Dinotefuran
Dinotefuran is an insecticide of the neonicotinoid class developed by Mitsui Chemicals for control of insect pests such as aphids, whiteflies, thrips, leafhoppers, leafminers, sawflies, mole cricket, white grubs, lacebugs, billbugs, beetles, mealybugs, and cockroaches on leafy vegetables, in residential and commercial buildings, and for professional turf management.[2] Its mechanism of action involves disruption of the insect's nervous system by inhibiting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In order to avoid harming beneficial insects such as bees, it should not be applied during bloom. [3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
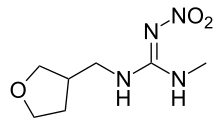
| IUPAC name
2-methyl-1-nitro-3-[(tetrahydro-3-furanyl) methyl] guanidine | |
| Other names
(RS)-1-methyl-2-nitro-3-[(tetrahydro-3-furanyl) methyl] guanidine; MTI-446 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.831 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C7H14N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 202.214 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 107.5 |
| 39.83 g/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
≥2000 mg/kg (oral, rat and mouse)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In July 2013, the state of Oregon temporarily restricted the use of dinotefuran pending the results of an investigation into a large bee kill.[4]
Dinotefuran is also used in veterinary medicine as a flea and tick preventive for dogs and as a flea preventive for cats. It is used in combination with pyriproxifen or permethrin.
Current studies show dinotefuran is effective at controlling the invasive Spotted lanternfly, first found in Berks County, PA, in 2014. [5]
References
- Dinotefuran, Mitsui Chemicals
- Dinotefuran Pesticide Fact Sheet, United States Environmental Protection Agency
- "Massive bee die-off found in Wilsonville". Portland Tribune. 20 June 2013.
- "Oregon Restricts Use of Certain Dinotefuran Pesticides", Pest Control Technology, 2 July 2013
- "How to Eliminate or Control Spotted Lanternfly Adults", PA Dept of Agriculture, 13 September 2017