UTC−12:00
UTC−12:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −12:00. It is the last to enter a new year, and is sometimes referred to as the International Date Line West time zone (IDLW).[1]
| UTC−12:00 | |
|---|---|
| time zone | |
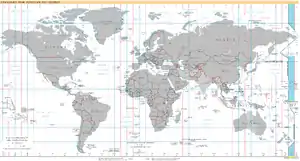 World map with the time zone highlighted | |
| UTC offset | |
| UTC | UTC−12:00 |
| Current time | |
| 12:30, 7 February 2021 UTC−12:00 [refresh] | |
| Central meridian | |
| 180 degrees | |
| Date-time group | |
| Y | |
As standard time (all year round)
Oceania
 United States
United States
- Baker Island and Howland Island (uninhabited islands belonging to the United States)
UTC−12:00 is a nautical time zone comprising the high seas between 180° and 172°30′W longitude, and the time is obtained by subtracting twelve hours from UTC.
Characteristics of UTC−12:00
A number of inhabited territories lie within the longitudinal limits of this time zone (Tonga, Wallis and Futuna and Chatham Islands as well as parts of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug of Russia, the US state of Alaska, Fiji and Samoa) but none of them keeps the date and time of UTC−12:00. Instead, they keep the time and date (or just the date) of one of the neighboring zones, usually because they belong, politically, to a country which lies mostly in the neighboring time zone.
Since the International Date Line West (IDLW) time zone represents the last place on Earth where a particular time and/or date exists, it is referred to as Anywhere on Earth (AoE). This means that, for instance, if a deadline has not passed in the UTC–12:00 zone, the deadline has not yet passed "Anywhere on Earth".[1]
The IDLW is also used in software testing for time zone related code that uses system default time zone, as in some cases they may be the same as on the developer's computer. Since the area of the IDLW has no programmers or data centers, there is no conflict.
References
- "IEEE 802.16 AOE Deadline Documentation". IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee. Retrieved 1 January 2018.