AM-1220
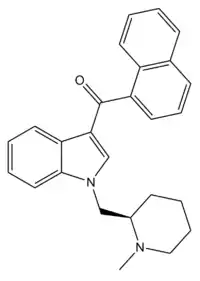
AM-1220 is a drug that acts as a potent and moderately selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1, with around 19 times selectivity for CB1 over the related CB2 receptor.[1] It was originally invented in the early 1990s by a team led by Thomas D'Ambra at Sterling Winthrop,[2] but has subsequently been researched by many others, most notably the team led by Alexandros Makriyannis at the University of Connecticut. The (piperidin-2-yl)methyl side chain of AM-1220 contains a stereocenter, so there are two enantiomers with quite different potency, the (R)-enantiomer having a Ki of 0.27 nM at CB1 while the (S)-enantiomer has a much weaker Ki of 217 nM.[3]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26N2O |
| Molar mass | 382.507 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Related compounds
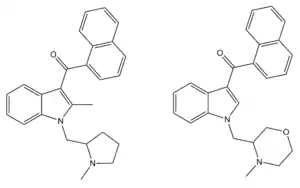
A number of related compounds are known with similar potent cannabinoid activity, with modifications such as substitution of the indole ring at the 2- or 6-positions, the naphthoyl ring substituted at the 4-position or replaced by substituted benzoyl rings or other groups, or the 1-(N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl) group replaced by similar heterocyclic groups such as N-methylpyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl or N-methylmorpholin-3-ylmethyl.[4][5][6] AM-1220 was first detected as an ingredient of synthetic cannabis smoking blends in 2010.[7]
Legal status
==United States== in the United States of America all CB1 receptor agonists of the 3-(1-naphthoyl)indole class such as AM-1220 are Schedule I Controlled Substances under the Controlled Substances Act s.[8] ==United Kingdom== it's illegal to supply, smuggle, distribute, transport, sell or trade the pharmaceutical drug under the Psychoactive Substances Act 2016 which was enforced on May26th 2016.
As of October 2015, AM-1220 is a controlled substance in China.[9]
References
- WO patent 200128557, Makriyannis A, Deng H, "Cannabimimetic indole derivatives", granted 2001-06-07
- US patent 5068234, D'Ambra TE, et al., "3-arylcarbonyl-1-(C-attached-N-heteryl)-1H-indoles", granted 1991-11-26
- D'ambra, T. (1996). "C-Attached aminoalkylindoles: potent cannabinoid mimetics". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 6 (1): 17–22. doi:10.1016/0960-894X(95)00560-G.
- Deng H (2000). Design and synthesis of selective cannabinoid receptor ligands: Aminoalkylindole and other heterocyclic analogs (PhD. Dissertation). University of Connecticut. ProQuest 304624325.
- Willis PG, Pavlova OA, Chefer SI, Vaupel DB, Mukhin AG, Horti AG (September 2005). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of a novel series of aminoalkylindoles with potential for imaging the neuronal cannabinoid receptor by positron emission tomography". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 48 (18): 5813–22. doi:10.1021/jm0502743. PMID 16134948.
- US patent 7820144, Makriyannis A, et al., "Receptor selective cannabimimetic aminoalkylindoles", granted 2010-10-26
- Head Shop ‘Legal Highs’ Active Constituents Identification Chart (July - August 2010)
- : Schedules of controlled substances
- "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.