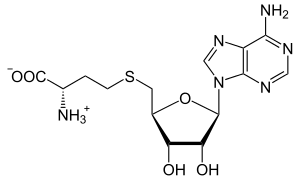
S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine
S-Adenosyl-l-homocysteine (SAH) is the biosynthetic precursor to homocysteine.[1] SAH is formed by the demethylation of S-adenosyl-l-methionine.[2][3] Adenosylhomocysteinase converts SAH into homocysteine and adenosine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
S-(5′-Deoxyadenos-5′-yl)-l-homocysteine | |
| Other names
AdoHcy, 2-S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine, 5′-S-(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)-5′-thioadenosine S-adenosylhomocysteine, SAH | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.328 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | S-Adenosylhomocysteine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H20N6O5S | |
| Molar mass | 384.412 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Finkelstein, J. D. (2000). "Pathways and regulation of homocysteine metabolism in mammals". Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 26 (3): 219–25. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8466. PMID 11011839.
- Ribbe, M. W.; Hu, Y.; Hodgson, K. O.; Hedman, B. (2014). "Biosynthesis of Nitrogenase Metalloclusters". Chem. Rev. 114 (8): 4063–4080. doi:10.1021/cr400463x. PMC 3999185. PMID 24328215.
- James, S. Jill; Melnyk, Stepan; Pogribna, Marta; Pogribny, Igor P; Caudill, Marie A (2002). "Elevation in S-Adenosylhomocysteine and DNA Hypomethylation: Potential Epigenetic Mechanism for Homocysteine-Related Pathology". The Journal of Nutrition. 132 (8): 2361S–2366S. doi:10.1093/jn/132.8.2361S. PMID 12163693.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.