Silesian Voivodeship
Silesian Voivodeship, or Silesia Province[3] (Polish: województwo śląskie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ ˈɕlɔ̃skʲɛ]) is a voivodeship, or province, in southern Poland, centered on the historic region known as Upper Silesia (Górny Śląsk), with Katowice serving as its capital.
Despite the Silesian Voivodeship's name, most of the historic Silesia region lies outside the present Silesian Voivodeship – divided among Lubusz, Lower Silesian, and Opole Voivodeships. The eastern half of Silesian Voivodeship (and, notably, Częstochowa in the north) was historically part of Lesser Poland.
The Voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Katowice, Częstochowa and Bielsko-Biała Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998.
It is the most densely populated voivodeship in Poland. Within the area of 12,300 square kilometres, there are almost 5 million inhabitants.[4] It is also the largest urbanised area in Central and Eastern Europe.[5] In relation to economy, over 13% of Poland's gross domestic product (GDP) is generated here, making the Silesian Voivodeship one of the wealthiest provinces in the country.[5][6][7]
History
The first Silesian Voivodeship was created in the Second Polish Republic. It had a much wider range of autonomy than other contemporary Polish voivodeships, and it covered all the historical lands of Upper Silesia which ended up in Interwar period Poland. Among these were Katowice (Kattowitz), Rybnik (Rybnik), Pszczyna (Pleß), Wodzisław (Loslau), Żory (Sohrau), Mikołów (Nikolai), Tychy (Tichau), Królewska Huta (Königshütte), Tarnowskie Góry (Tarnowitz), Miasteczko Śląskie (Georgenberg), Woźniki (Woischnik), Lubliniec (Lublinitz), Cieszyn (Teschen), Skoczów (Skotschau), and Bielsko (Bielitz). This Voivodeship did not include – as opposed to the present one – lands and cities of old pre-Partition Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Among the last ones the Southern part was included in Kraków Voivodeship Żywiec (Saybusch), Wilamowice (Wilmesau), Biała Krakowska (Biala) and Jaworzno), and the North Western part Będzin (Bendzin), Dąbrowa Górnicza (Dombrowa), Sosnowiec (Sosnowitz), Częstochowa (Tschenstochau), Myszków, Szczekociny (Schtschekotzin), Zawiercie, Sławków) belonged to Kielce Voivodeship.
After the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on 8 October 1939, Hitler published a decree called, "About division and administration of Eastern Territories". A Silesian Province (Gau Schlesien) was created, with a seat in Breslau (Wrocław). It consisted of four districts: Kattowitz, Oppeln, Breslau and Liegnitz.
The following counties were included in Kattowitz District: Kattowitz, Königshütte, Tarnowitz, Beuthen Hindenburg, Gleiwitz, Freistadt, Teschen, Biala, Bielitz, Saybusch, Pleß, Sosnowitz, Bendzin and parts of the following counties: Kranau, Olkusch, Riebnich and Wadowitz. However, according to Hitler's decree from 12 October 1939 about establishing General Government (Generalgouvernement), Tschenstochau (Częstochowa) belonged to GG.
In 1941 the Silesian Province (Provinz Schlesien) underwent new administrative division and as a result Upper Silesian Province was created (Provinz Oberschlesien):
- Kattowitz District (Regierungsbezirk Kattowitz) – entire Silesian Voivodeship without Lubinitz county, Bendzin County, part of Olkusch county, Biala county, Saybusch and parts of Kranau and Wadowitz counties.
- Oppeln District (Regierungsbezirk Oppeln) – Lubinitz county and parts of Tschenstochau and Warthenau counties.
After the War during 1945–1950 there existed a Silesian Voivodeship, commonly known as Śląsko-Dąbrowskie Voivodeship, which included a major part of today's Silesian Voivodeship. In 1950 Śląsko-Dąbrowskie Voivodeship was divided into Opole and Katowice Voivodeships. The latter one had borders similar to the borders of modern Silesian Voivodeship.
The present Silesian Voivodeship was formed in 1999 from the following voivodeships of the previous administrative division:
- Katowice Voivodeship excluding some gminas and powiats
- Bielsk Voivodeship excluding some gminas and powiats
- Częstochowa Voivodeship excluding some gminas and powiats
Geography
The Silesian Voivodeship borders both the Moravian-Silesian Region (Czech Republic), Žilina Region (Slovakia) to the south. It is also bordered by four other Polish voivodeships: those of Opole (to the west), Łódź (to the north), Świętokrzyskie (to the north-east), and Lesser Poland (to the east).
The region includes the Silesian Upland (Wyżyna Śląska) in the centre and north-west, and the Krakowsko-Częstochowska Upland (Jura Krakowsko-Czestochowska) in the north-east. The southern border is formed by the Beskidy Mountains (Beskid Śląski and Beskid Żywiecki).
The current administrative unit of Silesian Voivodeship is just a fraction of the historical Silesia which is within the borders of today's Poland (there are also fragments of Silesia in the Czech Republic and Germany). Other parts of today's Polish Silesia are administered as the Opole, the Lower Silesian Voivodeships and the Lubusz Voivodeship. On the other hand, a large part of the current administrative unit of the Silesian Voivodeship is not part of historical Silesia (e.g., Częstochowa, Zawiercie, Myszków, Jaworzno, Sosnowiec, Żywiec, Dąbrowa Górnicza, Będzin and east part of Bielsko-Biała, which are historically parts of Lesser Poland).
Demography
Silesian Voivodeship has the highest population density in the country (379 people per square kilometre, compared to the national average of 124). The region's considerable industrialisation gives it the lowest unemployment rate nationally (6.2%). The Silesian region is the most industrialized and the most urbanized region in Poland: 78% of its population live in towns and cities.
Tourism
Both the northern and southern parts of the voivodeship are surrounded by a green belt. Bielsko-Biała is enveloped by the Beskidy Mountains which are popular with winter sports fans. It offers over 150 ski lifts and 200 kilometres of ski routes. More and more slopes are illuminated and equipped with artificial snow generators. Szczyrk, Brenna, Wisła and Ustroń are the most popular winter mountain resorts. Rock climbing sites can be found in Jura Krakowsko-Czestochowska. The ruins of castles forming the Eagle Nests Trail are a famous attraction of the region. Often visited is the Black Madonna's Jasna Góra Sanctuary in Częstochowa – the annual destination of over 4 million pilgrims from all over the world. In the south-western part of the voivodeship are parks, palaces and old monasteries (Rudy Raciborskie, Wodzisław Śląski). Along the Oder River are interesting natural reserves and places for swimming during the summer.
With its more than two centuries of industrial history, the region has a number of technical heritage memorials. These include narrow and standard gauge railways, coal and silver mines, and shafts and their equipment from the 19th and 20th centuries.
Cities and towns



Due to its industrial and urban nature, the voivodeship has many cities and large towns. Of Poland's 40 most-populous cities, 12 are in Silesian Voivodeship. 19 of the cities in the voivodeship have the legal status of city-county (see powiat). In all it has 71 cities and towns (with legal city rights), listed below in descending order of population (as of 2019):[1]
- Katowice (293,636)
- Częstochowa (221,252)
- Sosnowiec (201,121)
- Gliwice (179,154)
- Zabrze (172,806)
- Bielsko-Biała (170,953)
- Bytom (165,975)
- Rybnik (138,319)
- Ruda Śląska (137,624)
- Tychy (127,664)
- Dąbrowa Górnicza (119,800)
- Chorzów (107,963)
- Jaworzno (91,263)
- Jastrzębie-Zdrój (88,808)
- Mysłowice (74,515)
- Siemianowice Śląskie (66,963)
- Żory (62,462)
- Tarnowskie Góry (61,422)
- Będzin (56,624)
- Piekary Śląskie (55,088)
- Racibórz (54,778)
- Świętochłowice (49,762)
- Zawiercie (49,334)
- Wodzisław Śląski (47,992)
- Mikołów (40,898)
- Knurów (38,310)
- Czechowice-Dziedzice (35,926)
- Cieszyn (34,513)
- Myszków (31,650)
- Czeladź (31,545)
- Żywiec (31,194)
- Czerwionka-Leszczyny (28,156)
- Pszczyna (26,804)
- Lubliniec (23,784)
- Łaziska Górne (22,298)
- Rydułtowy (21,616)
- Orzesze (21,043)
- Bieruń (19,539)
- Pyskowice (18,432)
- Radlin (17,776)
- Radzionków (16,826)
- Lędziny (16,776)
- Ustroń (16,073)
- Skoczów (14,385)
- Pszów (13,896)
- Kłobuck (12,934)
- Wisła (11,132)
- Blachownia (9,545)
- Imielin (9,175)
- Wojkowice (8,927)
- Kalety (8,607)
- Poręba (8,525)
- Miasteczko Śląskie (7,437)
- Sławków (7,017)
- Łazy (6,811)
- Koniecpol (5,910)
- Szczyrk (5,734)
- Siewierz (5,581)
- Kuźnia Raciborska (5,359)
- Żarki (4,556)
- Krzepice (4,456)
- Woźniki (4,305)
- Ogrodzieniec (4,282)
- Strumień (3,718)
- Szczekociny (3,612)
- Toszek (3,600)
- Wilamowice (3,100)
- Koziegłowy (2,245)
- Krzanowice (2,157)
- Pilica (1,936)
- Sośnicowice (1,919)
Economy
The gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was 61 billion € in 2018, accounting for 12.3% of the Polish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 22,200 € or 74% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 83% of the EU average. Silesia Voivodship is the province with the fourth highest GDP per capita in Poland.[8]
The Silesian voivodship is predominantly an industrial region. Most of the mining is derived from one of the world's largest bituminous coalfields of the Upper Silesian Industrial District (Górnośląski Okręg Przemysłowy) and the Rybnik Coal District (Rybnicki Okręg Węglowy) with its major cities Rybnik, Jastrzębie Zdrój, Żory and Wodzisław Śląski. Lead and zinc can be found near Bytom, Zawiercie and Tarnowskie Góry; iron ore and raw materials for building – near Częstochowa. The most important regional industries are: mining, iron, lead and zinc metallurgy, power industry, engineering, automobile, chemical, building materials and textile. In the past, the Silesian economy was determined by coal mining. Now, considering the investment volume, car manufacturing is becoming more and more important. The most profitable company in the region is Fiat Auto-Poland S.A. in Bielsko-Biała with a revenue of PLN 6.2 billion in 1997. Recently a new car factory has been opened by GM Opel in Gliwice. There are two Special Economic Zones in the area: Katowice and Częstochowa. The voivodship's economy consists of about 323,000, mostly small and medium-sized, enterprises employing over 3 million people. The biggest Polish steel-works "Huta Katowice" is situated in Dąbrowa Górnicza.
The unemployment rate stood at 3.9% in 2017 and was lower than the national average.[9]
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unemployment rate (in %) |
14.2 | 8.1 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 9.7 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 5.4 | 3.9 |
Transport

Katowice International Airport (in Tarnowskie Góry County) is used for domestic and international flights, Other Nearby Airports are John Paul II International Airport Kraków-Balice and Warsaw Frédéric Chopin Airport. The Silesian agglomeration railway network has the largest concentration in the country. The voivodship capital enjoys good railway and road connections with Gdańsk (motorway A1) and Ostrava (motorway A1), Kraków (motorway A4), Wrocław (motorway A4), Łódź (motorway A1) and Warsaw. It is also the crossing point for many international routes like E40 connecting Calais, Brussels, Cologne, Dresden, Wrocław, Kraków and Kiev and E75 from Scandinavia to the Balkans. A relatively short distance to Vienna facilitates cross-border co-operation and may positively influence the process of European integration. Linia Hutnicza Szerokotorowa (known by its acronym LHS, English: Broad gauge metallurgy line) in Sławków is the longest broad gauge railway line in Poland. The line runs on a single track for almost 400 km from the Polish-Ukrainian border, crossing it just east of Hrubieszów. It is the westernmost broad gauge railway line in Europe that is connected to the broad gauge rail system of the countries of the former Soviet Union.
Education
There are eleven public universities in the voivodship. The biggest university is the University of Silesia in Katowice, with 43,000 students. The region's capital boasts the Medical University, The Karol Adamiecki University of Economics in Katowice, the University of Music in Katowice, the Physical Education Academy and the Academy of Fine Arts. Częstochowa is the seat of the Częstochowa University of Technology and Pedagogic University. The Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice is nationally renowned. Bielsko-Biała is home of the Technical-Humanistic Academy. In addition, 17 new private schools have been established in the region.
There are over 300,000 people currently studying in the Voivodeship.
Politics
.jpg.webp)
The Silesian voivodeship's government is headed by the province's voivode (governor) who is appointed by the Polish Prime Minister. The voivode is then assisted in performing his duties by the voivodeship's marshal, who is the appointed speaker for the voivodeship's executive and is elected by the sejmik (provincial assembly). The current voivode of Silesia is Jarosław Wieczorek, whilst the present marshal is Wojciech Saługa.
The Sejmik of Silesia consists of 48 members.
2018 election
| Political groups[10] | Mandates | |
|---|---|---|
| Prawo i Sprawiedliwość | 22 | |
| Koalicja Obywatelska | 20 | |
| SLD Lewica Razem | 2 | |
| Polskie Stronnictwo Ludowe | 1 | |
| Total | 45 |
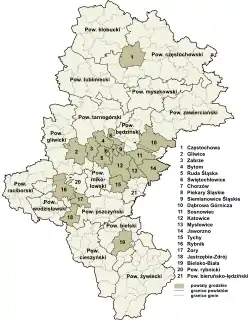
Administrative division
Silesian Voivodeship is divided into 36 counties (powiats). These include 19 city counties (far more than any other voivodeship) and 17 land counties. The counties are further divided into 167 gminas.
The counties are listed in the following table (ordering within categories is by decreasing population).
| English and Polish names |
Area (km²) |
Population (2019) |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas |
| City counties | |||||
| Katowice | 165 | 293,636 | 1 | ||
| Częstochowa | 160 | 221,252 | 1 | ||
| Sosnowiec | 91 | 201,121 | 1 | ||
| Gliwice | 134 | 179,154 | 1 | ||
| Zabrze | 80 | 172,806 | 1 | ||
| Bielsko-Biała | 125 | 170,953 | 1 | ||
| Bytom | 69 | 165,975 | 1 | ||
| Rybnik | 148 | 138,319 | 1 | ||
| Ruda Śląska | 78 | 137,624 | 1 | ||
| Tychy | 82 | 127,664 | 1 | ||
| Dąbrowa Górnicza | 188 | 119,800 | 1 | ||
| Chorzów | 33 | 107,963 | 1 | ||
| Jaworzno | 152 | 91,263 | 1 | ||
| Jastrzębie-Zdrój | 85 | 88,808 | 1 | ||
| Mysłowice | 66 | 74,515 | 1 | ||
| Siemianowice Śląskie | 25 | 66,963 | 1 | ||
| Żory | 65 | 62,462 | 1 | ||
| Piekary Śląskie | 40 | 55,088 | 1 | ||
| Świętochłowice | 13 | 49,762 | 1 | ||
| Land counties | |||||
| Cieszyn County powiat cieszyński |
730 | 178,145 | Cieszyn | Ustroń, Skoczów, Wisła, Strumień | 12 |
| Bielsko County powiat bielski |
457 | 165,374 | Bielsko-Biała* | Czechowice-Dziedzice, Szczyrk, Wilamowice | 10 |
| Wodzisław County powiat wodzisławski |
287 | 157,346 | Wodzisław Śląski | Rydułtowy, Radlin, Pszów | 9 |
| Żywiec County powiat żywiecki |
1,040 | 152,877 | Żywiec | 15 | |
| Będzin County powiat będziński |
368 | 148,516 | Będzin | Czeladź, Wojkowice, Sławków, Siewierz | 8 |
| Tarnowskie Góry County powiat tarnogórski |
643 | 140,022 | Tarnowskie Góry | Radzionków, Kalety, Miasteczko Śląskie | 9 |
| Częstochowa County powiat częstochowski |
1,519 | 134,637 | Częstochowa* | Blachownia, Koniecpol | 16 |
| Zawiercie County powiat zawierciański |
1,003 | 118,020 | Zawiercie | Poręba, Łazy, Ogrodzieniec, Szczekociny, Pilica | 10 |
| Gliwice County powiat gliwicki |
663 | 115,571 | Gliwice* | Knurów, Pyskowice, Toszek, Sośnicowice | 8 |
| Pszczyna County powiat pszczyński |
473 | 111,324 | Pszczyna | 6 | |
| Racibórz County powiat raciborski |
544 | 108,388 | Racibórz | Kuźnia Raciborska, Krzanowice | 8 |
| Mikołów County powiat mikołowski |
232 | 98,689 | Mikołów | Łaziska Górne, Orzesze | 5 |
| Kłobuck County powiat kłobucki |
889 | 84,762 | Kłobuck | Krzepice | 9 |
| Rybnik County powiat rybnicki |
225 | 78,148 | Rybnik* | Czerwionka-Leszczyny | 5 |
| Lubliniec County powiat lubliniecki |
822 | 76,470 | Lubliniec | Woźniki | 8 |
| Myszków County powiat myszkowski |
479 | 70,959 | Myszków | Żarki, Koziegłowy | 5 |
| Bieruń-Lędziny County powiat bieruńsko-lędziński |
157 | 59,715 | Bieruń | Lędziny, Imielin | 5 |
| * seat not part of the county | |||||
Protected areas
.jpg.webp)
Protected areas in Silesian Voivodeship include eight areas designated as Landscape Parks:
- Eagle Nests Landscape Park (partly in Lesser Poland Voivodeship)
- Little Beskids Landscape Park (partly in Lesser Poland Voivodeship)
- Rudy Landscape Park
- Silesian Beskids Landscape Park
- Stawki Landscape Park
- Upper Liswarta Forests Landscape Park
- Załęcze Landscape Park (partly in Łódź Voivodeship)
- Żywiec Landscape Park
See also
References
- "Population. Size and structure and vital statistics in Poland by territorial divison in 2019. As of 30th June". stat.gov.pl. Statistics Poland. 2019-10-15. Retrieved 2020-02-14.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- Arkadiusz Belczyk,Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine [Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English], 2002–2006.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-08-16. Retrieved 2017-07-24.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Śląskiego, Urząd Marszałkowski Województwa. "Województwo Śląskie - Śląskie. Pozytywna energia" (PDF). www.silesia-europa.pl. Retrieved 15 March 2018.
- "Śląski Urząd Wojewódzki w Katowicach - strona oficjalna". Archived from the original on 19 October 2009. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- Art4net. "The Śląskie Voivodeship". Archived from the original on 30 June 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- "Regional Unemployment by NUTS2 Region". Eurostat.
- Serwis PKW – Wybory 2018
External links
- The Website of Silesia
- Województwo Śląskie Official website


.png.webp)