Allolevivirus
Allolevivirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family Leviviridae. Enterobacteria serve as natural hosts.[1] There are currently only two species in this genus including the type species Escherichia virus Qbeta.[2]
| Allolevivirus | |
|---|---|
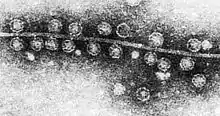 | |
| TEM of Bacteriophage Qβ attached to the pilus of E. coli and its genome | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Lenarviricota |
| Class: | Allassoviricetes |
| Order: | Levivirales |
| Family: | Leviviridae |
| Genus: | Allolevivirus |
| Type species | |
| Escherichia virus Qbeta | |
Structure
Viruses in Allolevivirus are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and Spherical geometries, and T=3 symmetry. The diameter is around 26 nm.[1]
Genome
Alloleviviruses have a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. The genome is linear and non-segmented and around 4kb in length. The genome codes for four proteins, which are the coat, replicase, maturation, and lysis protein.[1]
Life cycle
Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. Replication follows the positive-strand RNA virus replication model. Positive-strand RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by suppression of termination. The virus exits the host cell by bacteria lysis. Enterobacteria serve as the natural host.[1]
Taxonomy
The genus Allolevivirus has two species:[2]
- Allolevirus
- Escherichia virus FI
- Escherichia virus Qbeta
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). "Virus Taxonomy: 2019 Release". talk.ictvonline.org. Retrieved 2 September 2020.