Three-body problem
In physics and classical mechanics, the three-body problem is the problem of taking the initial positions and velocities (or momenta) of three point masses and solving for their subsequent motion according to Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation.[1] The three-body problem is a special case of the n-body problem. Unlike two-body problems, no general closed-form solution exists,[1] as the resulting dynamical system is chaotic for most initial conditions, and numerical methods are generally required.
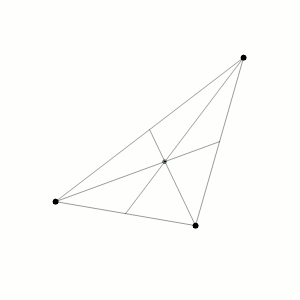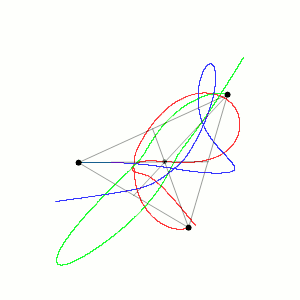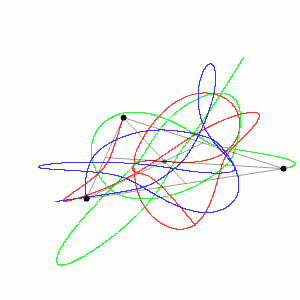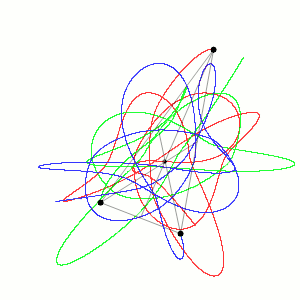
Historically, the first specific three-body problem to receive extended study was the one involving the Moon, the Earth, and the Sun.[2] In an extended modern sense, a three-body problem is any problem in classical mechanics or quantum mechanics that models the motion of three particles.
Mathematical description
The mathematical statement of the three-body problem can be given in terms of the Newtonian equations of motion for vector positions of three gravitationally interacting bodies with masses :
where is the gravitational constant.[3][4] This is a set of 9 second-order differential equations. The problem can also be stated equivalently in the Hamiltonian formalism, in which case it is described by a set of 18 first-order differential equations, one for each component of the positions and momenta :
where is the Hamiltonian:
In this case is simply the total energy of the system, gravitational plus kinetic.
Restricted three-body problem
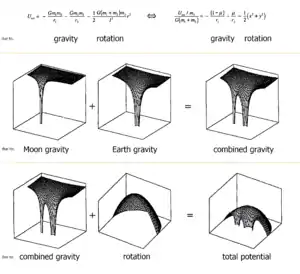
In the restricted three-body problem,[3] a body of negligible mass (the "planetoid") moves under the influence of two massive bodies. Having negligible mass, the force that the planetoid exerts on the two massive bodies may be neglected, and the system can be analysed and can therefore be described in terms of a two-body motion. Usually this two-body motion is taken to consist of circular orbits around the center of mass, and the planetoid is assumed to move in the plane defined by the circular orbits.
The restricted three-body problem is easier to analyze theoretically than the full problem. It is of practical interest as well since it accurately describes many real-world problems, the most important example being the Earth–Moon–Sun system. For these reasons, it has occupied an important role in the historical development of the three-body problem.
Mathematically, the problem is stated as follows. Let be the masses of the two massive bodies, with (planar) coordinates and , and let be the coordinates of the planetoid. For simplicity, choose units such that the distance between the two massive bodies, as well as the gravitational constant, are both equal to . Then, the motion of the planetoid is given by
where . In this form the equations of motion carry an explicit time dependence through the coordinates . However, this time-dependence can be removed through a transformation to a rotating reference frame, which simplifies any subsequent analysis.
Solutions
General solution

There is no general closed-form solution to the three-body problem, meaning there is no general solution that can be expressed in terms of a finite number of standard mathematical operations.[1] Moreover, the motion of three bodies is generally non-repeating, except in special cases.[5]
However, in 1912 the Finnish mathematician Karl Fritiof Sundman proved that there exists an analytic solution to the three-body problem in the form of a power series in terms of powers of t1/3.[6] This series converges for all real t, except for initial conditions corresponding to zero angular momentum. In practice, the latter restriction is insignificant since initial conditions with zero angular momentum are rare, having Lebesgue measure zero.
An important issue in proving this result is the fact that the radius of convergence for this series is determined by the distance to the nearest singularity. Therefore, it is necessary to study the possible singularities of the three-body problems. As will be briefly discussed below, the only singularities in the three-body problem are binary collisions (collisions between two particles at an instant) and triple collisions (collisions between three particles at an instant).
Collisions, whether binary or triple (in fact, any number), are somewhat improbable, since it has been shown that they correspond to a set of initial conditions of measure zero. However, there is no criterion known to be put on the initial state in order to avoid collisions for the corresponding solution. So Sundman's strategy consisted of the following steps:
- Using an appropriate change of variables to continue analyzing the solution beyond the binary collision, in a process known as regularization.
- Proving that triple collisions only occur when the angular momentum L vanishes. By restricting the initial data to L ≠ 0, he removed all real singularities from the transformed equations for the three-body problem.
- Showing that if L ≠ 0, then not only can there be no triple collision, but the system is strictly bounded away from a triple collision. This implies, by using Cauchy's existence theorem for differential equations, that there are no complex singularities in a strip (depending on the value of L) in the complex plane centered around the real axis (shades of Kovalevskaya).
- Find a conformal transformation that maps this strip into the unit disc. For example, if s = t1/3 (the new variable after the regularization) and if |ln s| ≤ β, then this map is given by
This finishes the proof of Sundman's theorem.
Unfortunately, the corresponding series converges very slowly. That is, obtaining a value of meaningful precision requires so many terms that this solution is of little practical use. Indeed, in 1930, David Beloriszky calculated that if Sundman's series were to be used for astronomical observations, then the computations would involve at least 108000000 terms.[7]
Special-case solutions
In 1767, Leonhard Euler found three families of periodic solutions in which the three masses are collinear at each instant. See Euler's three-body problem.
In 1772, Lagrange found a family of solutions in which the three masses form an equilateral triangle at each instant. Together with Euler's collinear solutions, these solutions form the central configurations for the three-body problem. These solutions are valid for any mass ratios, and the masses move on Keplerian ellipses. These four families are the only known solutions for which there are explicit analytic formulae. In the special case of the circular restricted three-body problem, these solutions, viewed in a frame rotating with the primaries, become points which are referred to as L1, L2, L3, L4, and L5, and called Lagrangian points, with L4 and L5 being symmetric instances of Lagrange's solution.
In work summarized in 1892–1899, Henri Poincaré established the existence of an infinite number of periodic solutions to the restricted three-body problem, together with techniques for continuing these solutions into the general three-body problem.
In 1893, Meissel stated what is now called the Pythagorean three-body problem: three masses in the ratio 3:4:5 are placed at rest at the vertices of a 3:4:5 right triangle. Burrau[8] further investigated this problem in 1913. In 1967 Victor Szebehely and C. Frederick Peters established eventual escape for this problem using numerical integration, while at the same time finding a nearby periodic solution.[9]
In the 1970s, Michel Hénon and Roger A. Broucke each found a set of solutions that form part of the same family of solutions: the Broucke–Henon–Hadjidemetriou family. In this family the three objects all have the same mass and can exhibit both retrograde and direct forms. In some of Broucke's solutions two of the bodies follow the same path.[10]
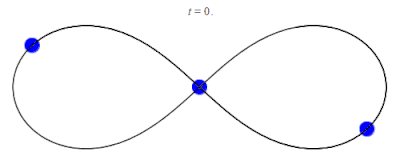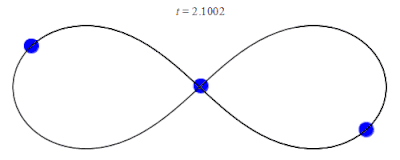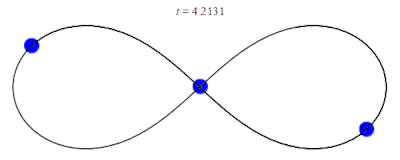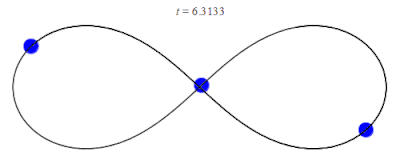
In 1993, a zero angular momentum solution with three equal masses moving around a figure-eight shape was discovered numerically by physicist Cris Moore at the Santa Fe Institute.[12] Its formal existence was later proved in 2000 by mathematicians Alain Chenciner and Richard Montgomery.[13][14] The solution has been shown numerically to be stable for small perturbations of the mass and orbital parameters, which raises the intriguing possibility that such orbits could be observed in the physical universe. However, it has been argued that this occurrence is unlikely since the domain of stability is small. For instance, the probability of a binary–binary scattering event resulting in a figure-8 orbit has been estimated to be a small fraction of 1%.[15]
In 2013, physicists Milovan Šuvakov and Veljko Dmitrašinović at the Institute of Physics in Belgrade discovered 13 new families of solutions for the equal-mass zero-angular-momentum three-body problem.[5][10]
In 2015, physicist Ana Hudomal discovered 14 new families of solutions for the equal-mass zero-angular-momentum three-body problem.[16]
In 2017, researchers Xiaoming Li and Shijun Liao found 669 new periodic orbits of the equal-mass zero-angular-momentum three-body problem.[17] This was followed in 2018 by an additional 1223 new solutions for a zero-momentum system of unequal masses.[18]
In 2018, Li and Liao reported 234 solutions to the unequal-mass "free-fall" three body problem.[19] The free fall formulation of the three body problem starts with all three bodies at rest. Because of this, the masses in a free-fall configuration do not orbit in a closed "loop", but travel forwards and backwards along an open "track".
Numerical approaches
Using a computer, the problem may be solved to arbitrarily high precision using numerical integration although high precision requires a large amount of CPU time. In 2019, Breen et al. announced a fast neural network solver, trained using a numerical integrator.[20]
History
The gravitational problem of three bodies in its traditional sense dates in substance from 1687, when Isaac Newton published his Principia (Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica). In Proposition 66 of Book 1 of the Principia, and its 22 Corollaries, Newton took the first steps in the definition and study of the problem of the movements of three massive bodies subject to their mutually perturbing gravitational attractions. In Propositions 25 to 35 of Book 3, Newton also took the first steps in applying his results of Proposition 66 to the lunar theory, the motion of the Moon under the gravitational influence of the Earth and the Sun.
The physical problem was addressed by Amerigo Vespucci and subsequently by Galileo Galilei; in 1499, Vespucci used knowledge of the position of the Moon to determine his position in Brazil. It became of technical importance in the 1720s, as an accurate solution would be applicable to navigation, specifically for the determination of longitude at sea, solved in practice by John Harrison's invention of the marine chronometer. However the accuracy of the lunar theory was low, due to the perturbing effect of the Sun and planets on the motion of the Moon around the Earth.
Jean le Rond d'Alembert and Alexis Clairaut, who developed a longstanding rivalry, both attempted to analyze the problem in some degree of generality; they submitted their competing first analyses to the Académie Royale des Sciences in 1747.[21] It was in connection with their research, in Paris during the 1740s, that the name "three-body problem" (French: Problème des trois Corps) began to be commonly used. An account published in 1761 by Jean le Rond d'Alembert indicates that the name was first used in 1747.[22]
Other problems involving three bodies
The term 'three-body problem' is sometimes used in the more general sense to refer to any physical problem involving the interaction of three bodies.
A quantum mechanical analogue of the gravitational three-body problem in classical mechanics is the helium atom, in which a helium nucleus and two electrons interact according to the inverse-square Coulomb interaction. Like the gravitational three-body problem, the helium atom cannot be solved exactly.[23]
In both classical and quantum mechanics, however, there exist nontrivial interaction laws besides the inverse-square force which do lead to exact analytic three-body solutions. One such model consists of a combination of harmonic attraction and a repulsive inverse-cube force.[24] This model is considered nontrivial since it is associated with a set of nonlinear differential equations containing singularities (compared with, e.g., harmonic interactions alone, which lead to an easily solved system of linear differential equations). In these two respects it is analogous to (insoluble) models having Coulomb interactions, and as a result has been suggested as a tool for intuitively understanding physical systems like the helium atom.[24][25]
The gravitational three-body problem has also been studied using general relativity. Physically, a relativistic treatment becomes necessary in systems with very strong gravitational fields, such as near the event horizon of a black hole. However, the relativistic problem is considerably more difficult than in Newtonian mechanics, and sophisticated numerical techniques are required. Even the full two-body problem (i.e. for arbitrary ratio of masses) does not have a rigorous analytic solution in general relativity.[26]
n-body problem
The three-body problem is a special case of the n-body problem, which describes how n objects will move under one of the physical forces, such as gravity. These problems have a global analytical solution in the form of a convergent power series, as was proven by Karl F. Sundman for n = 3 and by Qiudong Wang for n > 3 (see n-body problem for details). However, the Sundman and Wang series converge so slowly that they are useless for practical purposes;[27] therefore, it is currently necessary to approximate solutions by numerical analysis in the form of numerical integration or, for some cases, classical trigonometric series approximations (see n-body simulation). Atomic systems, e.g. atoms, ions, and molecules, can be treated in terms of the quantum n-body problem. Among classical physical systems, the n-body problem usually refers to a galaxy or to a cluster of galaxies; planetary systems, such as stars, planets, and their satellites, can also be treated as n-body systems. Some applications are conveniently treated by perturbation theory, in which the system is considered as a two-body problem plus additional forces causing deviations from a hypothetical unperturbed two-body trajectory.
In popular culture
- The problem is a plot device in the science fiction trilogy Remembrance of Earth's Past by Chinese author Cixin Liu. The problem's name is the title of the first volume, and is used also for the trilogy as a whole, especially by Chinese readership.[28]
See also
References
- Barrow-Green, June (2008), "The Three-Body Problem", in Gowers, Timothy; Barrow-Green, June; Leader, Imre (eds.), The Princeton Companion to Mathematics, Princeton University Press, pp. 726–728
- "Historical Notes: Three-Body Problem". Retrieved 19 July 2017.
- Barrow-Green, June (1997). Poincaré and the Three Body Problem. American Mathematical Soc. pp. 8–12. Bibcode:1997ptbp.book.....B. ISBN 978-0-8218-0367-7.
- The Three-Body Problem
- Cartwright, Jon (8 March 2013). "Physicists Discover a Whopping 13 New Solutions to Three-Body Problem". Science Now. Retrieved 2013-04-04.
- Barrow-Green, J. (2010). The dramatic episode of Sundman, Historia Mathematica 37, pp. 164–203.
- Beloriszky, D. (1930). "Application pratique des méthodes de M. Sundman à un cas particulier du problème des trois corps". Bulletin Astronomique. Série 2. 6: 417–434. Bibcode:1930BuAst...6..417B.
- Burrau (1913). "Numerische Berechnung eines Spezialfalles des Dreikörperproblems". Astronomische Nachrichten. 195 (6): 113–118. Bibcode:1913AN....195..113B. doi:10.1002/asna.19131950602.
- Victor Szebehely; C. Frederick Peters (1967). "Complete Solution of a General Problem of Three Bodies". Astronomical Journal. 72: 876. Bibcode:1967AJ.....72..876S. doi:10.1086/110355.
- Šuvakov, M.; Dmitrašinović, V. "Three-body Gallery". Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- Here the gravitational constant G has been set to 1, and the initial conditions are r1(0) = −r3(0) = (−0.97000436, 0.24308753); r2(0) = (0,0); v1(0) = v3(0) = (0.4662036850, 0.4323657300); v2(0) = (−0.93240737, −0.86473146). The values are obtained from Chenciner & Montgomery (2000).
- Moore, Cristopher (1993), "Braids in classical dynamics" (PDF), Physical Review Letters, 70 (24): 3675–3679, Bibcode:1993PhRvL..70.3675M, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.3675, PMID 10053934
- Chenciner, Alain; Montgomery, Richard (2000). "A remarkable periodic solution of the three-body problem in the case of equal masses". Annals of Mathematics. Second Series. 152 (3): 881–902. arXiv:math/0011268. Bibcode:2000math.....11268C. doi:10.2307/2661357. JSTOR 2661357. S2CID 10024592.
- Montgomery, Richard (2001), "A new solution to the three-body problem" (PDF), Notices of the American Mathematical Society, 48: 471–481
- Heggie, Douglas C. (2000), "A new outcome of binary–binary scattering", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 318 (4): L61–L63, arXiv:astro-ph/9604016, Bibcode:2000MNRAS.318L..61H, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.04027.x
- Hudomal, Ana (October 2015). "New periodic solutions to the three-body problem and gravitational waves" (PDF). Master of Science Thesis at the Faculty of Physics, Belgrade University. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- Li, Xiaoming; Liao, Shijun (December 2017). "More than six hundreds new families of Newtonian periodic planar collisionless three-body orbits". Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. 60 (12): 129511. arXiv:1705.00527. Bibcode:2017SCPMA..60l9511L. doi:10.1007/s11433-017-9078-5. ISSN 1674-7348. S2CID 84838204.
- Li, Xiaoming; Jing, Yipeng; Liao, Shijun (13 September 2017). "The 1223 new periodic orbits of planar three-body problem with unequal mass and zero angular momentum". arXiv:1709.04775. doi:10.1093/pasj/psy057. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Li, Xiaoming; Liao, Shijun (2019). "Collisionless periodic orbits in the free-fall three-body problem". New Astronomy. 70: 22–26. arXiv:1805.07980. Bibcode:2019NewA...70...22L. doi:10.1016/j.newast.2019.01.003. S2CID 89615142.
- Breen, Philip G.; Foley, Christopher N.; Boekholt, Tjarda; Portegies Zwart, Simon (2019). "Newton vs the machine: Solving the chaotic three-body problem using deep neural networks". arXiv:1910.07291. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa713. S2CID 204734498. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - The 1747 memoirs of both parties can be read in the volume of Histoires (including Mémoires) of the Académie Royale des Sciences for 1745 (belatedly published in Paris in 1749) (in French):
- Clairaut: "On the System of the World, according to the principles of Universal Gravitation" (at pp. 329–364); and
- d'Alembert: "General method for determining the orbits and the movements of all the planets, taking into account their mutual actions" (at pp. 365–390).
- Jean le Rond d'Alembert, in a paper of 1761 reviewing the mathematical history of the problem, mentions that Euler had given a method for integrating a certain differential equation "in 1740 (seven years before there was question of the Problem of Three Bodies)": see d'Alembert, "Opuscules Mathématiques", vol. 2, Paris 1761, Quatorzième Mémoire ("Réflexions sur le Problème des trois Corps, avec de Nouvelles Tables de la Lune ...") pp. 329–312, at sec. VI, p. 245.
- Griffiths, David J. (2004). Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 311. ISBN 978-0-13-111892-8. OCLC 40251748.
- Crandall, R.; Whitnell, R.; Bettega, R. (1984). "Exactly soluble two‐electron atomic model". American Journal of Physics. 52 (5): 438–442. Bibcode:1984AmJPh..52..438C. doi:10.1119/1.13650.
- Calogero, F. (1969). "Solution of a Three‐Body Problem in One Dimension". Journal of Mathematical Physics. 10 (12): 2191–2196. Bibcode:1969JMP....10.2191C. doi:10.1063/1.1664820.
- Musielak, Z E; Quarles, B (2014). "The three-body problem". Reports on Progress in Physics. 77 (6): 065901. arXiv:1508.02312. Bibcode:2014RPPh...77f5901M. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/77/6/065901. ISSN 0034-4885. PMID 24913140. S2CID 38140668.
- Florin Diacu. "The Solution of the n-body Problem", The Mathematical Intelligencer, 1996.
- Qin, Amy (November 10, 2014). "In a Topsy-Turvy World, China Warms to Sci-Fi". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 9, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2020.
Further reading
- Poincaré, H. (1967). New Methods of Celestial Mechanics, 3 vols. (English trans.). American Institute of Physics. ISBN 978-1-56396-117-5.
- Aarseth, S. J. (2003). Gravitational n-Body Simulations. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43272-6.
- Bagla, J. S. (2005). "Cosmological N-body simulation: Techniques, scope and status". Current Science. 88: 1088–1100. arXiv:astro-ph/0411043. Bibcode:2005CSci...88.1088B.
- Chambers, J. E.; Wetherill, G. W. (1998). "Making the Terrestrial Planets: N-Body Integrations of Planetary Embryos in Three Dimensions". Icarus. 136 (2): 304–327. Bibcode:1998Icar..136..304C. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.64.7797. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.6007.
- Efstathiou, G.; Davis, M.; White, S. D. M.; Frenk, C. S. (1985). "Numerical techniques for large cosmological N-body simulations". Astrophysical Journal. 57: 241–260. Bibcode:1985ApJS...57..241E. doi:10.1086/191003.
- Hulkower, Neal D. (1978). "The Zero Energy Three Body Problem". Indiana University Mathematics Journal. 27 (3): 409–447. Bibcode:1978IUMJ...27..409H. doi:10.1512/iumj.1978.27.27030.
- Hulkower, Neal D. (1980). "Central Configurations and Hyperbolic-Elliptic Motion in the Three-Body Problem". Celestial Mechanics. 21 (1): 37–41. Bibcode:1980CeMec..21...37H. doi:10.1007/BF01230244. S2CID 123404551.
- Moore, Cristopher (1993), "Braids in classical dynamics" (PDF), Physical Review Letters, 70 (24): 3675–3679, Bibcode:1993PhRvL..70.3675M, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.3675, PMID 10053934.
- Šuvakov, Milovan; Dmitrašinović, V. (2013). "Three Classes of Newtonian Three-Body Planar Periodic Orbits". Physical Review Letters. 110 (10): 114301. arXiv:1303.0181. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.110k4301S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.114301. PMID 25166541. S2CID 118554305.
- Li, Xiaoming; Liao, Shijun (2014). "On the stability of the three classes of Newtonian three-body planar periodic orbits". Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. 57 (11): 2121–2126. arXiv:1312.6796. Bibcode:2014SCPMA..57.2121L. doi:10.1007/s11433-014-5563-5. S2CID 73682020.
External links
- Chenciner, Alain (2007). "Three body problem". Scholarpedia. 2 (10): 2111. Bibcode:2007SchpJ...2.2111C. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.2111.