Austrian Grand Prix
The Austrian Grand Prix (German: Großer Preis von Österreich) is a Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile sanctioned auto race which was held in 1964, 1970–1987 and 1997–2003. The Grand Prix returned to the Formula One calendar in 2014.
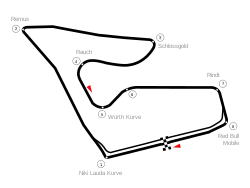
| Red Bull Ring (1997–2003, 2014–present) | |
 | |
| Race information | |
|---|---|
| Number of times held | 39 |
| First held | 1963 |
| Most wins (drivers) | |
| Most wins (constructors) | |
| Circuit length | 4.318 km (2.683 mi) |
| Race length | 306.452 km (190.420 mi) |
| Laps | 71 |
| Last race (2020) | |
| Pole position | |
| Podium | |
| Fastest lap | |
History
The Austrian Grand Prix has been held at two different locations in southeastern Austria, being originally held in Zeltweg, about 70 km (43 mi) west of Graz. Since 1969 the Austrian Grand Prix has taken place in neighbouring Spielberg, with the two venues being within approximately 4 km (2.5 mi) of each other.[1] It was first held at the Zeltweg Air Base for six years, before a permanent track, originally called the Österreichring and later known as the A-1 ring and Red Bull Ring, was built.
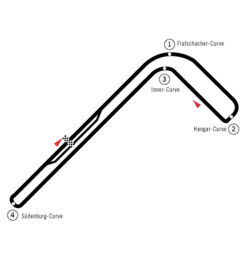
Zeltweg Airfield circuit
A non-championship event was held in 1963 at a race track on the Zeltweg Airfield and it was won by Australian Jack Brabham. The first championship event took place in the following year, and Italian Lorenzo Bandini won his only Formula One championship race in a Ferrari. The race was a success, but the track was deemed too dangerous; it was narrow and very bumpy, and spectators complained of poor viewing areas. The FIA removed the race from the F1 calendar until a suitable track was built.
The event was run in 1965 as a non-championship sports car race, the Zeltweg 200 Miles, before being adopted by the World Sportscar Championship from 1966 to 1969 as the 1000 km Zeltweg.[2]
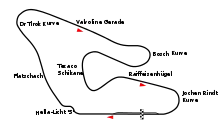
Österreichring
From 1970 until 1987, the event was held at the Österreichring (translated literally as "Austria circuit") (also located near Zeltweg). It was built in the scenic Styrian mountains and it was a fast, flowing track where every corner was high speed and long. The Austrian Grand Prix was designated the European Grand Prix once, 1975, when this title was an honorary designation given each year to one Grand Prix race in Europe. The very fast track was popular with drivers, and the events were moderately successful. The first race on this track was dominated by Ferrari, with their more powerful Flat-12 engines enabled them to be 10 mph faster- which is a lot in racing terms. The 1971 race saw Swiss driver Jo Siffert dominate in his BRM and Briton Jackie Stewart took his second Drivers' Championship. The 1975 event was marred by the fatal accident of American Mark Donohue, and the race itself was rain-soaked and was won by Vittorio Brambilla, winning the only F1 race of his career, and, true to form, he crashed when he crossed the finish line when the race was stopped early because the rain got worse. In 1976, home favourite Niki Lauda's appalling crash at the Nürburgring caused him to miss the race, which was won by Briton John Watson in the short-lived Penske F1 team, winning his first Formula One race.
1976 had seen the Voest-Hugel corner changed slightly into one corner instead of two corners; but 1977 saw a slow three corner chicane installed at Voest-Hugel, which was where Donohue had crashed 2 years before. What was the fastest corner on the track was now the slowest corner there and would become known as the Hella-Licht Chicane. This race was won by Australian Alan Jones in a Shadow; and like Brambilla and Watson, it was his first Grand Prix victory. 1978 saw the dominant Lotus 79s on the front row, and American Mario Andretti crashed at the Glatz Kurve on the first lap, and his teammate, Swede Ronnie Peterson took victory. 1979 started to show the superiority of turbo-charged engines on this fast and high-altitude circuit. Although Jones won again in a Williams, Jean-Pierre Jabouille and Rene Arnoux in their Renaults were able to dominate this event and the following year's race, which Jabouille won. 1981 saw three turbo-charged cars dominate the front row; and into the race, the immense power and dreadful handling of Didier Pironi's Ferrari helped him to hold up four better handling cars and get into a five-way battle for third place, which went on for a while but the four cars passed eventually passed him, one of which was Jacques Laffite who went on to win the race. 1982 saw a spectacular show in which five turbocharged cars dominated the grid; all but one of these cars retired with mechanical troubles, including Italian Riccardo Patrese who had a spectacular accident at the Texaco Bends and Frenchman Alain Prost, whose engine expired with a few laps to go while in the lead. After Prost's retirement, the race turned into a dead-heat sprint between Italian Elio de Angelis in a Lotus and Finn Keke Rosberg in a Williams. Rosberg had been steadily chipping away at De Angelis; but after Prost retired, Rosberg began to make up 1.5 seconds a lap on De Angelis; and on the last lap the two so-far winless drivers battled for victory, and De Angelis was able to hold off Rosberg and win by less than half a car's length; .05 seconds. 1984 saw Lauda finally take victory at home in his McLaren, and Prost won the next two races. The 1985 race saw a fearsome crash at the Panorama Curve when Andrea de Cesaris spectacularly rolled his Ligier, which led to him being fired from the team. 1986 saw Austrian driver Gerhard Berger lead the early laps in his 1,400 bhp (1,044 kW; 1,419 PS) Benetton-BMW, but electrical problems saw his race ruined allowing Alain Prost to take the win by over a lap from the Ferraris of Michele Alboreto and Stefan Johansson.
The 1987 race was restarted twice due to accidents on the narrow pit-straight grid; and this track was also deemed too dangerous by FIA standards, because of the amount of high-speed corners, lack of protection from trees and embankments and accidents at the start of many races on the narrow and confined pit straight. Increasing speeds were also a growing problem at the Österreichring, polesitter Nelson Piquet averaged 159.457 mph (255.756 km/h) in his 1,100 hp Honda-powered Williams. Piquet finished second to his teammate, Briton Nigel Mansell. Attempts to bring the race back were unsuccessful, and the event disappeared for a decade.
A1-Ring

In 1995 and 1996, the Österreichring was refurbished and brought up to date, which allowed the race to run again in 1997. Since the track, which was renamed A1-Ring after a sponsor, is located on the municipal territory of Spielberg, Spielberg was now given as the site of the Grand Prix. The whole layout was redesigned by Hermann Tilke, and the track lost all of its long, sweeping corners, aside from the Texaco Bends (which were made shorter and slower) and the Hella-Licht chicane, Flatschach, Dr. Tiroch curve and the first half of the backstretch run up to where the Bosch-Kurve was taken out and replaced with a bypass that went directly to the second half of the fast, uphill backstretch. The 2002 event received negative publicity after Ferrari instructed Rubens Barrichello to cede his victory to Michael Schumacher. It was a mainstay on the calendar until hosting its final race in 2003.
Red Bull Ring
In July 2013, it was reported that the circuit's new owners Red Bull GmbH had reached an agreement with Bernie Ecclestone to revive the Austrian Grand Prix after a ten-year absence from the calendar. The race was given a provisional date of July 2014.[3] On 6 December, the officially released calendar included the Austrian Grand Prix on it.[4]
Official names
- 1963, 1998: Großer Preis von Österreich (no official sponsor)[5]
- 1964, 1986–1987, 1997, 1999, 2014–2017: Grosser Preis von Österreich (no official sponsor)[6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
- 1970–1972: Grand Prix von Österreich (no official sponsor)[15][16]
- 1973: Memphis Grand Prix von Österreich[17]
- 1974–1975: Memphis Grand Prix[18][19]
- 1976: Raiffeisen Grand Prix/Großer Preis von Österreich[20]
- 1977: Gröbl Möbel Grand Prix/Großer Preis von Österreich[21]
- 1978–1979: Grand Prix (no official sponsor)[22][23]
- 1980–1981: Grand Prix/Großer Preis von Österreich (no official sponsor)[24][25]
- 1982–1983: Grand Prix/Holiday Grand Prix (no official sponsor)[26][27]
- 1984–1985: Grosser Preis von Österreich/Holiday Grand Prix (no official sponsor)[28][29]
- 2000–2002: Grosser A1 Preis von Österreich[30]
- 2003: A1 Grand Prix von Österreich[31]
- 2018: Eyetime Grosser Preis von Österreich[32][33]
- 2019, 2021: myWorld Grosser Preis von Österreich[34][35]
- 2020: Rolex Grosser Preis von Österreich[36]
Winners of the Austrian Grand Prix
Repeat winners (drivers)
Drivers in bold are competing in the Formula One championship in the current season.
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
| Wins | Driver | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1968, 1969*, 1971 | |
| 1983, 1985, 1986 | ||
| 2 | 1973, 1978 | |
| 1977, 1979 | ||
| 1998, 2000 | ||
| 2002, 2003 | ||
| 2014, 2015 | ||
| 2018, 2019 | ||
| 2017, 2020 |
* Shared win with Kurt Ahrens, Jr.
Repeat winners (constructors)
Teams in bold are competing in the Formula One championship in the current season.
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
| Wins | Constructor | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 1984, 1985, 1986, 1998, 2000, 2001 | |
| 1964, 1965, 1970, 1999, 2002, 2003 | ||
| 5 | 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2020 | |
| 4 | 1972, 1973, 1978, 1982 | |
| 3 | 1966, 1968, 1969 | |
| 1979, 1987, 1997 | ||
| 2 | 1963, 1974 | |
| 1980, 1983 | ||
| 2018, 2019 |
Repeat winners (engine manufacturers)
Manufacturers in bold are competing in the Formula One championship in the current season.
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
| Wins | Manufacturer | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1967, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976, 1977, 1978, 1979, 1982 | |
| 8 | 1998, 2000, 2001, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2020 | |
| 6 | 1964, 1965, 1970, 1999, 2002, 2003 | |
| 3 | 1966, 1968, 1969 | |
| 1984, 1985, 1986 | ||
| 1980, 1983, 1997 | ||
| 2 | 1987, 2019 |
* Built by Cosworth, funded by Ford (except 1967)
** Between 1998 and 2001 built by Ilmor, funded by Mercedes
*** Built by Porsche
Year by year

A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
References
- "Zeltweg Air Base". Google Maps. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- "Zeltweg 200 Miles 1965 - Race Results - Racing Sports Cars". www.racingsportscars.com. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "Austrian Grand Prix set to return to F1 calendar in 2014". Autosport.com. Haymarket Publications. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- "2015". Formula1.com. Retrieved 17 December 2015.
- "1998 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1964 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1986 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1987 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1997 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1999 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "2014 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "2015 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "2016 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "2017 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1971 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1972 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- Mitchell, Malcolm. "1973 Formula 1 Programmes – The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- "1974 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1975 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- Mitchell, Malcolm. "1976 Formula 1 Programmes – The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- Mitchell, Malcolm. "1977 Formula 1 Programmes – The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- "1978 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1979 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1980 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1981 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1982 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1983 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1984 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1985 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- Mitchell, Malcolm. "2000 Formula 1 Programmes – The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- Mitchell, Malcolm. "2003 Formula 1 Programmes – The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- "2018 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "eyetime to be title sponsor at the Austrian Grand Prix". Formula1.com. Formula One World Championship Limited. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- "2019 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "Austria". Formula1.com. Formula One World Championship Limited. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- "Austria". Formula1.com. Formula One World Championship Limited. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- Higham, Peter (1995). The Guinness Guide to International Motor Racing. p. 350. ISBN 0851126421.
