playable pipe organ
Crystal Tea Room

Wanamaker's also was home to the Crystal Tea Room restaurant on the 9th floor, which closed to the public in 1995; it was restored as a private banquet hall, accommodating sit-down receptions of up to 1,000 people. A Wanamaker's guidebook from the 1920s states that the Crystal Tea Room was the largest dining room in Philadelphia, and one of the largest in the world. It once could serve 1,400 people at a time. It served breakfast in the morning, luncheon, and afternoon tea. The kitchen's big ovens could roast 75 turkeys at a time and the facility was equipped with lockers and baths for the employees. In acknowledgment of John Wanamaker's promotion of temperance causes, alcohol was not served in the Tea Room until after the family trust sold the store. There was informal modeling in the Tea Room.[15]
There was also a balcony cafe, the Terrace on the Court, on the third floor facing the Grand Court, where shoppers could hear the Wanamaker Organ as they dined. Macy's closed this restaurant in 2008.
In popular culture
See also
- Wanamaker Mile
- Millrose Games
- Wanamaker Trophy for golf's PGA Champion
- Please Touch Museum (Wanamaker's Rocket Express Monorail)
- List of National Historic Landmarks in Philadelphia
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Center City, Philadelphia
References
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. January 23, 2007.
- Listing of John Wanamaker Store at the National Park Service
- Kelly, john. "New book details the history of Woodward & Lothrop, a vanished D.C. department store". The Washington Post. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- Jackson, Kimberlly L. (September 4, 1995). "Wanamakers' Faithful Flock To Hecht's Department Store Begins Its Two-month Transition". The Morning Call. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- https://archive.org/stream/goldenbookofwana00wana#page/n13/mode/2up pg. 48
- Herbert Ershkowitz, John Wanamaker: Philadelphia Merchant (1999))
- "Who Made America? | Innovators | John Wanamaker". www.pbs.org.
- Friends of the Wanamaker Organ schedule for recitals Retrieved 2010-12-24
- "WANAMAKER Cien Secciones Especiales en Una sola Tienda". El Mundo. 21 March 1919. Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- Melamed, Samantha. "Skyline changes: PNB letters removed by 'copter from atop 1 S. Broad". philly.com. The Philadelphia Inquirer. Retrieved November 17, 2014.
- "Friends of Wanamaker Organ".
- http://www.wanamakerorgan.com/xmas.php Friends of the Wanamaker Organ website.
- "Wanamaker Eagle".
- "John Wanamaker Monorail". National Endowment for the Humanities.
- Nicole C. Kirk, Wanamaker's Temple: The Business of Religion in an Iconic Department Store (NYU Press, 2018).
- "Filming Locations for Blow Out (1981)". The Worldwide Guide to Movie Locations.
- "Why Mannequin Is the Best Movie Ever Made About Philadelphia". December 4, 2013.
- Call, The Morning. "MOVIE WILL BE FILMED AT WANAMAKER'S IN PHILA. BRIEFLY". themorningcall.com.
- Fenn, Mike (July 19, 2016). "Phillywood: 7 key sites in Philly movie history". Metro Philadelphia.
Further reading
- Arceneaux, Noah. "Wanamaker's Department Store and the Origins of Electronic Media, 1910-1922." Technology and culture' 51.4 (2010): 809-828 online.
- Arrigale, Lawrence M., and Thomas H. Keels. Philadelphia's Golden Age of Retail (Arcadia Publishing, 2012).
- Ershkowitz, Herbert. John Wanamaker: Philadelphia Merchant (Signpost Biographies-Da Capo Press, 1999)
- Kirk, Nicole C. Wanamaker's Temple: The Business of Religion in an Iconic Department Store (NYU Press, 2018).
- Robert Sobel The Entrepreneurs: Explorations Within the American Business Tradition (Weybright & Talley 1974), chapter 3, John Wanamaker: The Triumph of Content Over Form ISBN 0-679-40064-8
- Wanamaker's: Meet Me at the Eagle. The History Press. 2010. ISBN 978-1-62619-068-9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wanamaker's. |
- About May - Company History
- Crystal Tea Room today
- Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) No. PA-1692, "John Wanamaker Store", 2 photos, 2 photo caption pages
- A history of the Christmas Light Show
- A history of the Wanamaker Organ
- Video Clip 1991
- Video Clip 1995
- Capano ownership of old Wanamaker bldg
- The John Wanamaker Collection, 1827-1987, including an extensive collection of correspondence, accounts, scrapbooks, legal papers, photographs and other materials which detail the history of Wanamaker's store, is available for research use at the Historical Society of Pennsylvania.