Landau distribution
In probability theory, the Landau distribution[1] is a probability distribution named after Lev Landau. Because of the distribution's "fat" tail, the moments of the distribution, like mean or variance, are undefined. The distribution is a particular case of stable distribution.
|
Probability density function 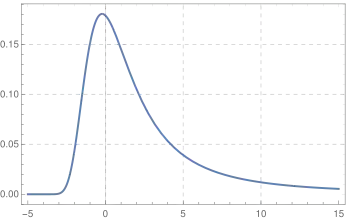 | |||
| Parameters | — location parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| Mean | Undefined | ||
| Variance | Undefined | ||
| MGF | Undefined | ||
| CF | |||
Definition
The probability density function, as written originally by Landau, is defined by the complex integral:
where a is an arbitrary positive real number, meaning that the integration path can be any parallel to the imaginary axis, intersecting the real positive semi-axis, and refers to the natural logarithm.
The following real integral is equivalent to the above:
The full family of Landau distributions is obtained by extending the original distribution to a location-scale family of stable distributions with parameters and ,[2] with characteristic function:[3]
where and , which yields a density function:
Let us note that the original form of is obtained for and , while the following is an approximation[4] of for and :
Related distributions
- If then .
- The Landau distribution is a stable distribution with stability parameter and skewness parameter both equal to 1.
References
- Landau, L. (1944). "On the energy loss of fast particles by ionization". J. Phys. (USSR). 8: 201.
- Gentle, James E. (2003). Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods. Statistics and Computing (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Springer. p. 196. doi:10.1007/b97336. ISBN 978-0-387-00178-4.
- Zolotarev, V.M. (1986). One-dimensional stable distributions. Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society. ISBN 0-8218-4519-5.
- Behrens, S. E.; Melissinos, A.C. Univ. of Rochester Preprint UR-776 (1981).