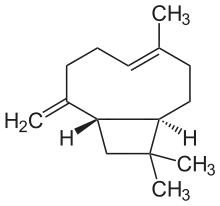
Caryophyllene
Caryophyllene /ˌkærioʊˈfɪliːn/, more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene, is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of Syzygium aromaticum (cloves),[3] the essential oil of Cannabis sativa, rosemary,[4] and hops.[5] It is usually found as a mixture with isocaryophyllene (the cis double bond isomer) and α-humulene (obsolete name: α-caryophyllene), a ring-opened isomer. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,4E,9S)-4,11,11-Trimethyl-8-methylidenebicyclo[7.2.0]undec-4-ene | |
| Other names
β-Caryophyllene trans-(1R,9S)-8-Methylene-4,11,11-trimethylbicyclo[7.2.0]undec-4-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.588 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9052 g/cm3 (17 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 262–264 °C (504–507 °F; 535–537 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The first total synthesis of caryophyllene in 1964 by E. J. Corey was considered one of the classic demonstrations of the possibilities of synthetic organic chemistry at the time.[6]
Caryophyllene is one of the chemical compounds that contributes to the aroma of black pepper.[7]
Caryophyllene helps to improve cold tolerance at low ambient temperatures. Wild giant pandas frequently roll in horse manure, which contains beta-caryophyllene/caryophyllene oxide, to inhibit transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8), an archetypical cold-activated ion channel of mammals.[8]
Metabolism and derivatives
14-Hydroxycaryophyllene oxide (C15H24O2) was isolated from the urine of rabbits treated with (−)-caryophyllene (C15H24). The X-ray crystal structure of 14-hydroxycaryophyllene (as its acetate derivative) has been reported.
The metabolism of caryophyllene progresses through (−)-caryophyllene oxide (C15H24O) since the latter compound also afforded 14-hydroxycaryophyllene (C15H24O) as a metabolite.[9]
- Caryophyllene (C15H24) → caryophyllene oxide (C15H24O) → 14-hydroxycaryophyllene (C15H24O) → 14-hydroxycaryophyllene oxide (C15H24O2).
Caryophyllene oxide,[10] in which the alkene group of caryophyllene has become an epoxide, is the component responsible for cannabis identification by drug-sniffing dogs[11][12] and is also an approved food flavoring.
Natural sources
The approximate quantity of caryophyllene in the essential oil of each source is given in square brackets ([ ]):
- Cannabis (Cannabis sativa) [3.8–37.5% of cannabis flower essential oil][13]
- Black caraway (Carum nigrum) [7.8%][14]
- Cloves (Syzygium aromaticum)[3] [1.7–19.5% of clove bud essential oil][15]
- Hops (Humulus lupulus)[16] [5.1–14.5%][17]
- Basil (Ocimum spp.)[18] [5.3–10.5% O. gratissimum; 4.0–19.8% O. micranthum][19]
- Oregano (Origanum vulgare)[20] [4.9–15.7%][21][22]
- Black pepper (Piper nigrum) [7.29%][7]
- Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) [4.62–7.55% of lavender oil][23][24]
- Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis)[4] [0.1–8.3%]
- True cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) [6.9–11.1%][25]
- Malabathrum (Cinnamomum tamala) [25.3%][26]
- Ylang-ylang (Cananga odorata) [3.1–10.7%]
- Copaiba oil (Copaifera)[27][28]
Biosynthesis
Caryophyllene is a common sesquiterpene among plant species. It is biosynthesized from the common terpene precursors dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP). First, single units of DMAPP and IPP are reacted via an SN1-type reaction with the loss of pyrophosphate, catalyzed by the enzyme GPPS2, to form geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP). This further reacts with a second unit of IPP, also via an SN1-type reaction catalyzed by the enzyme IspA, to form farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP). Finally, FPP undergoes QHS1 enzyme-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization to form caryophyllene.[29]
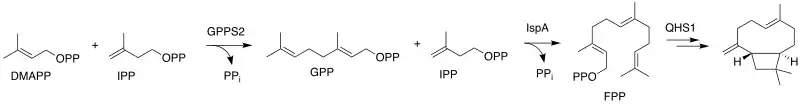 Biosynthesis of caryophyllene
Biosynthesis of caryophyllene
Compendial status
Notes and references
- SciFinder Record, CAS Registry Number 87-44-5
- Baker, R. R. (2004). "The pyrolysis of tobacco ingredients". Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis. 71 (1): 223–311. doi:10.1016/s0165-2370(03)00090-1.
- Ghelardini, C.; Galeotti, N.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Mazzanti, G.; Bartolini, A. (2001). "Local anaesthetic activity of beta-caryophyllene". Farmaco. 56 (5–7): 387–389. doi:10.1016/S0014-827X(01)01092-8. PMID 11482764.
- Ormeño, E.; Baldy, V.; Ballini, C.; Fernández, C. (September 2008). "Production and diversity of volatile terpenes from plants on calcareous and siliceous soils: effect of soil nutrients". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 34 (9): 1219–1229. doi:10.1007/s10886-008-9515-2. PMID 18670820. S2CID 28717342.
- Tinseth, G. (January–February 1993). "Hop Aroma and Flavor". Brewing Techniques. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
- Corey, E. J.; Mitra, R. B.; Uda, H. (1964). "Total Synthesis of d,l-Caryophyllene and d,l-Isocaryophyllene". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 86 (3): 485–492. doi:10.1021/ja01057a040.
- Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Ngassoum, M. B.; Geissler, M. (November 2002). "Aroma compound analysis of Piper nigrum and Piper guineense essential oils from Cameroon using solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography, solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and olfactometry". Journal of Chromatography A. 976 (1–2): 265–275. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00376-X. PMID 12462618.
- Zhou, Wenliang; Yang, Shilong; Li, Bowen; Nie, Yonggang; Luo, Anna; Huang, Guangping; Liu, Xuefeng; Lai, Ren; Wei, Fuwen (2020-12-02). "Why wild giant pandas frequently roll in horse manure". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi:10.1073/pnas.2004640117. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 33288697.
- "Caryophyllene oxide – C15H24O". PubChem. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- Yang, D.; Michel, L.; Chaumont, J. P.; Millet-Clerc, J. (1999-11-01). "Use of caryophyllene oxide as an antifungal agent in an in vitro experimental model of onychomycosis". Mycopathologia. 148 (2): 79–82. doi:10.1023/A:1007178924408. ISSN 0301-486X. PMID 11189747. S2CID 24242933.
- Russo, E. (2011). "Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects". British Journal of Pharmacology. 163 (7): 1344–1364. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x. PMC 3165946. PMID 21749363.
- Stahl, E.; Kunde, R. (1973). "Die Leitsubstanzen der Haschisch-Suchhunde" [The tracing substances of hashish search dogs]. Kriminalistik (in German). 27: 385–389.
- Mediavilla, V.; Steinemann, S. "Essential oil of Cannabis sativa L. strains". International Hemp Association. Retrieved 11 July 2008.
- Singh, G.; Marimuthu, P.; De Heluani, C. S.; Catalan, C. A. (January 2006). "Antioxidant and biocidal activities of Carum nigrum (seed) essential oil, oleoresin, and their selected components". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 54 (1): 174–181. doi:10.1021/jf0518610. PMID 16390196.
- Alma, M. H.; Ertaş, M.; Nitz, S.; Kollmannsberger, H. (May 2007). Lucia, L. A.; Hubbe, M. A. (eds.). "Chemical composition and content of essential oil from the bud of cultivated Turkish clove" (PDF). BioResources. 2 (2): 265–269. doi:10.15376/biores.2.2.265-269. ISSN 1930-2126. Retrieved September 6, 2010.
The results showed that the essential oils mainly contained about [...] 3.56% β-Caryophyllene
- Wang, G.; Tian, L.; Aziz, N.; et al. (November 2008). "Terpene biosynthesis in glandular trichomes of hop". Plant Physiology. 148 (3): 1254–1266. doi:10.1104/pp.108.125187. PMC 2577278. PMID 18775972.
- Bernotienë, G.; Nivinskienë, O.; Butkienë, R.; Mockutë, D. (2004). "Chemical composition of essential oils of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) growing wild in Auktaitija" (PDF). Chemija. 2. 4: 31–36. ISSN 0235-7216. Retrieved September 6, 2010.
- Zheljazkov, V. D.; Cantrell, C. L.; Tekwani, B.; Khan, S. I. (January 2008). "Content, composition, and bioactivity of the essential oils of three basil genotypes as a function of harvesting". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 56 (2): 380–5. doi:10.1021/jf0725629. PMID 18095647.
- Vasconcelos Silva, M. G.; Abreu Matos, F. J.; Oliveira Lopes, P. R.; Oliveira Silva, F.; Tavares Holanda, M. (August 2, 2004). Cragg, G. M.; Bolzani, V. S.; Rao, G. S. R. S. (eds.). "Composition of essential oils from three Ocimum species obtained by steam and microwave distillation and supercritical CO2 extraction" (PDF). Arkivoc. 2004 (6): 66–71. doi:10.3998/ark.5550190.0005.609. ISSN 1424-6376. Retrieved September 6, 2010.
- Harvala C, Menounos P, Argyriadou N (February 1987). "Essential oil from Origanum dictamnus". Planta Medica. 53 (1): 107–109. doi:10.1055/s-2006-962640. PMID 17268981.
- Calvo Irabién, L. M.; Yam-Puc, J. A.; Dzib, G.; Escalante Erosa, F.; Peña Rodríguez, L. M. (July 2009). "Effect of postharvest drying on the composition of Mexican oregano (Lippia graveolens) essential oil". Journal of Herbs, Spices & Medicinal Plants. 15 (3): 281–287. doi:10.1080/10496470903379001. ISSN 1540-3580. S2CID 86208062.
- Mockutė, D.; Bernotienė, G.; Judžentienė, A. (May 2001). "The essential oil of Origanum vulgare L. ssp. vulgare growing wild in Vilnius district (Lithuania)". Phytochemistry. 57 (1): 65–69. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)00474-x. PMID 11336262.
- Prashar, A.; Locke, I. C.; Evans, C. S. (2004). "Cytotoxicity of lavender oil and its major components to human skin cells". Cell Proliferation. 37 (3): 221–229. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.2004.00307.x. PMC 6496511. PMID 15144499.
- Umezu, T.; Nagano, K.; Ito, H.; Kosakai, K.; Sakaniwa, M.; Morita, M. (December 2006). "Anticonflict effects of lavender oil and identification of its active constituents". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 85 (4): 713–721. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.10.026. PMID 17173962. S2CID 21779233.
- Kaul, P. N.; Bhattacharya, A. K.; Rao, B. R.; et al. (2003). "Volatile constituents of essential oils isolated from different parts of cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume)". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 83 (1): 53–55. doi:10.1002/jsfa.1277.
- Ahmed, A.; Choudhary, M. I.; Farooq, A.; et al. (2000). "Essential oil constituents of the spice Cinnamomum tamala (Ham.) Nees & Eberm". Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 15 (6): 388–390. doi:10.1002/1099-1026(200011/12)15:6<388::AID-FFJ928>3.0.CO;2-F.
- Leandro, L. M.; Vargas, F. S.; Barbosa, P. C.; Oliveira Neves, J. K.; Da Silva, J. A.; Da Veiga Junior, V. F. (2012). "Chemistry and biological activities of terpenoids from copaiba (Copaifera spp.) oleoresins". Molecules. 17 (4): 3866–3889. doi:10.3390/molecules17043866. PMC 6269112. PMID 22466849.
- Sousa, J. P.; Brancalion, A. P.; Souza, A. B.; Turatti, I. C.; Ambrósio, S. R.; Furtado, N. A.; Lopes, N. P.; Bastos, J. K. (Mar 2011). "Validation of a gas chromatographic method to quantify sesquiterpenes in copaiba oils". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 54 (4): 653–9. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.10.006. PMID 21095089.
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Du, J.; Bae, H.-J. (2016-12-01). "Biosynthesis of β-caryophyllene, a novel terpene-based high-density biofuel precursor, using engineered Escherichia coli". Renewable Energy. 99: 216–223. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2016.06.061. ISSN 0960-1481.
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. "Revisions to FCC, First Supplement". Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 29 June 2009.
- Therapeutic Goods Administration. "Chemical substances" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 April 2011. Retrieved 29 June 2009.