North American T-6 Texan
The North American Aviation T-6 Texan is an American single-engined advanced trainer aircraft used to train pilots of the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), United States Navy, Royal Air Force, and other air forces of the British Commonwealth during World War II and into the 1970s. Designed by North American Aviation, the T-6 is known by a variety of designations depending on the model and operating air force. The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) and USAAF designated it as the AT-6, the United States Navy the SNJ, and British Commonwealth air forces the Harvard, the name by which it is best known outside the US. Starting in 1948, the new United States Air Force (USAF) designated it the T-6, with the USN following in 1962. It remains a popular warbird aircraft used for airshow demonstrations and static displays. It has also been used many times to simulate various Japanese aircraft, including the Mitsubishi A6M Zero, in movies depicting World War II in the Pacific. A total of 15,495 T-6s of all variants were built.
| T-6 Texan/SNJ/Harvard | |
|---|---|
 | |
| USAAF AT-6Cs near Luke Field, 1943 | |
| Role | Trainer aircraft |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | North American Aviation |
| First flight | 1 April 1935 |
| Retired | 1995 (South African Air Force) |
| Primary users | United States Army Air Forces United States Navy Royal Air Force Royal Canadian Air Force |
| Number built | 15,495 |
| Developed from | North American NA-16 |
| Variants | North American A-27 Bacon Super T-6 |
| Developed into | North American P-64 CAC Wirraway |
Development


01.jpg.webp)

The Texan originated from the North American NA-16 prototype (first flown on April 1, 1935). In 1935, NAA submitted this design for the U.S. Army Air Corps Basic Trainer Competition. Yet, NAA was also targeting the export market as well.[1]
The modified NA-26 was submitted as an entry for a USAAC "Basic Combat Trainer " aircraft competition in March 1937. Based on the NA-18, but with a foot longer wingspan, it was the first of the NA-16 series with retractable gear. It was similar to the BT-9, but with a larger engine, the 550-hp (410 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp, and could accommodate two .30-cal guns. The BC-1 (NA-36) was the production version, with 177 built using R-1340-47 engines, the first delivered on 9 June 1937. Some 30 were modified as BC-1-I instrument trainers. The armed version, the BC-1A (NA-55-1), carried a .30-cal M-2 machine gun on the starboard nose, and a flexible M-2 in the rear. The 83 BC-1As built, used a NACA 2215 airfoil at the wing root, and a NACA 4412 airfoil at the tip, with a 178 gallon fuel capacity. Based on the BT-9s, the US Navy received 40 NA-28 aircraft, designated NJ-1, 16 NA-52 aircraft, designated the SNJ-1, 36 SNJ-2s based on the NA-65, and 25 SNJ-2s based on the NA-79.[1]:33–44,214
In March 1937, the Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation of Australia purchased a NA-32 (NA-16-1A), followed by a NA-33 (NA-16-2K)), including a manufacturing license. The first CAC Wirraway flew on 27 March 1939, of which 755 were built.[1]:52–53
In August 1937, Mitsubishi Jukogyo K.K. purchased a single NA-16, NA-16-4R (NA-37), powered by the 450-hp Pratt & Whitney R-985-9CG, including manufacturing rights. A second N-16, NA-16-4RW (NA-47), powered by a smaller Wright engine, was ordered in December 1937. After being evaluated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, K.K. Watanabe Tekkosho built 26 aircraft highly modified versions called the K10W1, powered by a Nakajima Aircraft Company 600-hp Kotobuki 2 Kai radial engine, from 1941 to 1942. Kyushu Aircraft Company built another 150 aircraft (Allied Recognition Code name Oak). After WWII, the Japanese Air Self Defense Force operated 195 Texans (9 T-6Ds, 11 T-6Fs, and 175 T-6Gs). The Japanese Maritime Self Defence Force operated 62 Texans (10 SNJ-4s, 41 SNJ-5s, and 11 SNJ-6s)[1]:56–57,214
According to Dan Hagedorn, "For all intents and purposes, the BC-1A series may be regarded as the true beginning of the modern AT-6 series as we know it today." In December 1938, the British Commonwealth started receiving the first of 400 Harvard Mark Is (NA-49), for use in the Central Flying School. The plane was powered by the 600-hp Pratt & Whitney R-1340-S3H1 Wasp. In May 1939, the Royal Canadian Air Force ordered 30 Harvard Mark Is (NA-61). Then in November 1939, the British Purchasing Commission ordered the first of eventually 1275 Harvard Mark IIs (NA-66, NA-75, NA-76, and NA-81) for the RAF and RCAF.[1]:46,63–66,69,77–79,92,214
On 23 April 1939, NAA received a contract for 251 BT-14s and 94 AT-6s. The BT-14 (NA-58) was a fixed gear aircraft with a fuselage 14 inches longer than the BT-9. In 1941, 27 BT-14s were refitted with the 400-hp R-985-11, and designated as BT-14A-NAs. In June 1939, NAA received an order for 94 AT-6-NAs (NA-59), powered by the wright R-1340-47 and able to mount two .30-cal machines guns.[1]:46–47,73–74,214
The USAAC AT-6A, and the U.S. Navy SNJ-3, were based on the NA-77 and NA-78 designs. The Pratt & Whitney R-1340-49 Wasp radial engine powered the USAAC aircraft, while the R-1340-38s powered the Navy aircraft. The USAAC received 1847 AT-6As, while the Navy received 270 SNJ-3s.[1]:80–91,214
The AT-6B (NA-84) was built for armament training, and could mount a .30 caliber machine gun on the right nose cowl, right wing, and in the rear cockpit, besides having a light bomb rack. The aircraft was powered by the 600-hp R-1340-AN-1 engine. The USAAC received 400 of the aircraft.[1]:93–97,214
The NA-88 design was used to build 2970 AT-6Cs (747 of which went to the British Commonwealth as Harvard IIas), 2401 SNJ-4s, 2604 AT-6Ds (537 of which went to the British Commonwealth as Harvard IIIs), and 1357 SNJ-5s. The first AT-6C aircraft was delivered on 12 February 1942. The 12-volt electrical system was changed to a 24-volt system in the AT-6D, for standardization amongst the service. The AT-6D, which was also armament capable, and early versions included a wing gun camera, and a high-pressure oxygen system. The AT-6D used two toggle starter switches, rather than the foot pedal starter, and the first AT-6D was delivered on 22 July 1943. The Navy received an additional 630 AT-6Ds direct from the USAAF, redesignating them SNJ-5s, for a total of 1987. Similarly, the NA-121 design was used to build the final wartime Texans, and included 800 AT-6Ds (of which 211 went to the Navy as SNJ-5s), and 956 AT-6Fs (of which 411 went to the Navy as SNJ-6s). They were capable of carrying a 20-gallon centerline drop tank.[1]:98–128,214
Starting in 1942, Canada's Noorduyn Aviation built an R-1340-AN-1-powered version of the AT-6A, under license and paid from the USAAF Lend-Lease fund. Referred to as the AT-16, and British Commonwealth Harvard IIB, a total of 2557 were built. After WWII, several aircraft continued serving in the RCAF.[1]:122–124
The NA-168 series consisted of remanufactured AT-6s and SNJs for the USAF, starting in 1949. The Air Training Command received 641 aircraft, designated T-6G-NT, of which 416 eventually were sent to U.S. Military Assistance Program countries. U.S. National Guard units received an additional 50 aircraft, of which 28 eventually were sent to France. An additional 59 aircraft were Liaison/Trainer aircraft, designated LT-6G-NA, for the Korean War. These aircraft could be deployed with 2 detachable .30-cal machine gun pods, and 4 HVARs, or 4 100-pound bombs, plus a 55-gallon auxiliary drop tank. Alternatively, they could carry the gun pods and 12 2.25-inch SCA markings rockets, or 6 100-pound bombs. The T-6G-NAs had a 140 U.S. gallon fuel capacity, while previous models had a 110 gallon capacity. The rear cockpit also had the same instruments as the front cockpit. Then, in 1951, the USAF placed an order for 824 T-6Gs, designated T-6G-1-NH, for the Air Training Command.[1]:139–153,214
Under the Mutual Defense Assistance Program (MDAP), the Canada Car and Foundry built 285 Harvard IVs, designated NA-186. They built an additional 270 Harvard 4s for the RCAF.[1]:153–155,214
In April 1951, the USAF ordered an additional 107 T-6Gs for the MDAP, designated NA-188. They placed an order for 11 training aircraft in March 1952, designated NA-195, and then a final batch of 110 aircraft in June for MDAP, designated NA-197.[1]:155–159,214
Operational history
Combat use
Peru used its seven T-6 fighter bombers in the Ecuadorian-Peruvian War. They were equipped with two 7.65 mm guns, while carrying up to four 116-pound bombs.[1]:176–178
Twenty AT-6 Texans were employed by the 1st and 2nd fighter squadrons of the Syrian Air Force in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, providing ground support for Syrian troops, and launching air strikes against Israeli airfields, ships, and columns, losing one aircraft to antiaircraft fire. They also engaged in air-to-air combat on a number of occasions, with a rear gunner shooting down an Israeli Avia S-199 fighter.[2]
The Israeli Air Force (IAF) bought 17 Harvards, and operated nine of them in the final stages of the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, against the Egyptian ground forces, with no losses. In the Sinai Campaign, IAF Harvards attacked Egyptian ground forces in Sinai Peninsula with two losses.

The Royal Hellenic Air Force employed three squadrons of British- and American-supplied T-6D and G Texans for close air support, observation, and artillery spotting duties during the Greek Civil War, providing extensive support to the Greek army during the Battle of Gramos. Communist guerillas called these aircraft "O Galatas" ("The Milkman"), because they saw them flying very early in the morning. After the "Milkmen", the guerillas waited for the armed Spitfires and Helldivers.
During the Korean War and, to a lesser extent, the Vietnam War, T-6s were pressed into service as forward air control aircraft. These aircraft were designated T-6 "Mosquitos".[3][4][1]:148–151
No. 1340 Flight RAF used the Harvard in Kenya against the Mau Mau in the 1950s, where they operated with 20 lb bombs and machine guns against the rebels. Some operations took place at altitudes around 20,000 ft above mean sea level. A Harvard was the longest-serving RAF aeroplane, with an example, taken on strength in 1945, still serving in the 1990s (as a chase plane for helicopter test flights—a role for which the Shorts Tucano's high stall speed was ill-suited).
The T-6G was also used in a light attack or counter insurgency role by France during the Algerian War in special Escadrilles d'Aviation Légère d'Appui (EALA), armed with machine guns, bombs and rockets. At its peak, 38 EALAs were active. The largest unit was the Groupe d'Aviation Légère d'Appui 72, which consisted of up to 21 EALAs.
From 1961 to 1975, Portugal used more than a hundred T-6Gs, also in the counterinsurgency role, during the Portuguese Colonial War. During this war, almost all the Portuguese Air Force bases and air fields in Angola, Mozambique, and Portuguese Guinea had a detachment of T-6Gs.
On 16 June 1955, rebel Argentine Navy SNJ-4s bombed Plaza de Mayo in Buenos Aires, Argentina; one was shot down by a loyalist Gloster Meteor. Navy SNJ-4s were later used by the colorado rebels in the 1963 Argentine Navy Revolt, launching attacks on the 8th Tank Regiment columns on 2 and 3 April, knocking out several M4 Sherman tanks, and losing one SNJ to anti-aircraft fire.[5]
In 1957–58, the Spanish Air Force used T-6s as counterinsurgency aircraft in the Ifni War, armed with machine guns, iron bombs, and rockets, achieving an excellent reputation due to its reliability, safety record, and resistance to damage.
The Pakistan Air Force used T-6Gs in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 as a night ground-support aircraft, hitting soft transport vehicles of the Indian army. In the early hours of 5 December, during a convoy interdiction mission in the same area, Squadron Leader Israr Quresh's T-6G Harvard was hit by Indian antiaircraft ground fire and a shell fractured the pilot's right arm. Profusely bleeding, the pilot flew the aircraft back with his left hand and landed safely. The World War II-vintage propellered trainers were pressed into service and performed satisfactorily in the assigned role of convoy escorters at night.
The South African Air Force received their first T-6s in October 1942 to be used by the Joint Air Training Scheme. By July 1944, 633 Harvard Mk IIA T-6s and IIIs had been shipped to South Africa with another 555 (379 MkIIAs and 176 Mk IIIs) to arrive by October 1945. Another 65 (AT-6Ds and 30 T-6Gs) were ordered between 1952-1956.[6] The T-6 remained in service until 1995 as a basic trainer, mainly as a result of the United Nations arms embargo against South Africa's apartheid policies. They were replaced by Pilatus PC-7 MkII turboprop trainers.[7]
Research testbed
The Harvard 4 has been used in Canada as a testbed aircraft for evaluating cockpit attitude displays. Its aerobatic capability permits the instructor pilot to maneuver the aircraft into unusual attitudes, then turn the craft over to an evaluator pilot in the "blind" rear cockpit to recover, based on one of several digitally generated attitude displays.[8]
Variants
Operators
.jpg.webp)



- Argentine Army Aviation (SNJ-4)
- Argentine Naval Aviation (SNJ-4 and 30 SNJ-5Cs for carrier operations)


- Bolivian Air Force
- Naval Aviation
- Royal Khmer Aviation (AVRK)
- Royal Canadian Air Force
- Royal Canadian Navy
- National Research Council (still in use)

- Congolese Air Force

- Air Force of El Salvador
- Gabon Air Force



- German Air Force (Bundeswehr Luftwaffe)
- Haiti Air Corps
- Indonesian Air Force – buying 25 from US.
- Iranian Air Force
- Italian Air Force operated 238 aircraft from 1949 until 1979[10]

- Force Aérienne Katangaise[11]
- Mexican Air Force Total of 120 delivered, 47 AT-6 and 73 T-6C
- Royal Netherlands Air Force
- Dutch Naval Aviation Service
- Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force – Post war
- Royal New Zealand Air Force (1 maintained for historic flight)

- Royal Norwegian Air Force (1 maintained for historic flight)
- Fuerza Aérea de Nicaragua (G.N) Escuela Militar de Aviación 1948-1979
- Paraguayan Air Force
- Paraguayan Naval Aviation


- Swedish Air Force 145 Harvard IIb as Sk 16A, 106 T-6A, T-6B, SNJ-3, SNJ-4 as Sk 16B and 6 SNJ-2 as Sk 16C.
 Syrian Harvard
Syrian Harvard Switzerland
Switzerland
- Turkish Air Force: 196 planes of various types

- Royal Air Force
- Royal Navy
- Qinetiq (retired in 2016)[12][13]

- United States Army Air Corps/Army Air Forces
- United States Air Force
- United States Navy
- United States Marine Corps
- United States Coast Guard
- Uruguayan Air Force
- Aviacion Naval Uruguaya

Specifications (T-6G)
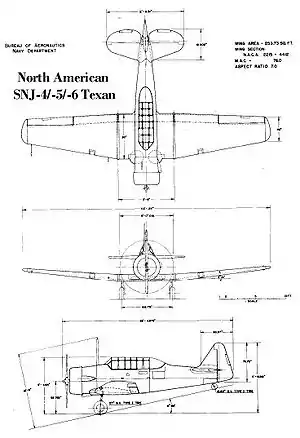
Data from Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II.[14]
General characteristics
- Crew: two (student and instructor)
- Length: 29 ft 0 in (8.84 m)
- Wingspan: 42 ft 0 in (12.81 m)
- Height: 11 ft 8 in (3.57 m)
- Wing area: 253.7 sq ft (23.6 m2)
- Empty weight: 4,158 lb (1,886 kg)
- Gross weight: 5,617 lb (2,548 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-1340-AN-1 Wasp radial engine, 600 hp (450 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 208 mph (335 km/h, 181 kn) at 5000 ft (1,500 m)
- Cruise speed: 145 mph (233 km/h, 126 kn)
- Range: 730 mi (1,175 km, 630 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 24,200 ft (7,400 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,200 ft/min (6.1 m/s)
- Wing loading: 22.2 lb/sq ft (108 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.11 hp/lb (kW/kg)
Armament
- Provision for up to 3 × 0.30 in (7.62 mm) machine guns
In popular culture
In the September 1944 issue of The Sportsman Pilot, USAAF Capt. Paul K. Jones' article states, "The Six is a plane that can do anything a fighter can do - and even more. Naturally not as fast, she makes up for speed in her ease of handling and her maneuverability. She's a war machine, yes, but more than that she's a flyer's airplane. Rolls, Immelmans, loops, spins, snaps, vertical rolls - she can do anything - and do it beautifully. For actual combat, more guns, more speed and more power is needed. But for the sheer joy of flying - give me an AT-6."[1]:8–9
After World War II, the National Air Races established a unique racing class for the AT-6/Texan/Harvard aircraft; this class continues today at the Reno National Air Races each year.

.jpg.webp)
Since the Second World War, the T-6 has been a regular participant at air shows, and was used in many movies and television programs. For example, converted single-seat T-6s painted in Japanese markings to represent Mitsubishi Zeros made appearances in A Yank in the R.A.F. (1941), Tora! Tora! Tora! (1970), Baa Baa Black Sheep (1976-1978), and The Final Countdown (1980). In A Bridge too Far (1977) it represented the razorback Republic P-47 Thunderbolt. Some were modified for the Dutch film Soldaat van Oranje (1977) to represent the Dutch pre-World War II fighter Fokker D.XXI. The T-6 also appeared in the Pat Benatar video for Shadows of the Night. The New Zealand Warbirds "Roaring 40s" aerobatic team use ex-Royal New Zealand Air Force Harvards. The Flying Lions Aerobatic Team uses Harvards acquired from the South African Air Force.[15]
See also
- T-6 Texan variants
- T-6 Texan II
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Arado Ar 96
- Fiat G.49
- Kyushu K10W
- FMA I.Ae. 22 DL
- Macchi MB.323
- Miles Master
- Percival Provost
- Piaggio P.150
- Soko 522
- Valmet Vihuri
- VL Pyry
- Yakovlev Yak-11
- PZL TS-8 Bies
Related lists
References
- Hagedorn, Dan (2009). North American's T-6: a definitive history of the world's most famous trainer. North Branch, MN: Specialty Press. pp. 11–15. ISBN 9781580071246.
- Nicolle, David. "Syria's Fighting Texans". ACIG.org. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- "AF Museum – North American T-6D "Mosquito"". National Museum of the US Air Force. Retrieved 4 October 2015.
- "North American AT-6/SNJ-6". Lyon Air Museum.
- Cooper, Tom. "Argentina, 1955–1965". ACIG.org. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- "The South African Air Force". www.saairforce.co.za. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- "The History of the SAAF". www.af.mil.za. Archived from the original on 2012-05-05. Retrieved 2009-11-12.
- http://archive.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/obj/iar-ira/doc/harvard_eng.pdf%5B%5D
- Jowett, Philip (2016). Modern African Wars (5): The Nigerian-Biafran War 1967-70. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-1472816092.
- "Italian Air Force Aircraft Types". www.aeroflight.co.uk.
- "Congo, Part 1; 1960–1963". ACIG. 2003. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- KF183 Retrieved March 8, 2017
- Qinetiq's Last Harvard Departs Air Forces Monthly p8 January 2017
- Bridgeman, Leonard. "The North American Texan." Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London: Studio, 1946. p. 251. ISBN 1 85170 493 0.
- "Team fact sheet" (PDF). Eqstra.co.za. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2014. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
Bibliography
- Becker, Dave and Brent, Winston. AT-6 Harvard in South African Service (African Aviation Series No.1). Nelspruit, South Africa:, Freeworld Publications CC, 2000. ISBN 0-9583880-2-4.
- Bergése, Francis. North American T-6 (in French). Rennes, France: Ouest France, 1979. ISBN 2-85882-183-6.
- Cortet, Pierre (January 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes" [From NA-16 to T-6: The North American Two-seat Trainer: The Fixed-gear Era]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (58): 32–37. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (February 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes (2e partie)". Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (59): 28–35. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (March 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes (3e partie)". Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (60): 37–42. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (April 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes (4e partie)". Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (61): 32–34. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (May 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes (5e partie: les NA-57 en France)" [From NA-16 to T-6: The North American Two-seat Trainer: The Fixed-gear Era (The NA-57 in France)]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (62): 22–29. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (January 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: les trains fixes (6ème partie: les NA-57 de Vichy et de la France Libre)" [From NA-16 to T-6: The North American Two-seat Trainer: The Fixed-gear Era (The NA-57s of Vichy and Free France]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (58): 31–37. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (July 1998). "Du NA-16 au T-6: les biplaces d'entrainement North American: première époque: à train fixe (dernière partie)". Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (64): 30–34. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Davis, Larry. T-6 Texan in Action (Aircraft Number 94). Carrollton, TX: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1989. ISBN 0-89747-224-1.
- Donald, David. American Warplanes of World War II. London:Aerospace Publishing, 1995. ISBN 1-874023-72-7.
- Fletcher, David C. and MacPhail, Doug. Harvard! the North American Trainers in Canada. San Josef, BC/Dundee, Ont: DCF Flying Books, 1990. ISBN 0-9693825-0-2.
- Hagedorn, Dan. North American NA-16/AT-6/SNJ (WarbirdTech Volume 11). North Branch, MN: Speciality Press, 1997. ISBN 0-933424-76-0.
- Hamlin, John F. The Harvard File. Tonbridge, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1988. ISBN 0-85130-160-6.
- Jesse. William. T-6 Texan, the Immortal Pilot Trainer. London: Osprey Publishing Ltd., 1991. ISBN 1-85532-154-8.
- Kohn, Leo J. The Story of the Texan (American Flight Manuals). Aviation Publications Co., 1975. ISBN 0-87994-034-4.
- MacPhail, Doug and Östberg, Mikael. Triple Crown BT-9: The ASJA/Saab Sk 14, A Pictorial Essay (in English/Swedish). San Josef, BC/Dundee, Ont: DCF Flying Books, 2003.
- Marchand, Patrick and Takamori, Junko. North American T-6 et derives (in French). Le Muy, France: Editions d'Along, 2004. ISBN 2-914403-21-6.
- Morgan, Len. Famous Aircraft Series: The AT-6 Harvard. New York: Arco Publishing Co., 1965.
- Nicolle, David (December 1997). "Texans sur l'arabe: la 1ère victoire aérienne syrienne" [Texans over Arabia: The First Syrian Aerial Victory]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (57): 9–13. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Olrich, Walter and Ethell, Jeffrey L. Pilot maker; the Incredible T-6. North Branch, MN: Specialty Press, 1982. ISBN 0-933424-34-5.
- Sapienza, Antonio Luis (January 1997). "Les North American T-6 "Texan" de la Force Aérienne Paraguayenne, de 1943 à nos jours" [North American T-6 Texans of the Paraguayan Air Force from 1943 to Today]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (46): 15–17. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Smith, Peter Charles. North American T-6: SNJ, Harvard and Wirraway. Ramsbury, Marlborough, Wiltshire, UK: The Crowood Press Ltd., 2000. ISBN 1-86126-382-1.
- Smith, Peter Charles. T-6: The Harvard, Texan & Wirraway – A Pictorial Record. North Branch, MN: Speciality Press, 1995. ISBN 0-7603-0191-3.
- Sonck, Jean-Pierre (January 2002). "1964: l'ONU au Congo" [The United Nations in the Congo, 1964]. Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (106): 31–36. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Sonck, Jean-Pierre (February 2002). "1964: l'ONU au Congo". Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (107): 33–38. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Spring, Ivan and Rivers, Reg. Colour schemes and special markings of the North American "Harvard" in service with the SAAF 1940 to 1995. Pretoria, SOuth Africa: Spring Air Publishers, 1996. ISBN 0-9583977-3-2.
- Starkings, Peter. From American Acorn to Japanese Oak – The tale of an unsung Japanese training aircraft with roots extending across the Pacific Ocean. Arawasi International, Asahi Process, September–December 2007, Issue 7.
- Swanborough, Gordon and Bowers, Peter M. United States Military Aircraft since 1909. London:Putnam, 1963.
- Wache, Siegfried. CCF Harvard Mk. IV (T-6) (series F-40 – Die Flugzeuge der Bundeswehr Nr.09) (in German). Buchholz, Germany: Buchholz Medien Verlag, 1989. ISBN 3-935761-09-0.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to North American T-6 Texan. |
- Warbird Alley: T-6/SNJ/Harvard page – History, photos, specs, and links
- Texan, Harvard & SNJ Registry – Lists approximately 1,200 extant T-6's by serial number
- The Canadian Harvard Aircraft Association
- Backgrounder on the Harvard 4 (includes photographs)
- AT-6: School Marm With an Attitude (pilot report)
- "A Yank at Grantham: First North American "Basic" Trainer Delivered to the R.A.F. : The Harvard Described Flight 1939
- T.O. TT-6C-2 Handbook Erection and Maintenance Instructions T-6, -6A, 6B USAF Model T-6C, T-6D Navy Models SNJ-3, SNJ-4, SNJ-5, SNJ-6 (1956)
- Pacific Warbirds: North American SNJ – History, restoration, service & more