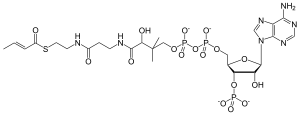
Crotonyl-CoA
Crotonyl-coenzyme A is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid, and in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan.[1] It is important in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.360 |
| MeSH | Crotonyl-coenzyme+A |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H40N7O17P3S | |
| Molar mass | 835.609 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Crotonyl-coA and reductases
Before a 2007 report by Alber and coworkers, crotonyl-coA carboxylases and reductases (CCRs) were known for reducing crotonyl-coA to butyryl-coA.[3] A report by Alber and coworkers concluded that a specific CCR homolog was able to reduce crotonyl-coA to (2S)-ethyl malonyl-coA which was a favorable reaction.[3] The specific CCR homolog came from the bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides.[3]
Role of Crotonyl-coA in Transcription
Post-translational modification of histones either by acetylation or crotonylation is important for the active transcription of genes.[4] Histone crotonylation is regulated by the concentration of crotonyl-coA which can change based on environmental cell conditions or genetic factors.[4]
References
- Ray, Lauren; Valentic, Timothy R; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Withall, David M; Song, Lijiang; Milligan, Jacob C; Osada, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Shunji; Tsai, Shiou-Chuan; Challis, Gregory L (2016). "A crotonyl-CoA reductase-carboxylase independent pathway for assembly of unusual alkylmalonyl-CoA polyketide synthase extender units". Nature Communications. 7: 13609. doi:10.1038/ncomms13609. PMC 5187497. PMID 28000660.
- "Crotonyl-CoA".
- Wilson, Micheal C.; Moore, Bradley S. (2012). "Beyond ethylmalonyl-CoA: The functional role of crotonyl-CoAcarboxylase/reductase homologs in expanding polyketide diversity". Nat. Prod. Rep. 29 (1): 72–86. doi:10.1039/c1np00082a. ISSN 0265-0568.
- Sabari, Benjamin R.; Tang, Zhanyun; Huang, He; Yong-Gonzalez, Vladimir; Molina, Henrik; Kong, Ha Eun; Dai, Lunzhi; Shimada, Miho; Cross, Justin R.; Zhao, Yingming; Roeder, Robert G. (2015-04-16). "Intracellular Crotonyl-CoA Stimulates Transcription through p300-Catalyzed Histone Crotonylation". Molecular Cell. 58 (2): 203–215. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.02.029. ISSN 1097-2765. PMID 25818647.