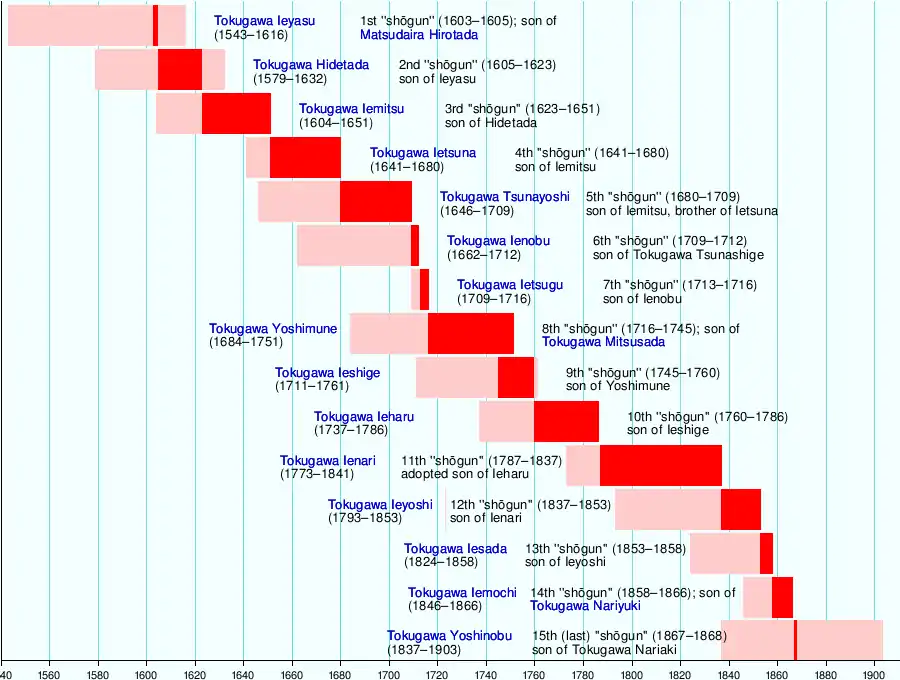
Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (徳川家康, January 31, 1543 – June 1, 1616) was the founder and first shōgun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hideyoshi.

Son of a minor daimyo, Tokugawa once lived as a hostage, on behalf of his father, under another Daimyo.[1] He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as vassal and general under Oda Nobunaga,[1] building up his strength.[2] After Oda's death, Tokugawa was briefly a rival of fellow Oda subordinate Toyotomi Hideyoshi, before declaring allegiance to Toyotomi and fighting on his behalf.[1] Under Toyotomi, Tokugawa was relocated to the Kanto plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in Osaka.[1] He built his castle in the fishing village of Edo (now Tokyo).[1] He became the most powerful daimyo and the most senior officer under the Toyotomi regime.[2]
Tokugawa preserved his strength in Toyotomi's failed attempt to conquer Korea.[1] After Toyotomi's death, Ieyasu seized power in 1600, after the Battle of Sekigahara.[1] He received appointment as shōgun in 1603, and voluntarily abdicated from office in 1605, but remained in power until his death in 1616. He implemented a set of careful rules known as the bakuhan system, designed to keep the daimyos and samurai in check under the Tokugawa Shogunate.[1][2]
His given name is sometimes spelled Iyeyasu,[3][4] according to the historical pronunciation of the kana character we. Ieyasu was posthumously enshrined at Nikkō Tōshō-gū with the name Tōshō Daigongen (東照大權現).
Background
During the Muromachi period, the Matsudaira clan controlled a portion of Mikawa Province (the eastern half of modern Aichi Prefecture). Ieyasu's father, Matsudaira Hirotada, was a minor local warlord based at Okazaki Castle who controlled a portion of the Tōkaidō highway linking Kyoto with the eastern provinces. His territory was sandwiched between stronger and predatory neighbors, including the Imagawa clan based in Suruga Province to the east and the Oda clan to the west. Hirotada's main enemy was Oda Nobuhide, the father of Oda Nobunaga.[5]
Early life (1542–1556)

Tokugawa Ieyasu was born in Okazaki Castle on the 26th day of the twelfth month of the eleventh year of Tenbun, according to the Japanese calendar. Originally named Matsudaira Takechiyo (松平 竹千代), he was the son of Matsudaira Hirotada (松平 廣忠), the daimyō of Mikawa of the Matsudaira clan, and Odai no Kata (於大の方, Lady Odai), the daughter of a neighbouring samurai lord, Mizuno Tadamasa (水野 忠政). His mother and father were step-siblings. They were just 17 and 15 years old, respectively, when Ieyasu was born.[6]
In the year of Ieyasu's birth, the Matsudaira clan was split. In 1543, Hirotada's uncle, Matsudaira Nobutaka defected to the Oda clan. This gave Oda Nobuhide the confidence to attack Okazaki. Soon afterwards, Hirotada's father-in-law died, and his son Mizuno Nobumoto revived the clan's traditional enmity against the Matsudaira and declared for Oda Nobuhide as well. As a result, Hirotada divorced Odai-no-kata and sent her back to her family.[5] Hirotdada later remarried to different wives, and Ieyasu eventually had 11 half-brothers and sisters.[6]
As Oda Nobuhide continued to attack Okazaki, Hirotada turned to his powerful eastern neighbour, Imagawa Yoshimoto for assistance. Yoshimoto agreed to an alliance under the condition that Hirotada send his young heir to Sunpu Domain as a hostage.[5] Oda Nobuhide learned of this arrangement and had Ieyasu abducted and taken to Sunpu.[7] Ieyasu was just five years old at the time.[8] Nobuhide threatened to execute Ieyasu unless his father severed all ties with the Imagawa clan. However, Hirotada refused, stating that sacrificing his own son would show his seriousness in his pact with the Imagawa. Despite this refusal, Nobuhide chose not to kill Ieyasu, but instead held him as a hostage for the next three years at the Honshōji temple in Nagoya.
In 1549, when Ieyasu was 6,[8] his father Hirotada was murdered by his own vassals, who had been bribed by the Oda clan. At about the same time, Oda Nobuhide died during an epidemic. Nobuhide's death dealt a heavy blow to the Oda clan. In 1551, an army under the command of Imagawa Sessai laid siege to the castle where Oda Nobuhiro, Nobuhide's eldest son and the new head of the Oda, was living. Nobuhiro was trapped by the Imagawa clan, but was saved by Oda Nobunaga, Nobuhide's second son, through negotiations. Sessai made a agreement with Nobunaga to take Ieyasu to the Imagawa, and he agreed. So Ieyasu (now nine years old) was taken as a hostage to Sunpu. At Sunpu, he remained a hostage, but was treated fairly well as a potentially useful future ally of the Imagawa clan until 1556 when he was 14 years old.[8]
Service under Yoshimoto (1556–1560)
In 1556, Ieyasu officially came of age, with Imagawa Yoshimoto presiding over his genpuku ceremony. Following tradition, he changed his name from Matsudaira Takechiyo to Matsudaira Jirōsaburō Motonobu (松平 次郎三郎 元信). He was also briefly allowed to visit Okazaki to pay his respects to the tomb of his father, and receive the homage of his nominal retainers, led by the karō Torii Tadayoshi.[5]
One year later, at the age of 15 (according to East Asian age reckoning), he married his first wife, Lady Tsukiyama, a relative of Imagawa Yoshimoto, and changed his name again to Matsudaira Kurandonosuke Motoyasu (松平 蔵人佐 元康). A year later, their son, Matsudaira Nobuyasu, was born. He was then allowed to return to Mikawa Province. There, the Imagawa then ordered him to fight the Oda clan in a series of battles.
Motoyasu fought his first battle in 1558 at the Siege of Terabe. The lord of Terabe, Suzuki Shigeteru, betrayed the Imagawa by defecting to Oda Nobunaga. This was nominally within Matsudaira territory, so Imagawa Yoshimoto entrusted the campaign to Ieyasu and his retainers from Okazaki. Ieyasu led the attack in person, but after taking the outer defences, he burned the main castle and withdrew. As anticipated, the Oda forces attacked his rear lines, but Motoyasu was prepared and drove off the Oda army.[9]
He then succeeded in delivering supplies in the Siege of Odaka a year later. Odaka was the only one of five disputed frontier forts under attack by the Oda which remained in Imagawa hands. Motoyasu launched diversionary attacks against the two neighboring forts, and when the garrisons of the other forts went to their assistance, Ieyasu's supply column was able to reach Odaka.[10]
Death of Yoshimoto
By 1560 the leadership of the Oda clan had passed to the brilliant leader Oda Nobunaga. Imagawa Yoshimoto, leading a large army of 25,000 men, invaded Oda clan territory. Motoyasu was assigned a separate mission to capture the stronghold of Marune. As a result, he and his men were not present at the Battle of Okehazama where Yoshimoto was killed in Nobunaga's surprise assault.[7]:37
Early Rise (1560–1570)

Alliance with Nobunaga
With Yoshimoto dead, and the Imagawa clan in a state of confusion, Motoyasu used the opportunity to assert his independence and marched his men back into the abandoned Okazaki Castle and reclaimed his ancestral seat.[9] Motoyasu then decided to ally with Oda Nobunaga.[11] A secret deal was needed because Motoyasu's wife, Lady Tsukiyama, and infant son, Nobuyasu, were held hostage in Sumpu by Imagawa Ujizane, Yoshimoto's heir.
In 1561, Motoyasu openly broke with the Imagawa and captured the fortress of Kaminogō. Kaminogō was held by Udono Nagamochi. Resorting to stealth, Motoyasu forces under Hattori Hanzō attacked under cover of darkness, setting fire to the castle, and capturing two of Udono's sons, whom he used as hostages to exchange for his wife and son.[10]:216
In 1563, Nobuyasu, the first son of Motoyasu, was married to Nobunaga's daughter Tokuhime. In the same year in February, Motoyasu changed his name to Ieyasu.[12][13] For the next few years Ieyasu was occupied with reforming the Matsudaira clan and pacifying Mikawa. He also strengthened his key vassals by awarding them land and castles. These vassals included Ōkubo Tadayo, Ishikawa Kazumasa, Kōriki Kiyonaga, Sakai Tadatsugu, Honda Tadakatsu, Sakakibara Yasumasa and Hattori Hanzō.
During this period, the Matsudaira clan also faced a threat from a different source. Mikawa was a major center for the Ikkō-ikki movement, where peasants banded together with militant monks under the Jōdo Shinshū sect, and rejected the traditional feudal social order. Ieyasu undertook several battles to suppress this movement in his territories, including the Battle of Azukizaka (1564).[10]:216
Battle of Batogahara

On January 15, 1564, Ieyasu had decided to concentrate his forces to attack and eliminating the Ikki from Mikawa. In the Ikki ranks were some of Ieyasu's vassals, like Honda Masanobu and Natsume Yoshinobu, who had turned over to the Ikki rebellion on religious sympathy.
Ieyasu was fighting in the front line and was nearly killed when struck by several bullets which did not penetrate his armour. Both sides were using the new gunpowder weapons which the Portuguese had introduced to Japan just 20 years earlier. Ieyasu's brave conduct in the battle convinced many of the samurai in the Ikki to switch sides and the Ikki were defeated.
Tokugawa clan
In 1565, Matsudaira Ieyasu became master of all of Mikawa Province. In 1567 Ieyasu changed his name yet again and started the family name "Tokugawa", this time to Tokugawa Ieyasu. As he was a member of the Matsudaira clan, he claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji branch of the Minamoto clan. However, there was no proof the Matsudaira clan are descendants of Emperor Seiwa.[14] Yet, his surname was changed with the permission of the Imperial Court, after writing a petition, and he was bestowed the courtesy title "Mikawa-no-kami" and the court rank of "Junior 5th Rank, Lower Grade (從五位下, ju go-i no ge)". Though the Tokugawa could claim some modicum of freedom, they were very much subject to the requests of Oda Nobunaga. Ieyasu remained an ally of Nobunaga and his Mikawa soldiers were part of Nobunaga's army which captured Kyoto in 1568. At the same time, Ieyasu was eager to expand eastward to Tōtōmi province. Ieyasu and Takeda Shingen, the head of the Takeda clan in Kai Province, made an alliance for the purpose of conquering all the Imagawa territory.[15]:279
Tōtōmi campaign
In 1569, Ieyasu's troops penetrated into Tōtōmi Province. Meanwhile, Shingen's troops captured Suruga Province (including the Imagawa capital of Sunpu). Imagawa Ujizane fled to Kakegawa Castle, which lead to Ieyasu to lead the Siege of Kakegawa. Ieyasu then negotiated with Ujizane, promising that if he should surrender himself and the remainder of Tōtōmi, he would assist Ujizane in regaining Suruga. Ujizane had nothing left to lose, and Ieyasu immediately ended his alliance with Takeda, instead making a new alliance with Takeda's enemy to the north, Uesugi Kenshin of the Uesugi clan. Through these political manipulations, Ieyasu gained the support of the samurai of Tōtōmi Province.[9]
In 1570, Ieyasu established Hamamatsu as the capital of his territory, placing his son Nobuyasu in charge of Okazaki.[16]
Ieyasu and Nobunaga (1570-1582)
Battle of Anegawa
In 1570, Asai Nagamasa, brother in law of Oda Nobunaga, during Siege of Kanegasaki broke their alliance with the Oda clans. Soon Nobunaga was ready to punish Nagamasa for his treachery. Ieyasu led 5,000 of his men to support Nobunaga at the battle.[7]:62 The Battle of Anegawa occurred near Lake Biwa in Ōmi Province, Japan. The allied forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu defeated the combined forces of the Azai clans and Asakura clans, and saw Nobunaga's prodigious use of firearms. It is notable as the first battle that involved the alliance between Nobunaga and Ieyasu.
Conflict with Takeda
In October 1571, Takeda Shingen broke the alliance with Oda-Tokugawa clan and now allied with the Odawara Hōjō clan. He decided to make a drive for Kyoto at the urgings of the shōgun Ashikaga Yoshiaki, starting with invading Tokugawa lands in Tōtōmi. Takeda Shingen's first objective in his campaign against Ieyasu is Nishikawa Castle, Yoshida Castle and Futamata Castle. In 1572, after besieged Futamata, Shingen would press on past Futamata towards the major Tokugawa home castle at Hamamatsu. Later, Ieyasu asked for help from Nobunaga, who sent him some 3,000 troops. Early in 1573 the two armies met at the Battle of Mikatagahara, north Hamamatsu. The considerably larger Takeda army, under the expert direction of Shingen, overwhelmed Ieyasu's troops and caused heavy casualties. Despite his initial reticence, Ieyasu was convinced by his generals to retreat.[17][16] The battle was a major defeat, but in the interests of maintaining the appearance of dignified withdrawal, Ieyasu brazenly ordered the men at his castle to light torches, sound drums, and leave the gates open, to properly receive the returning warriors. To the surprise and relief of the Tokugawa army, this spectacle made the Takeda generals suspicious of being led into a trap, so they did not besiege the castle and instead made camp for the night.[17] This error would allow a band of Tokugawa soldiers to raid the camp in the ensuing hours, further upsetting the already disoriented Takeda army, and ultimately resulting in Shingen's decision to call off the offensive altogether. Incidentally, Takeda Shingen would not get another chance to advance on Hamamatsu, much less Kyoto, since he would perish shortly after the Siege of Noda Castle later that same year.[11]:153–156
Shingen was succeeded by his less capable son Takeda Katsuyori. In 1574, Katsuyori took Takatenjin fortress. Then, in 1575, during Takeda Katsuyori's raid through Mikawa Province, he attacked Yoshida castle and besieged Nagashino castle in Mikawa Province. Ieyasu appealed to Nobunaga for help and Nobunaga came with 30,000 strong men. The Oda-Tokugawa forces of 38,000 won a great victory and successfully defended Nagashino castle. Though Takeda forces destroyed, Katsuyori survived the battle and retreated back to Kai Province.[18] For the next seven years, Ieyasu and Katsuyori fought a series of small battles, as the result of which Ieyasu's troops managed to wrest control of Suruga Province away from the Takeda clan.
In 1579, Lady Tsukiyama, Ieyasu' wife, and his heir Nobuyasu, were accused by Nobunaga of conspiring with Takeda Katsuyori to assassinate Nobunaga, whose daughter Tokuhime was married to Nobuyasu. For this reason, Ieyasu ordered his wife to be executed and forced his son to commit seppuku. Ieyasu then named his third son, Tokugawa Hidetada, as heir, since his second son was adopted by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who would later become an extremely powerful daimyo.
In 1580, Oda-Tokugawa forces launched the second siege of Takatenjin; the siege came only six years after Takeda Katsuyori took the fortress. This second siege lasted from 1580 until 22 March 1581, and ended with the deaths of 680 men in the Okabe Motonobu garrison.
The end of the war with Takeda came in 1582 when a combined Oda-Tokugawa force attacked and conquered Kai Province. Takeda Katsuyori was defeated at the Battle of Tenmokuzan, and then committed seppuku.[10]:231
Death of Nobunaga
In late June 1582, before the incident at Honnō-ji temple, Nobunaga invited Ieyasu to tour the Kansai region in celebration of the demise of the Takeda clan. When he learned that Nobunaga had been killed at the Honnō-ji temple by Akechi Mitsuhide, this meant that some provinces, ruled by Nobunaga's vassals, were ripe for conquest. Later, Ieyasu traveled back to Mikawa for gathering his forces. With the help of his retainer and ninja leader Hattori Hanzō, Ieyasu first went through Sakai, then crossed the mountains of Iga Province, finally reaching the shore in Ise Province. He returned to his home Mikawa Province by sea. Ieyasu was mobilizing his army when he learned Hideyoshi had defeated Akechi Mitsuhide at the Battle of Yamazaki.[15]:314–315
Ieyasu and Hideyoshi (1582–1598)
After the death of Nobunaga at Honnō-ji castle, the leader of Kai province made the mistake of killing one of Ieyasu's aides. Because of this, Ieyasu promptly invaded Kai and took control. Hōjō Ujimasa, leader of the Hōjō clan responded by sending his much larger army into Shinano and then into Kai province. Later, both Ieyasu and the Hōjō clan agreed to a settlement which left Ieyasu in control of both Kai and Shinano Provinces, while the Hōjō took control of Kazusa Province (as well as bits of both Kai and Shinano Provinces).
In 1583, a war for rule over Japan was fought between Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Shibata Katsuie. Ieyasu did not take a side in this conflict, building on his reputation for both caution and wisdom. Hideyoshi defeated Katsuie at Battle of Shizugatake. With this victory, Hideyoshi became the single most powerful daimyō in Japan.[15]:314
Conflict with Hideyoshi
In 1584, Ieyasu decided to support Oda Nobukatsu, the eldest surviving son and heir of Oda Nobunaga, against Hideyoshi. This was a dangerous act and could have resulted in the annihilation of the Tokugawa, due to the fact that the Oda clan collapsed after Nobunaga's death.
Tokugawa troops took the traditional Oda stronghold of Owari. Hideyoshi responded by sending an army into Owari. The Komaki and Nagakute Campaign was the only time any of the great unifiers of Japan fought each other.
The Komaki and Nagakute campaign proved indecisive and after months of fruitless marches and feints, Hideyoshi and Ieyasu settled the war through negotiation. First, Hideyoshi made peace with Oda Nobukatsu, and then he offered a truce to Ieyasu. The deal was made at the end of the year; as part of the terms Ieyasu's second son, Ogimaru (also known as Yuki Hideyasu) became an adopted son of Hideyoshi.
Ieyasu's aide, Ishikawa Kazumasa, chose to join the pre-eminent daimyō and so he moved to Osaka to be with Hideyoshi. However, few other Tokugawa retainers followed this example.
Alliance with Hideyoshi
Hideyoshi was understandably distrustful of Ieyasu, and five years passed before they fought as allies. The Tokugawa did not participate in Hideyoshi's successful Invasion of Shikoku (1585) and Kyūshū Campaign (1587).
In 1590, Hideyoshi attacked the last independent daimyō in Japan, Hōjō Ujimasa. The Hōjō clan ruled the eight provinces of the Kantō region in eastern Japan. Hideyoshi ordered them to submit to his authority and they refused. Ieyasu, though a friend and occasional ally of Ujimasa, joined his large force of 30,000 samurai with Hideyoshi's enormous army of some 160,000. Odawara Campaign is the first battle of Ieyasu and Hideyoshi as allies. They attacked several castles on the borders of the Hōjō clan with most of his army laying siege to the castle at Odawara. Hideyoshi's and Ieyasu's army captured Odawara after six months (oddly for the time period, deaths on both sides were few). During this siege, Hideyoshi offered Ieyasu a radical deal: He offered Ieyasu the eight Kantō provinces which they were about to take from the Hōjō in return for the five provinces that Ieyasu currently controlled (including Ieyasu's home province of Mikawa). Ieyasu accepted this proposal. Bowing to the overwhelming power of the Toyotomi army, the Hōjō accepted defeat, their leaders committed suicide and Ieyasu marched in and took control of their provinces, ending the clan's reign of over 100 years.
The Sannohe faction led by Nanbu Nobunao organized a coalition of most of the Nanbu clans and pledged allegiance to Toyotomi Hideyoshi at the Siege of Odawara. In return, he was recognized as chieftain of the Nanbu clans, and confirmed as daimyō of his existing holdings in the northern districts of Mutsu Province. However, Kunohe Masazane, who felt that he had a stronger claim to the title of clan chieftain, immediately rose in rebellion. In 1591, Hideyoshi and Ieyasu took the Kunohe Rebellion as a personal affront to Toyotomi authority and by mid-year organized a retaliatory army to retake northern Tōhoku and to restore the area to Nanbu Nobunao's control.
Rise to Power (1591–1598)
Daimyō of Kantō region
Ieyasu now gave up control of his five provinces (Mikawa, Tōtōmi, Suruga, Shinano, and Kai) and moved all his soldiers and vassals to the Kantō region. He himself occupied the castle town of Edo in Kantō. This was possibly the riskiest move Ieyasu ever made—to leave his home province and rely on the uncertain loyalty of the formerly Hōjō samurai in Kantō. In the end, it worked out brilliantly for Ieyasu. He reformed the Kantō region, controlled and pacified the Hōjō samurai and improved the underlying economic infrastructure of the lands. Also, because Kantō was somewhat isolated from the rest of Japan, Ieyasu was able to maintain a unique level of autonomy from Hideyoshi's rule. Within a few years, Ieyasu had become the second most powerful daimyō in Japan. There is a Japanese proverb which likely refers to this event: "Ieyasu won the Empire by retreating."[19]
Council of Five Elders
In 1592, Hideyoshi invaded Korea as a prelude to his plan to attack China. The Tokugawa samurai never actually took part in this campaign, though in early 1593, Ieyasu himself was summoned to Hideyoshi's court in Nagoya (in Kyūshū, different from the similarly spelled city in Owari Province) as a military advisor and given command of a body of troops meant as reserves for the Korean campaign. He stayed in Nagoya off and on for the next five years.[15] Despite his frequent absences, Ieyasu's sons, loyal retainers and vassals were able to control and improve Edo and the other new Tokugawa lands.
In 1593, Toyotomi Hideyoshi fathered a son and heir, Toyotomi Hideyori.
In 1598, with Hideyoshi health clearly failing, Hideyoshi called a meeting that would determine the Council of Five Elders, who would be responsible for ruling on behalf of his son after his death. The five that were chosen as tairō (regent) for Hideyori were Maeda Toshiie, Mōri Terumoto, Ukita Hideie, Uesugi Kagekatsu, and Ieyasu himself, who was the most powerful of the five. This change in the pre-Sekigahara power structure became pivotal as Ieyasu turned his attention towards Kansai; and at the same time, other ambitious (albeit ultimately unrealized) plans, such as the Tokugawa initiative establishing official relations with New Spain (modern-day Mexico), continued to unfold and advance.[20][21]
Death of Hideyoshi
Hideyoshi, after three more months of increasing sickness, died on September 18, 1598. He was nominally succeeded by his young son Hideyori but as he was just five years old, real power was in the hands of the regents. Over the next two years Ieyasu made alliances with various daimyōs, especially those who had no love for Hideyoshi. Happily for Ieyasu, the oldest and most respected of the regents, Maeda Toshiie, died after just one year.
Unification of Japan (1598–1603)

Conflict with Mitsunari
With the death of Hideyoshi in 1598 and Toshiie in 1599, Ieyasu led an army to Fushimi and took over Osaka Castle, the residence of Hideyori. This angered the three remaining regents and plans were made on all sides for war.
Opposition to Ieyasu centered around Ishida Mitsunari, one of Hideyoshi's five bugyō, or top administrators of Hideyoshi's government and a powerful daimyō who was not one of the regents. Mitsunari plotted Ieyasu's death and news of this plot reached some of Ieyasu's generals. They attempted to kill Mitsunari but he fled and gained protection from none other than Ieyasu himself. It is not clear why Ieyasu protected a powerful enemy from his own men but Ieyasu was a master strategist and he may have concluded that he would be better off with Mitsunari leading the enemy army rather than one of the regents, who would have more legitimacy.[22]
Nearly all of Japan's daimyō and samurai now split into two factions—The Western Army (Mitsunari's group) and The Eastern Army (anti-Mitsunari Group). Ieyasu supported the anti-Mitsunari Group, and formed them as his potential allies. Ieyasu's allies were Katō Kiyomasa, Fukushima Masanori, Date Masamune, the Mogami clan, the Hosokawa clan and many daimyō from eastern Japan. Mitsunari allied himself with the three other regents: Ukita Hideie, Mōri Terumoto, and Uesugi Kagekatsu as well as Ōtani Yoshitsugu, Chosokabe clan, Shimazu clan and many daimyō from the western end of Honshū.
However, Uesugi Kagekatsu, one of Hideyoshi's appointed regents, defied Ieyasu by building up his military at Aizu. When Ieyasu officially condemned him and demanded that he come to Kyoto to explain himself, Kagekatsu's chief advisor, Naoe Kanetsugu responded with a counter-condemnation that mocked Ieyasu's abuses and violations of Hideyoshi's rules, and Ieyasu was infuriated.
In June 1600, Ieyasu and his allies moved their armies to defeat the Uesugi clan, which was accused of planning to revolt against Toyotomi administration. Before arriving at Uesugi's territory, Ieyasu received information that Mitsunari and his allies had moved their army against Ieyasu. Ieyasu held a meeting with the daimyōs, and they agreed to follow Ieyasu. Ieyasu and his allies marched along the Tōkaidō, while his son Hidetada went along through Nakasendō with 38,000 soldiers (a battle against Sanada Masayuki in Shinano Province delayed Hidetada's forces, and they did not arrive in time for the main Battle of Sekigahara).
Ieyasu led the majority of his army west towards Kyoto. On August 23, Ieyasu's army took Gifu castle. Following the Battle of Gifu Castle, In late summer September 8, Ishida's forces captured Fushimi castle. On October 20, they meet at Sekigahara, Gifu and the battle began.
Battle of Sekigahara
Battle of Sekigahara fought near Sekigahara, was the biggest and one of the most important battles in Japanese feudal history. It began on October 21, 1600. Initially, the Eastern Army led by Tokugawa Ieyasu had 75,000 men, while the Western Army numbered 120,000 men under Ishida Mitsunari. Ieyasu had also sneaked in a supply of arquebuses. Knowing that the Tokugawa forces were heading towards Osaka, Mitsunari decided to abandon his positions and marched to Sekigahara. Even though the Western army had tremendous tactical advantages, Ieyasu had already been in contact with many of the daimyō in the Western Army for months, promising them land and leniency after the battle should they switch sides, also having secretly communicated with Hideyoshi nephew, Kobayakawa Hideaki. With a total of 170,000 soldiers facing each other, the Battle of Sekigahara ensued and ended with a complete Tokugawa victory.[23] Later, The Western bloc was crushed and over the next few days Ishida Mitsunari and many other western nobles were captured and killed. Tokugawa Ieyasu was now the de facto ruler of Japan.
Immediately after the victory at Sekigahara, Ieyasu redistributed land to the vassals who had served him. Ieyasu left some western daimyōs unharmed, such as the Shimazu clan, but others were completely destroyed. Toyotomi Hideyori (the son of Hideyoshi) lost most of his territory which were under management of western daimyōs, and he was degraded to an ordinary daimyō, not a ruler of Japan. In later years the vassals who had pledged allegiance to Ieyasu before Sekigahara became known as the fudai daimyō, while those who pledged allegiance to him after the battle (in other words, after his power was unquestioned) were known as tozama daimyō. Tozama daimyō were considered inferior to fudai daimyōs.
Shōgun (1603–1605)

On March 24, 1603, Tokugawa Ieyasu received the title of shōgun from Emperor Go-Yōzei.[24] Ieyasu was 60 years old. He had outlasted all the other great men of his times: Nobunaga, Shingen, Hideyoshi, and Kenshin. As shōgun, he used his remaining years to create and solidify the Tokugawa shogunate, which ushered in the Edo period, and was the third shogunal government (after the Kamakura (Minamoto) and the Ashikaga). He claimed descent from the Minamoto clan, by way of the Nitta clan. His descendants would marry into the Taira clan and the Fujiwara clan. The Tokugawa shogunate would rule Japan for the next 260 years.[1]
Following a well established Japanese pattern, Ieyasu abdicated his official position as shōgun in 1605. His successor was his son and heir, Tokugawa Hidetada. There may have been several factors that contributed to his decision, including his desire to avoid being tied up in ceremonial duties, to make it harder for his enemies to attack the real power center, and to secure a smoother succession of his son.[25] The abdication of Ieyasu had no effect on the practical extent of his powers or his rule; but Hidetada nevertheless assumed a role as formal head of the shogunal bureaucracy.
Ōgosho (1605–1616)
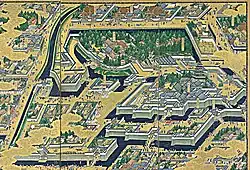
Construction of Edo castle
In 1605, Ieyasu, acting as the retired shōgun (大御所, ōgosho), remained the effective ruler of Japan until his death. Ieyasu retired to Sunpu Castle in Sunpu, but he also supervised the building of Edo Castle, a massive construction project which lasted for the rest of Ieyasu's life. The result was the largest castle in all of Japan, the costs for building the castle being borne by all the other daimyōs, while Ieyasu reaped all the benefits. The central donjon, or tenshu, burned in the 1657 Meireki fire. Today, the Imperial Palace stands on the site of the castle.
In 1611, Ieyasu, at the head of 50,000 men, visited Kyoto to witness the enthronement of Emperor Go-Mizunoo. In Kyoto, Ieyasu ordered the remodeling of the Imperial court and buildings, and forced the remaining western daimyōs to sign an oath of fealty to him.
In 1613, he composed the Kuge Shohatto (公家諸法度), a document which put the court daimyōs under strict supervision, leaving them as mere ceremonial figureheads.
In 1615, Ieyasu prepared the Buke shohatto (武家諸法度), a document setting out the future of the Tokugawa regime.[26]
Relations with foreign powers


As Ōgosho, Ieyasu also supervised diplomatic affairs with the Netherlands, Spain, and England. Ieyasu chose to distance Japan from European influence starting in 1609, although the shogunate did still grant preferential trading rights to the Dutch East India Company and permitted them to maintain a "factory" for trading purposes.
From 1605 until his death, Ieyasu frequently consulted English shipwright and pilot, William Adams.[27] Adams, fluent in Japanese, assisted the shogunate in negotiating trading relations, but was cited by members of the competing Jesuit and Spanish-sponsored mendicant orders as an obstacle to improved relations between Ieyasu and the Roman Catholic Church.[28][29][30]
Significant attempts to curtail the influence of Christian missionaries in Japan date to 1587 during the shogunate of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. However, in 1614, Ieyasu was sufficiently concerned about Spanish territorial ambitions that he signed a Christian Expulsion Edict. The edict banned the practice of Christianity and led to the expulsion of all foreign missionaries. Although some smaller Dutch trading operations remained in Nagasaki, this edict dramatically curtailed foreign trade and marked the end of open Christian witness in Japan until the 1870s.[31] The immediate cause of the prohibition was the Okamoto Daihachi incident, a case of fraud involving Ieyasu's Catholic vavasor, but the shogunate was also concerned about a possible invasion by the Iberian colonial powers, which had previously occurred in the New World and the Philippines.
Conflict with Hideyori

The last remaining threat to Ieyasu's rule was Toyotomi Hideyori, the son and rightful heir to Hideyoshi.[1] He was now a young daimyō living in Osaka Castle. Many samurai who opposed Ieyasu rallied around Hideyori, claiming that he was the rightful ruler of Japan. Ieyasu found fault with the opening ceremony of a temple built by Hideyori; it was as if he prayed for Ieyasu's death and the ruin of the Tokugawa clan. Ieyasu ordered Hideyori to leave Osaka Castle, but those in the castle refused and summoned samurai to gather within the castle. Then in 1614, Tokugawa besieged the Osaka Castle against Hideyori.
Siege of Osaka
The Tokugawa forces, with a huge army led by Ieyasu and shōgun Hidetada, laid Siege of Osaka castle in what is now known as "the Winter Siege of Osaka". Eventually, Tokugawa was able to precipitate negotiations and an armistice after directed cannon fire threatened Hideyori's mother, Yodo-dono. However, once the treaty was agreed, Tokugawa filled the castle's outer moats with sand so his troops could walk across. Through this ploy, Tokugawa gained a huge tract of land through negotiation and deception that he could not through siege and combat. Ieyasu returned to Sunpu Castle once, but after Toyotomi refused another order to leave Osaka, he and his allied army of 155,000 soldiers attacked Osaka Castle again in "the Summer Siege of Osaka".
Finally, in late 1615, Osaka Castle fell and nearly all the defenders were killed, including Hideyori, his mother (Hideyoshi's widow, Yodo-dono), and his infant son. His wife, Senhime (a granddaughter of Ieyasu), pleaded to save Hideyori and Yodo-dono's lives. Ieyasu refused and either required them to commit ritual suicide, or killed both of them. Eventually, Senhime was sent back to Tokugawa alive. After killing two people at Kamakura, who have escaped from Osaka Castle. With the Toyotomi line finally extinguished, no threats remained to the Tokugawa clan's domination of Japan.
Death

In 1616, Ieyasu died at age 73.[8] The cause of death is thought to have been cancer or syphilis. The first Tokugawa shōgun was posthumously deified with the name Tōshō Daigongen (東照大權現), the "Great Gongen, Light of the East". (A Gongen is believed to be a buddha who has appeared on Earth in the shape of a kami to save sentient beings). In life, Ieyasu had expressed the wish to be deified after his death to protect his descendants from evil. His remains were buried at the Gongens' mausoleum at Kunōzan, Kunōzan Tōshō-gū (久能山東照宮). As a common view, many people believe that "after the first anniversary of his death, his remains were reburied at Nikkō Shrine, Nikkō Tōshō-gū (日光東照宮). His remains are still there." Neither shrine has offered to open the graves, so the location of Ieyasu's physical remains is still a mystery. The mausoleum's architectural style became known as gongen-zukuri, that is gongen-style.[32] He was first given the Buddhist name Tosho Dai-Gongen (東照大權現), then after his death it was changed to Hogo Onkokuin (法號安國院).
Era of Ieyasu's rule
Ieyasu ruled directly as shōgun or indirectly as Ōgosho (大御所) during the Keichō era (1596–1615).
Ieyasu's character


Ieyasu had a number of qualities that enabled him to rise to power. He was both careful and bold—at the right times, and in the right places. Calculating and subtle, Ieyasu switched alliances when he thought he would benefit from the change. He allied with the Late Hōjō clan; then he joined Hideyoshi's army of conquest, which destroyed the Hōjō; and he himself took over their lands. In this he was like other daimyōs of his time. This was an era of violence, sudden death, and betrayal. He was not very well liked nor personally popular, but he was feared and he was respected for his leadership and his cunning. For example, he wisely kept his soldiers out of Hideyoshi's campaign in Korea.
He was capable of great loyalty: once he allied with Oda Nobunaga, he never went against him, and both leaders profited from their long alliance. He was known for being loyal towards his personal friends and vassals, whom he rewarded. He was said to have a close friendship with his vassal Hattori Hanzō. However, he also remembered those who had wronged him in the past. It is said that Ieyasu executed a man who came into his power because he had insulted him when Ieyasu was young.[33]
Ieyasu protected many former Takeda retainers from the wrath of Oda Nobunaga, who was known to harbour a bitter grudge towards the Takeda. He managed successfully to transform many of the retainers of the Takeda, Hōjō, and Imagawa clans—all whom he had defeated himself or helped to defeat—into loyal followers. At the same time, he could be ruthless when crossed. For example, he ordered the executions of his first wife and his eldest son—a son-in-law of Oda Nobunaga; Oda was also an uncle of Hidetada's wife Oeyo.[34]
He was cruel, relentless and merciless in the elimination of Toyotomi survivors after Osaka. For days, dozens and dozens of men and women were hunted down and executed, including an eight-year-old son of Hideyori by a concubine, who was beheaded.[35]
Unlike Hideyoshi, he did not harbor any desires to conquer outside Japan—he only wanted to bring order and an end to open warfare, and to rule Japan.[36]
While at first tolerant of Christianity,[37] his attitude changed after 1613 and the executions of Christians sharply increased.[38]
Ieyasu's favorite pastime was falconry. He regarded it as excellent training for a warrior. "When you go into the country hawking, you learn to understand the military spirit and also the hard life of the lower classes. You exercise your muscles and train your limbs. You have any amount of walking and running and become quite indifferent to heat and cold, and so you are little likely to suffer from any illness.".[39] Ieyasu swam often; even late in his life he is reported to have swum in the moat of Edo Castle.
Later in life he took to scholarship and religion, patronizing scholars like Hayashi Razan.[40]
Two of his famous quotes:
Life is like unto a long journey with a heavy burden. Let thy step be slow and steady, that thou stumble not. Persuade thyself that imperfection and inconvenience are the lot of natural mortals, and there will be no room for discontent, neither for despair. When ambitious desires arise in thy heart, recall the days of extremity thou hast passed through. Forbearance is the root of all quietness and assurance forever. Look upon the wrath of thy enemy. If thou only knowest what it is to conquer, and knowest not what it is to be defeated; woe unto thee, it will fare ill with thee. Find fault with thyself rather than with others.[41]
The strong manly ones in life are those who understand the meaning of the word patience. Patience means restraining one's inclinations. There are seven emotions: joy, anger, anxiety, adoration, grief, fear, and hate, and if a man does not give way to these he can be called patient. I am not as strong as I might be, but I have long known and practiced patience. And if my descendants wish to be as I am, they must study patience.[42][43]
He said that he fought, as a warrior or a general, in 90 battles.
He was interested in various kenjutsu skills, was a patron of the Yagyū Shinkage-ryū school, and also had them as his personal sword instructors.
Honours
- Senior First Rank (April 14, 1617; posthumous)
Parents and Siblings
Parents
| Status | Image | Name | Posthumous Name | Birth | Death | Parents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Father | Matsudaira Hirotada | Oseidokantokoji | June 9, 1526 | April 3, 1549 | Matsudaira Kiyoyasu Aoki family's daughter | |
| Mother |  | Odai no Kata | Denzu-in | 1528 | October 13, 1602 | Mizuno Tadamasa Otomi-no-Kata |
Mother Side
| Image | Name | Posthumous Name | Birth | Death | Father | Marriage | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsudaira Yasumoto of Sekiyado Domain | Daiko-in-dono sugurudensoeidaikoji | 1552 | September 19, 1603 | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | Matsudaira Tadayoshi (1582–1624) of Ōgaki Domain Matsudaira Masayoshi Matsudaira Yasuhisa Matsudaira Nobusuke (d.1655) Dōsen-in married Okabe Nagamori (1568–1632) of Ōgaki Domain Ryuko-in married Suganuma Sadayori (1576–1605) of Nagashima Domain Matehime (1598–1638) married Fukushima Masayuki (1858–1602) later married Tsugaru Nobuhira of Hirosaki Domain Tsubakihime married Tanaka Tadamasa (1585–1620) of Yanagawa Domain later married Matsudaira Narishige (1594–1633) of Tamba-Kameyama Domain Shoshitsu’in married Osuga Tadamasa (1581–1607) of Yokosuka Domain later married Suganuma Sadayoshi (1587–1643) of Tamba-Kameyama Domain Jomyo-in married Nakamura Kazutada (1590–1609) of Yonogo Domain later married Mōri Hidemoto of Chofu Domain | ||
| Matsudaira Yasutoshi | 1552 | April 2, 1586 | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | Daughter married Matsudaira Katsumasa | |||
 | Hisamatsu Sadakatsu of Kuwana Domain | Sogen-in-dono denyonshinatsugishoukugaentodaikoji | 1560 | May 1, 1624 | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | Okudaira Tatsu, Okudaira Sadatomo (d.1585)’s daughter | Matsudaira Sadayoshi (1585–1603) Matsudaira Sadayuki (1587–1668) of Kuwana Domain Matsudaira Sadatsuna (1592–1625) of Kuwana Domain Matsudaira Sadazane (1597–1632) Matsudaira Sadafusa (1604–1676) of Imabari Domain Matsudaira Sadamasa (1610–1673) of Kariya Domain Matsuohime married Hattori Masanari Kumahime (1595–1632) married Yamauchi Tadayoshi (1592–1665) of Tosa Domain Daughter married Nakagawa Hisanori (1594–1653) of Oka Domain Kikuhime married Sakai Tadayuki (1599–1636) of Maebashi Domain Shōjuin Married Abe Shigetsugu (1598–1651) of Iwatsuki Domain Tamako married Ikeda Tsunemoto (1611–1671) of Yamasaki Domain |
| Take-hime | Chogen-in | 1553 | July 28, 1618 | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | First: Matsudaira Tadamasa (1543–1577) of Sakurai-Matsudaira clan Second: Matsudaira Tadayoshi (1559–1582) of Sakurai-Matsudaira clan Third: Hoshina Masanao | By First: Matsudaira Iehiro (1577–1601) of Musashi-Matsuyama Domain By Second: Matsudaira Nobuyoshi (1580–1620) of Sasayama Domain Matsudaira Tadayori of Hamamatsu Domain By Third: Hoshina Masasada of Iino Domain Hojo Ujishige (1595–1658) of Kakegawa Domain Seigen’in married Anbe Nobumori (1584–1674) of Okabe Domain Yōhime (1591–1664) married Koide Yoshihide (1587–1666) of Izushi Domain Eihime (1585–1635) married Kuroda Nagamasa of Fukuoka Domain Kōun-in married Kato Akinari (1592–1661) of Aizu Domain | |
| Matsuhime | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | Matsudaira Yasunaga (1562–1633) of Matsumoto Domain | Matsudaira Nagakane (1580–1619) Matsudaira Tadamitsu (1562–1633) Matsudaira Yasunao (1617–1634) of Akashi Domain | ||||
| Tenkeiin | Hisamatsu Toshikatsu (1526–1587) | Matsudaira Iekiyo of Yoshida Domain | Matsudaira Tadakiyo (1585–1612) of Yoshida Domain |
Wives and Concubines
| Status | Image | Name | Posthumous Name | Birth | Death | Parents | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Wife |  | Tsukiyama-dono | Shoge-in | - | September 19, 1579 | Sekiguchi Chikanaga (1518–1562) Ii Naohira’s daughter | Matsudaira Nobuyasu Kamehime married Okudaira Nobumasa of Kano Domain |
| Second Wife |  | Asahi no kata | Nanmeiin | 1543 | February 18, 1590 | Chikuami Ōmandokoro | |
| Concubine | Nishigori no Tsubone | Rensho-in | June 19, 1606 | Udono Nagamochi (1513–1557) | Tokuhime (Tokugawa) married Hojo Ujinao later to Ikeda Terumasa of Himeji Domain | ||
| Concubine | Shimoyama-dono | Moshin’in | 1564 | November 21, 1591 | Akiyama Torayasu | Takeda Nobuyoshi of Mito Domain | |
| Concubine |  | Kageyama-dono | Youjuin | 1580 | October 13, 1653 | Masaki Yoritada (1551–1622) Hojo Ujitaka (d.1609)’s daughter | Tokugawa Yorinobu of Kishu Domain Tokugawa Yorifusa of Mito Domain |
| Concubine | Kotoku-no-Tsubone | Chōshō-in | 1548 | January 10, 1620 | Nagami Sadahide | Yuki Hideyasu of Fukui Domain | |
| Concubine |  | Saigō-no-Tsubone | Hōdaiin | 1552 | July 1, 1589 | Tozuka Tadaharu Saigo Masakatsu's daughter | Tokugawa Hidetada Matsudaira Tadayoshi of Kiyosu Domain |
| Concubine | Otake no Kata | Ryōun-in | 1555 | April 7, 1637 | Ichikawa Masanaga | Furi-hime (1580–1617) married Gamō Hideyuki of Aizu Domain later to Asano Nagaakira of Hiroshima Domain | |
| Concubine | Chaa-no-Tsubone | Chokoin | July 30, 1621 | Matsudaira Tadateru of Takada Domain Matsudaira Matsuchiyo of Fukaya Domain | |||
| Concubine | Onatsu no Kata | Seiun’in | 1581 | October 24, 1660 | Hasegawa Fujinao | ||
| Concubine | Okaji no Kata | Eishō-in | December 7, 1578 | September 17, 1642 | Ota Yasusuke (1531–1581) | Ichihime (1607–1610) | |
| Concubine | Oume no Kata | Renge-in | 1586 | October 8, 1647 | Aoki Kazunori (d.1600) | ||
| Concubine |  | Acha no Tsubone | Unkoin | Maret 16, 1555 | February 16, 1637 | Ida Naomasa | |
| Concubine | Omusu no Kata | Shōei-in | July 26, 1692 | Mitsui Yoshimasa | Stillborn (1592) | ||
| Concubine |  | Okame no Kata | Sōōin | 1573 | October 9, 1642 | Shimizu Munekiyo | Matsudaira Senchiyo (1595–1600) Tokugawa Yoshinao of Owari Domain |
| Concubine | Osen no Kata | Taiei-in | November 30, 1619 | Miyazaki Yasukage | |||
| Concubine | Oroku no Kata | Yōgen'in | 1597 | May 4, 1625 | Kuroda Naojin | ||
| Concubine | Ohisa no Kata | Fushōin | March 24, 1617 | Mamiya Yasutoshi (1518–1590) | Matsuhime (1595–1598) | ||
| Concubine | Tomiko | Shinju-in | August 7, 1628 | Yamada clan | |||
| Concubine | Omatsu no Kata | Hōkōin | |||||
| Concubine | Sanjo Clan | ||||||
| Concubine | Matsudaira Shigetoshi (1498–1589) |
Children
| Image | Name | Posthumous Name | Birth | Death | Mother | Marriage | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Matsudaira Nobuyasu | Toun-in-dono ryugenchokookyoshiseiroji-dono densanshutegensensudaikoji | April 13, 1559 | October 5, 1579 | Tsukiyama-dono | Tokuhime (Oda) | Tokuhime (1576–1607) married Ogasawara Hidemasa (1569–1615) of Matsumoto domain Kamehime (1577–1626) married Honda Tadamasa of Himeji Domain By Concubine: Banchiyo |
| Kamehime | Seitokuin | July 27, 1560 | August 1, 1625 | Tsukiyama-dono | Okudaira Nobumasa of Kano Domain | Okudaira Iemasa (1577–1614) of Utsunomiya Domain Matsudaira Ieharu (1579–1592) Matsudaira Tadaaki of Himeji Domain Okudaira Tadamasa of Kano Domain daughter married Okubo Tadatsune (1580–1611) of Kisai Domain | |
 | Toku-hime | Ryōshō-in | 1565 | March 3, 1615 | Nishigori no Tsubone | First: Hojo Ujinao Second: Ikeda Terumasa of Himeji Domain | by First: Manshuin-dono (1593) Manhime (d.1602) Senhime (b.1596) married Kyokogu Takahiro (1599–1677) of Miyazu Domain By Second: Ikeda Tadatsugu (1599–1615) of Okayama Domain Ikeda Tadakatsu (1602–1632) of Okayama Domain Ikeda Teruzumi (1604–1662) of Shikano Domain Ikeda Masatsuna (1605–1631) Of Akō Domain Furihime (1607–1659) married Date Tadamune of Sendai Domain Ikeda Teruoki (1611–1647) Of Akō Domain |
 | Yuki Hideyasu of Fukui Domain | Jokoin-dono shingendoyounseidaikoji | March 1, 1574 | June 2, 1607 | Kotoku-no-Tsubone | Tsuruko, Edo Shigemichi's daughter | by Concubines: Matsudaira Tadanao of Fukui Domain Matsudaira Tadamasa of Fukui Domain Hisahime (1598–1655) married Mōri Hidenari Of Choshu Domain Matsudaira Naomasa (1601–1666) of Matsue Domain Matsudaira Naomoto (1604–1648) of Himeji Domain Matsudaira Naoyoshi (1605–1678) of Ōno Domain |
 | 2nd Shogun, Tokugawa Hidetada | Daitoku-in | May 2, 1579 | March 14, 1632 | Saigō-no-Tsubone | First: O-hime(1585–1591), Oda Nobukatsu’s daughter Second: Azai Oeyo | By second: Senhime married Toyotomi Hideyori later to Honda Tadatoki of Himeji Domain Tama-hime (1599–1622) married Maeda Toshitsune of Kaga Domain Katsu-hime (1601–1672) married Matsudaira Tadanao of Fukui Domain Hatsu-hime (1602–1630) married Kyōgoku Tadataka of Matsue Domain 3rd Shogun, Tokugawa Iemitsu Tokugawa Tadanaga of Sunpu Domain Kazuhime married Emperor Go-Mizunoo By Concubines: Chomaru (1601–1602) Hoshina Masayuki of Aizu Domain |
 | Matsudaira Tadayoshi of Kiyosu Domain | Shokoin-dono keneigenmodaikoji | October 18, 1580 | April 1, 1607 | Saigō-no-Tsubone | Masako, Ii Naomasa of Hikone Domain’s daughter | Umesada Daidoji (1597) |
| Furi-hime | Shōsei-in | 1580 | September 27, 1617 | Otake no Kata | First: Gamō Hideyuki of Aizu Domain Second: Asano Nagaakira of Hiroshima Domain | By first: Gamō Tadasato (1602–1627) of Aizu Domain Gamō Tadatomo (1604–1634) of Iyo-Matsuyama Domain Yorihime (1602–1656) married Kato Tadahiro (1601–1653) of Dewa-Maruoka Domain By Second: Asano Mitsuakira of Hiroshima Domain | |
| Takeda Nobuyoshi of Mito Domain | Joken-in-dono eiyozenkyozugendaizenjomon | October 18, 1583 | October 15, 1603 | Shimoyama-dono | Tenshoin, Kinoshita Katsutoshi's daughter | ||
 | Matsudaira Tadateru of Takada Domain | Shorin-in-dono shinyokisogesendaikoji | February 16, 1592 | August 24, 1683 | Chaa-no-Tsubone | Irohahime | By Concubine: Tokumatsu (1614–1632) Gotakehime |
| Matsudaira Matsuchiyo of Fukaya Domain | Eishoin-dono | 1594 | February 7, 1599 | Chaa-no-Tsubone | |||
| Matsudaira Senchiyo | Kogakuin-dono kesoiyodaidoji | April 22, 1595 | March 21, 1600 | Okame no Kata | |||
| Matsuhime | 1595 | 1598 | Ohisa no Kata | ||||
 | Tokugawa Yoshinao of Owari Domain | January 2, 1601 | June 5, 1650 | Okame no Kata | Haruhime (1693–1637), Asano Yoshinaga of Wakayama Domain’s daughter | By Concubines: Tokugawa Mitsutomo of Owari Domain Kyōhime (1626–1674) married Hirohata Tadayuki (1624–1669) | |
 | Tokugawa Yorinobu of Kishu Domain | Nanryuin-dono nihonzeneaiyotenkotakoji | April 28, 1602 | February 19, 1671 | Kageyama-dono | Yasohime (1601–1666), Katō Kiyomasa of Kumamoto Domain’s daughter | by Concubines: Tokugawa Mitsusada of Kishu Domain Shuri Matsudaira Yorizumi (1641–1711) of Saijō Domain |
 | Tokugawa Yorifusa of Mito Domain | September 15, 1603 | August 23, 1661 | Kageyama-dono | By Concubines: Matsudaira Yorishige of Takamatsu Domain Tokugawa Mitsukuni of Mito Domain Michiko (1624–1664) Kamemaru (1625–1628) Manhime (1627–1689) married Ota Sukemasa Kikuhime (1628–1706) married Matsudaira Yasuhiro Matsudaira Yoritomo (1629–1693) Of Nukada Domain Matsudaira Yorio (1630–1697) Of Shishido Domain Senhime (1635–1681) married Maki Kagenobu Matsuhime Ki-hime Koyan-hime (1628–1717) Matsudaira Yoritaka (1629–1707) Of Hitachi-Fuchū Domain Matsudaira Yoriyuki (1631–1717) Ritsuhime (1632–1711) married Yamanobe Yoshikata (1615–1669) Suzuki Shigeyoshi (1634–1668) Ohime (1627–1656) married Maeda Mitsutaka of Kaga Domain Matsudaira Yoritoshi (1630–1674) Matsudaira Yoriyuki (1631–1664) Matsudaira Fusatoki (1633–1682) Furihime (1633–1667) married Honda Masatoshi (1641–1707) of Ōkubo Domain Takehime (1636–1637) Umehime (1638–1697) married Utsunomiya Takatsuna (1627–1700) Inuhime (1634–1675) married Hosokawa Tsunatoshi (1641–1721) of Kumamoto Domain Ichihime (1639–1690) married Sakai Tadaharu Kumahime (1649–1709) married Ito Tomotsugu (1594–1655) | ||
| Ichi-hime | Seiun’in | January 28, 1607 | March 7, 1610 | Okaji no Kata |
Speculated Children
| Image | Name | Pusthomous Name | Birth | Death | Mother | Marriage | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzuki Ichizo | September 10, 1556 | Daughter of Hatago of post station in Totoumi Province | |||||
| Nagami Sadachika | March 1, 1574 | January 5, 1605 | Kotoku-no-Tsubone | Nagami clan's daughter | Nagami Sadayasu | ||
| Matsudaira Minbu | 1582 | 1616 | Omatsu-no-Kata | ||||
| Ogasawara Gonnojō | 1589 | May 7, 1615 | Sanjo Clan | Kondo Hidemochi (1547–1631) of Iinoya Domain's daughter | Son Daughter married Mamiya Nobukatsu Daughter married Nakagawa Tadayuki | ||
 | Ii Naotaka of Hikone Domain | Kyūshō-in-dono Gōtokuten'eidaikoji | March 16, 1590 | August 16, 1659 | Akihime, Hachisuka Iemasa’s daughter | by concubines: Ii Naoshige (1612–1661) Ii Naozumi (1625–1676) of Hikone Domain Ii Naotsuna (1622–1658) Matsuchiyo Ii Naohiro | |
 | Doi Toshikatsu of Koga Domain | Hōchiin-dono denshuhoonyotaiokyogendaikoji | April 19, 1573 | August 12, 1644 | Matsudaira Chikakiyo’s daughter | By concubines: Doi Toshitaka (1619–1685) of Koga Domain Doi Katsumasa Doi Toshinaga (1631–1696) of Nishio Domain Doi Toshifusa (1631–1683) of Ōno Domain Doi Toshinao (1637–1677) of Ōwa Domain Katsuhime married Ikoma Takatoshi of Yashima Domain Kazuhime married Hori Naotsugu (1614–1638) of Murakami Domain Katsuhime married Matsudaira Yorishige of Takamatsu Domain Inuhime married Inoue Yoshimasa Kahime married Nasu Sukemitsu (1628–1687) of Karasuyama Domain | |
| Goto Hiroyo | Juny 24, 1606 | March 14, 1680 | Ohashi-no-Tsubone, Aoyama Masanaga’s daughter | ||||
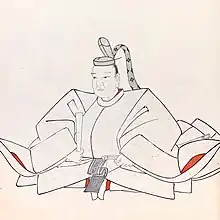 | Tokugawa Iemitsu, 3rd Shogun | Daiyūin-dono zosho | August 12, 1604 | June 8, 1651 | Lady Kasuga | Takako (1622–1683), Takatsukasa Nobufusa’s daughter | By concubines: Chiyohime (1637–1699) married Tokugawa Mitsutomo of Owari Domain Tokugawa Ietsuna, 4th Shogun Kamematsu (1643–1647) Tokugawa Tsunashige of Kofu Domain Tokugawa Tsunayoshi, 5th Shogun Tsurumatsu (1647–1648) |
Adopted children
| Image | Name | Posthumous Name | Birth | Death | Parents | Marriage | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Matsudaira Ieharu | Torin’in dokaisosakudaizenzomon | 1579 | April 15, 1592 | Okudaira Nobumasa of Kano Domain Kamehime | ||
.jpg.webp) | Okudaira Tadamasa of Kanō Domain | Oyamahoei Kokoku-in | 1580 | August 7, 1614 | Okudaira Nobumasa of Kano Domain Kamehime | Yoshun’in-dono, Satomi Yoshiyori (1543–1587)’s daughter | Okudaira Tadataka (1608–1632) of Kano Domain |
 | Matsudaira Tadaaki of Himeji Domain | Tenshoin shingangentetsudaikoji | 1583 | May 1, 1644 | Okudaira Nobumasa of Kano Domain Kamehime | first: Oda Nobukane of Kaibara Domain's daughter Second: Koide Yoshimasa (1565–1613) of Izushi Domain's daughter | From Concubines: Matsudaira Tadahiro (1631–1700) of Yamagata Domain Matsudaira Kiyomichi (1634–1645) of Himejishinden Domain Murihime married Nabeshima Tadanao (1613–1635) later married Nabeshima Naozumi of Hasunoike Domain daughter married Okubo Tadamoto (1604–1670) of Karatsu Domain daughter married Kyogoku Takatomo (1623–1674) of Mineyama Domain daughter married Shijo Takasube (1611–1647) daughter married Sakakibara Kiyoteru daughter married Osawa Naochika (1624–1681) |
 | Matehime | Yojuin | 1589 | May 5, 1638 | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | First: Fukushima Masayuki (1858–1608) Second: Tsugaru Nobuhira of Hirosaki Domain | By First: Daidōji Naohide II (1606–1636) By Second: Tsugaru Nobufusa (1620–1662) of Kuroishi Domain |
 | Ei-hime | Dairyō-in | 1585 | March 1, 1635 | Hoshina Masanao Takehime (1553–1618; ieyasu's half-sister) | Kuroda Nagamasa of Fukuoka Domain | Kuroda Tadayuki (1602–1654) of Fukuoka Domain Tokuko married Sakakibara Tadatsugu (1605–1665) of Himeji Domain Kuroda Nagaoki (1610–1665) of Akizuki Domain Kuroda Takamasa (1612–1639) of Torenji Domain Kameko married Ikeda Teruoki (1611–1647) of Ako Domain |
| Kumahime | Kōshō-in | 1595 | April 12, 1632 | Hisamatsu Sadakatsu of Kuwana Domain Tatsu (Okudaira Sadatomo {d.1585}’s daughter) | Yamauchi Tadayoshi (1592–1665) of Tosa Domain | Yamauchi Tadatoyo of Tosa Domain Yamauchi Tadanao of Tosa-Nakamura Domain Kiyohime married Matsushita Nagatsuna (1610–1658) of Miharu Domain | |
| Renhime | Chōju-in | 1582 | August 24, 1652 | Matsudaira Yasunao (1569–1593) of Fukaya Domain Honda Hirotaka’s daughter | Arima Toyouji (1569–1642) of Kurume Domain | Arima Tadayori (1603–1655) of Kurume Domain Arima Nobukata Arima Yoritsugu (1611–1649) | |
| Kunihime | Eijuin | 1595 | April 10, 1649 | Honda Tadamasa of Himeji Domain Kumahime (1577–1626; Matsudaira Nobuyasu’s daughter) | First: Hori Tadatoshi (1596–1622) of Takada Domain Second: Arima Naozumi of Nobeaka Domain | by Second: Arima Yasuzumi (1613–1692) of Nobeaka Domain Arima Zumimasa daughter married Honda Masakatsu (1614–1671) of Koriyama Domain Daughter adopted by Honda Masakatsu daughter married Akimoto Tomitomo (1610–1657) of Yamura Domain | |
| Kamehime | Enshō-in | 1597 | November 29, 1643 | Honda Tadamasa of Himeji Domain Kumahime (1577–1626; Matsudaira Nobuyasu’s daughter) | First: Ogawara Tadanaga (1595–1615) Second: Ogasawara Tadazane of Kokura Domain | By First: Shigehime (d.1655) married Hachisuka Tadateru of Tokushima Domain Ogasawara Nagatsugu (1615–1666) of Nakatsu Domain By second: Ogasawara Nagayasu (1618–1667) Ichimatsuhime (b.1627) married Kuroda Mitsuyuki (1628–1707) of Fukuoka Domain Ogasawara Naganobu (1631–1663) Tomohime married Matsudaira Yorimoto (1629–1693) of Nukada Domain Daughter | |
| Manhime | Kyōdaiin | 1592 | February 7, 1666 | Ogasawara Hidemasa (1569–1615) of Matsumoto Domain Tokuhime (1576–1607; Matsudaira Nobuyasu’s daughter) | Hachisuka Yoshishige of Tokushima Domain | Hachisuka Tadateru of Tokushima Domain Mihohime (1603–1632) married Ikeda Tadakatsu (1602–1632) of Okayama Domain Manhime (1614–1683) married Mizuno Narisada (1603–1650) | |
| Tsubakihime | Kyusho-in | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | First: Tanaka Tadamasa (1585–1620) of Yanagawa Domain Second: Matsudaira Narishige (1594–1633) of Tamba-Kameyama Domain | ||||
| Jomyo-in | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | First: Nakamura Kazutada (1590–1609) of Yonogo Domain Second: Mōri Hidemoto of Chofu Domain | |||||
| Hanahime | Tobai-in | August 2, 1639 | Matsudaira Yasuchika (1521–1683), Ebara Masahide's daughter | Ii Naomasa of Hikone Domain | Ii Naokatsu of Annaka Domain Masako married Matsudaira Tadayoshi of Oshi Domain Kotoko’in married Date Hidemune of Uwajima Domain | ||
| Ryuko-in | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | Suganuma Sadayori (1576–1605) of Nagashima Domain | |||||
| Kikuhime | Kogen’in | 1588 | October 28, 1661 | Abe Nagamori (1568–1632) of Ogaki Domain Matsudaira Kiyomune (1538–1605) of Hachiman'yama Domain's daughter | Nabeshima Katsushige of Saga Domain | Ichihime married Uesugi Sadakatsu (1604–1645) of Yonezawa Domain Tsuruhime married Takeu Shigetoki (1608–1669) Mitsuchiyo Nabeshima Tadanao (1613–1635) Nabeshima Naozumi of Hasunoike Domain Hojoin married Isahaya Shigetoshi (1608–1652)
| |
| Kanahime | Shōjō-in | 1582 | November 3, 1656 | Mizuno Tadashige | Katō Kiyomasa of Kumamoto Domain | Yasohime (1601–1666) married Tokugawa Yorinobu of Kishu Domain | |
| Yōhime | Teishō-in | 1591 | August 10, 1664 | Hoshina Masanao Takehime (1553–1618, Ieyasu's half-sister) | Koide Yoshihide (1587–1666) of Izushi Domain | Taitō Daughter Married Miura Katsushige (1605–1631) of Shimōsa-Miura Domain later Yamauchi Katsutada Koide Yoshishige (1607–1674) of Izushi Domain Daughter Daughter Hoshina Masahide (1611–1678) Koide Hidemoto Koide Hidenobu Kogaku-in married Tachibana Tanenaga (1625–1711) of Miike Domain Daughter Married Matsudaira Nobuyuki (1631–1686) of Koga Domain | |
| Seigen'in | Hoshina Masanao Takehime (1553–1618, Ieyasu's half-sister) | Anbe Nobumori (1584–1674) of Okabe Domain | Anbe Nobuyuki (1604–1683) of Okabe Domain | ||||
| Shosen'in | 1642 | Makino Yasunari (1555–1610) of Ogo Domain | Fukushima Masanori of Hiroshima Domain | daughter married Minase Kanetoshi daughter married Ono Inuoemon | |||
| Matsudaira Iekiyo of Yoshida Domain | Asano Nagashige (1588–1632) of Kasama Domain | Asano Naganao of Ako Domain daughter married Asano Nagaharu (1614–1675) of Miyoshi Domain daughter married Matsudaira Tadatake | |||||
| Shoshitsu'in | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | First: Osuga Tadamasa (1581–1607) of Yokosuka Domain Second: Suganuma Sadayoshi (1587–1643) of Tamba-Kameyama Domain | by First: Sakakibara (Osuga) Tadatsugu (1605–1665) of Himeji Domain By Second: Suganuma Sadaakira (1625–1647) of Tamba-Kameyama Domain daughter married Ogasawara Naganori (1624–1678) of Yoshida Domain | ||||
| Dōsen-in | Matsudaira Yasumoto (1552–1603) of Sekiyado Domain | Okabe Nagamori (1568–1632) of Ōgaki Domain | Okabe Nobukatsu (1597–1668) of Kishiwada Domain | ||||
| Hisamatsu Sadakatsu of Kuwana Domain Tatsu (Okudaira Sadatomo {d.1585}’s daughter) | Nakagawa Hisanori (1594–1653) of Oka Domain | Nakagawa Hisakiyo (1615–1681) of Oka Domain | |||||
 | Komatsuhime | Dairen-in | 1573 | March 27, 1620 | Honda Tadakatsu of Kuwana Domain | Sanada Nobuyuki of Matsushiro Domain | Manhime married Koriki Tadafusa of Shimabara Domain Masahime married Sakuma Katsumune (1589–1616) Sanada Nobumasa (1597–1658) of Matsushiro Domain Sanada Nobushige (1599–1648) of Hashina Domain |
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Tokugawa Ieyasu[44] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ieyasu in popular culture
In James Clavell's historical-novel Shōgun, Tokugawa served as basis for the character of "Toranaga". Toranaga was portrayed by Toshiro Mifune in the 1980 TV mini-series adaptation.
Hyouge Mono (へうげもの) is a Japanese manga written and illustrated by Yoshihiro Yamada. It was adapted into an anime series in 2011, and includes a fictional depiction of Tokugawa's life.
In Sengoku Basara game and anime series, he was shown with Honda Tadakatsu. In earlier games, he was armed with spears and led countless warriors, in later ones, he discards the spear and fights with his fists (similar to Boxing fighting style) and wants Japan united under the force of bonds.
Tokugawa is the leader of Japan in Sid Meier's Civilization IV. He is an aggressive and organized leader with an emphasis on mercantilism.
Honnōji theory
Among the many conspiracies surrounding the Honnō-ji Incident is Ieyasu's role in the event. Historically, Ieyasu was away from his lord at the time and, when he heard that Nobunaga was in danger, he wanted to rush to his lord's rescue in spite of the small number of attendants with him. However, Tadakatsu advised for his lord to avoid the risk and urged for a quick retreat to Mikawa. Masanari led the way through Iga and they returned home by boat.
However, skeptics think otherwise. While they usually accept the historically known facts about Ieyasu's actions during Mitsuhide's betrayal, theorists tend to pay more attention to the events before. Ever since Ieyasu lost his wife and son due to Nobunaga's orders, they reason, he held a secret resentment against his lord. Generally, there is some belief that he privately goaded Mitsuhide to take action when the two warlords were together in Azuchi Castle. Together, they planned when to attack and went their separate ways. When the deed was done, Ieyasu turned a blind eye to Mitsuhide's schemes and fled the scene to feign innocence. A variation of the concept states that Ieyasu was well aware of Mitsuhide's feelings regarding Nobunaga and simply chose to do nothing for his own benefit.
Notes
- Perez, Louis G. (1998). The history of Japan. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-00793-4. OCLC 51689128.
- "Japan - The bakuhan system". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved June 1, 2020.
- "Iyeyasu". Encyclopedia.com.
- "Iyeyasu". Merriam-Webster.
- Turnbull, Stephen (2012). Tokugawa Ieyasu. Osprey Publishing. pp. 5–9. ISBN 9781849085748.
- McLynn, Frank (November 10, 2009). Heroes & Villains: Inside the minds of the greatest warriors in history. Random House. p. 230. ISBN 978-1-4090-7034-4.
- Turnbull, Stephen (1987). Battles of the Samurai. Arms and Armour Press. p. 35. ISBN 0853688265.
- Screech, Timon (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779–1822. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0-7007-1720-X, pp. 85, 234; n.b., Screech explains
Minamoto-no-Ieyasu was born in Tenbun 11, on the 26th day of the 12th month (1542) and he died in Genna 2, on the 17th day of the 4th month (1616); and thus, his contemporaries would have said that he lived 75 years. In this period, children were considered one year old at birth and became two the following New Year's Day; and all people advanced a year that day, not on their actual birthday.
- Turnbull, Stephen (2012). Tokugawa Ieyasu. Osprey Publishing. p. 10. ISBN 9781849085748.
- Turnbull, Stephen (1998). The Samurai Sourcebook. Cassell & Co. p. 215. ISBN 1854095234.
- Turnbull, Stephen R. (1977). The Samurai: A Military History. New York: MacMillan Publishing Co. p. 144.
- Pitelka, Morgan (2015). Spectacular Accumulation: Material Culture, Tokugawa Ieyasu, and Samurai Sociability. University of Hawai'i Press. ISBN 9780824851576.
- Brinkley, Frank & Kikuchi (1912). A History of the Japanese People From the Earliest Times to the End of the Meiji Era. Library of Alexandria. ISBN 978-1-4655-1304-5.
- Screech, Timon (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779–1822. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0-7007-1720-X, p. 82.
- Sansom, Sir George Bailey (1961). A History of Japan, 1334–1615. Stanford University Press. p. 353. ISBN 0-8047-0525-9.
- Turnbull, Stephen (1987). Battle of the Samurai. London: Arms and Armour Press. pp. 67–78. ISBN 0853688265.
- Turnbull, Stephen (2000). The Samurai Sourcebook. London: Cassell & C0. pp. 222–223. ISBN 1854095234.
- Turnbull, Stephen (August 20, 2012). Nagashino 1575: Slaughter at the barricades. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-78200-229-1.
- Sadler, p. 164.
- Nutall, Zelia. (1906). The Earliest Historical Relations Between Mexico and Japan, p. 2
- "Japan to Decorate King Alfonso Today; Emperor's Brother Nears Madrid With Collar of the Chrysanthemum for Spanish King". The New York Times, November 3, 1930, p. 6.
- Sadler, p. 187
- Titsingh, Isaac (1834). [Siyun-sai Rin-siyo/Hayashi Gahō, 1652], Nipon o daï itsi ran; ou, Annales des empereurs du Japon. Paris: Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland, p. 405.
- Titsingh, Isaac (1822). Illustrations of Japan. London: Ackerman, p. 409.
- Van Wolferen, Karel (1990). The Enigma of Japanese Power: People and Politics in a Stateless Nation. New York: Vintage Books. p. 28. ISBN 0-679-72802-3.
- "Japan – The bakuhan system". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved May 19, 2020.
- Milton, Giles. Samurai William: The Englishman Who Opened Japan. New York: Farrar, Straus, and Giroux, 2003.
- Nutail, Zelia (1906). The Earliest Historical Relations Between Mexico and Japan. Berkeley: University of California Press, pp. 6–45.
- Milton, Giles (January 18, 2003). Samurai William : the Englishman Who Opened Japan. p. 265. ISBN 9780374706234. Quoting Le P. Valentin Carvalho, S.J.
- Murdoch, James; Yamagata, Isoh (1903). A History of Japan. Kelly & Walsh. p. 500.
- Mullins, Mark R. (1990). "Japanese Pentecostalism and the World of the Dead: a Study of Cultural Adaptation in Iesu no Mitama Kyokai". Japanese Journal of Religious Studies. 17 (4): 353–374. doi:10.18874/jjrs.17.4.1990.353-374.
- JAANUS / Gongen-zukuri 權現造
- Goethals, George R.; Sorenson, Georgia (March 19, 2004). Encyclopedia of leadership: A-E. SAGE. ISBN 978-0-7619-2597-2.
- "Jyoukouji:The silk coloured portrait of wife of Takatsugu Kyogoku". May 6, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved February 15, 2018.
- Sansom, George, A History of Japan, 1615–1867, Stanford University Press. 1960, p. 9
- Frederic, Louis, Daily Live in Japan at the Time of the Samurai, 1185–1603, Charles E. Tuttle Company, Inc., Rutland, Vermont, 1973, p. 180
- Leonard, Jonathan, Early Japan, Time-Life Books, New York, c1968, p.162
- Sansom, G. B., The Western World and Japan, Charles E. Tuttle Company, Rutland and Tokyo, 1950, p. 132
- Sadler, p. 344.
- Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1956). Kyoto: the Old Capital of Japan, 794–1969, p. 418.
- OldTokyo.com: Tōshō-gū Shrine; American Forum for Global Education, JapanProject Archived 2012-12-31 at the Wayback Machine; retrieved 2012-11-1.
- Storry, Richard. (1982). A History of Modern Japan, p. 60
- Thomas, J. E. (1996). Modern Japan: a social history since 1868, ISBN 0582259614, p. 4.
- "Genealogy". Reichsarchiv (in Japanese). Retrieved December 17, 2017.
Bibliography
- Sadler, A. L. (1937). The Maker of Modern Japan.
Further reading
- Bolitho, Harold (1974). Treasures Among Men: The Fudai Daimyo in Tokugawa Japan. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-01655-0. OCLC 185685588.
- McClain, James (1991). The Cambridge History of Japan Volume 4. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- McLynn, Frank (2008). The Greatest Shogun, BBC History Magazine, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp 52–53.
- あおもりの文化財 徳川家康自筆日課念仏 – 青森県庁ホームページ
- Sansom, George (1961). A History of Japan, 1334–1615. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-0525-9.
- Totman, Conrad D. (1967). Politics in the Tokugawa Bakufu, 1600–1843. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. OCLC 279623.
External links
- The Christian Century in Japan, by Charles Boxer
 Media related to Tokugawa Ieyasu at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tokugawa Ieyasu at Wikimedia Commons
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Tokugawa Ieyasu |
| Military offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Sengoku period |
Shōgun: Tokugawa Ieyasu 1603–1605 |
Succeeded by Tokugawa Hidetada |