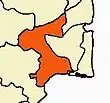
Thanjavur Maratha kingdom
The Thanjavur Maratha kingdom of bhonsle dynasty was a principality of Tamil Nadu between the 17th and 19th centuries. Their native language was Thanjavur Marathi. Venkoji was the founder of the dynasty.
Maratha Kingdom of Thanjavur Princely State of Thanjavur | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1674–1855 | |||||||||||
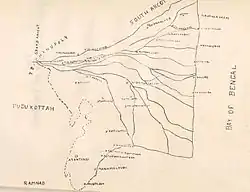 Map of Tanjore | |||||||||||
 Approximate extent of the Thanjavur Maratha Kingdom, at the time of its accession to the British in 1798 | |||||||||||
| Status | Kingdom from 1674 to 1799. Princely state under the paramountcy of the British Raj (1799–1855) | ||||||||||
| Capital | Tanjore | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Marathi, Telugu, Sanskrit, Tamil | ||||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism | ||||||||||
| Government | Principality | ||||||||||
| Ruler | |||||||||||
• (first) 1674 - 1684 | Venkoji | ||||||||||
• (last) 1832 - 1855 | Shivaji II of Thanjavur | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| 1674 | |||||||||||
• Earliest records | 1674 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1855 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 9,600 km2 (3,700 sq mi) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||||||
Maratha conquest of Thanjavur
Following the demise of Chola rule in the 13th century (specifically around 1279), the Thanjavur area came under the rule of the Pandyas and then, following the invasion of Malik Kafur, it fell into disorder.
Pandya nadu very quickly reasserted their independence and forced the Delhi Sultan to flee Thanjavur. Soon afterwards, however, they were conquered by the Vijayanagara Empire. The Emperor appointed his trusted Kin, who belonged to the Telugu Balija caste as Governors (Nayakas) of Madurai and Tanjavur. An internal family squabble between Chokkanatha Nayak of Madurai Nayak dynasty and his uncle Vijayaraghava Nayaka of Tanjavur, let to a war, and eventually defeated Thanjavur. The rule of the Thanjavur Nayaks lasted until 1673 when Chokkanatha Nayak the ruler of Madurai invaded Thanjavur and killed its ruler, Vijayaraghava.
Chokkanatha placed his brother Alagiri on the throne of Thanjavur, but within a year the latter threw off his allegiance, and Chokkanatha was forced to recognise the independence of Thanjavur. A son of Vijaya Raghava induced the Bijapur Sultan to help him get back the Thanjavur throne. In 1675, the Sultan of Bijapur sent a force commanded by the Maratha general Venkoji (alias Ekoji) to recapture the kingdom from the new invader. Venkoji defeated Alagiri, and occupied Thanjavur. He did not, however, place his protege on the throne as instructed by the Bijapur Sultan, but seized the kingdom and made himself king. Thus began the rule of the Marathas over Thanjavur.
Maratha kings
| Part of a series on |
| History of Tamil Nadu |
|---|
 |
Venkoji
Venkoji, a half-brother of the Maratha king Shivaji, was the first Raja of Thanjavur from the Bhosale dynasty. It is believed that he took over the administration of Thanjavur in April 1674 and ruled until 1684. During his reign, Shivaji invaded Gingee and Thanjavur in 1676–1677 and made his brother Santaji the ruler of all lands to the north of the Coleroon. During the last years of his reign, Venkoji also allied with Chokkanatha of Madurai to repulse an invasion from Mysore.
Shahuji I
Shahuji I was the eldest son of Venkoji and he ascended the throne at the age of twelve. During his reign, the Mughals occupied the Coromandel coast and Tiruchirapalli and forced him to pay tribute. Shahuji was a patron of literature. During his reign, there were frequent skirmishes and battles with the Raja of Madurai and Ramnad for control of the border lands.
Serfoji I
Serfoji I was a younger son of Venkoji and he ruled from 1712 to 1728. His rule was marked by regular warfare and disputes with the Madurai Nayak.
Tukkoji
Tukkoji, a younger brother of Serfoji I, ruled Thanjavur from 1728 to 1736. His reign witnessed the invasion of Chanda Sahib and he is credited with having repulsed a Muslim invasion of Madurai.
Pratapsingh
A period of anarchy followed the death of Tukkoji and came to an end when Pratapsingh came to the throne in 1739. He ruled until 1763. He allied with Muhammad Ali, the Nawab of the Carnatic, and aided the British East India Company against the French East India Company in the Carnatic Wars and the Seven Years' War. He was the last king to be addressed to be the Directors of the British East India Company as "His Majesty". In 1762, a tripartite treaty was signed between Thanjavur, Carnatic and the British by which he became a vassal of the Nawab of the Carnatic.
Thuljaji
Thuljaji was a very weak ruler and the last independent ruler of Thanjavur. In 1773, Thanjavur was annexed by the Nawab of the Carnatic who ruled till 1776. The throne was restored to him by the Directors of the British East India Company. But his restoration came at a heavy price as it deprived him of his independence.
Serfoji II
Thuljaji was succeeded by his teenage son Serfoji II in 1787. Soon afterwards, he was deposed by his uncle and regent Amarsingh who seized the throne for himself. With the help of the British, Serfoji II recovered the throne in 1798. A subsequent treaty forced him to hand over the reins of the kingdom to the British East India Company, becoming part of the Tanjore District (Madras Presidency). The district collectorate system was installed thereafter to manage the public revenues. Serfoji II was however left in control of the Fort and the surrounding areas. He reigned till 1832. His reign is noted for the literary, scientific and technological accomplishments of the Tanjore country.
Shivaji
Shivaji was the last Maratha ruler of Thanjavur and reigned from 1832 to 1855. He was a weak and feeble prince with barely any authority. As his first wife did not have any male heir, the Queen adopted her nephew, and the adoption took place after the Maharaja's (Shivaji I) death in 1855. The British did not accept this adoption and Thanjavur was annexed by them as per the provisions of the Doctrine of Lapse.
Literature

The Thanjavur Maratha Rajas favoured Sanskrit and Telugu to such an extent that classical Tamil began to decline. Most of the plays were in Sanskrit. Venkoji, the first ruler of the Bhonsle dynasty composed a 'Dvipada' Ramayana in Telugu. His son Shahuji was a great patron of learning and of literature. Most of the Thanjavur Maratha literature is from his period. Most of them were versions of the Ramayana or plays and short stories of a historical nature. Sanskrit and Telugu were the languages used in most of these plays while there were some Tamil 'koothu' as well. Advaita Kirtana is one of the prominent works from this period. Later Thanjavur rulers like Serfoji II and Shivaji immersed themselves in learning and literary pursuits when they were dispossessed of their empire. Serfoji built the Saraswathi Mahal Library within the precincts of the palace to house his enormous book and manuscript collection. Apart from Indian languages, Serfoji II was proficient in English, French, Dutch, Greek and Latin as well.
Administration
The king was assisted in the administration of his country by a council of ministers. The supreme head of this council of ministers was a Mantri or Dalavoy. The Dalavoy was also the Commander-in-chief of the Army. Next in importance at the court was a Pradhani or Dewan also called Dabir Pandit. The country was divided into subahs, seemais and maganams in the decreasing order of size and importance. The five subahs of the country were Pattukkottai, Mayavaram, Kumbakonam, Mannargudi and Tiruvadi.
Economy
The ruler collected his taxes from the people through his mirasdars or puttackdars. They were collected right from the village level onwards and were based on the agricultural produce of the village. Rice was one of the primary crops in the region and the land used for cultivation was owned by big landlords. It was Anatharama Sashtry who proposed collecting taxes to improve conditions for the poor. No foreign trade was carried out. The only foreign trade in the country was carried out by European traders who paid a particular amount of money as rent to the Raja. The currency system used was that of a chakram or pon (1 chakram = one and three-fourths of a British East India Company rupee). Other systems of coinage used were that of pagoda (1 pagoda = three and a half Company rupees), a big panam (one-sixth of a Company rupee) and a small panam (one-thirteenth of a Company rupee).