CONCACAF
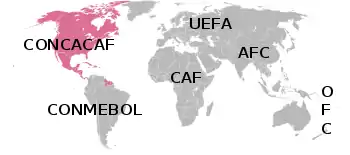
The Confederation of North, Central America and Caribbean Association Football[1][2] (CONCACAF /ˈkɒnkəkæf/ KON-kə-kaf; typeset for branding purposes since 2018 as Concacaf)[3] is one of FIFA's six continental governing bodies for association football. Its 41 member associations represent countries and territories mainly in North America, including the Caribbean and Central America, and due to geopolitical reasons, three nations from The Guianas subregion of South America — Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana (an overseas region of France).[4] The CONCACAF's primary functions are to organize competitions for national teams and clubs, and to conduct the World Cup and Women's World Cup qualifying tournaments.
 | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | CONCACAF |
|---|---|
| Formation | 18 September 1961 |
| Founded at | Mexico City, Mexico |
| Type | Sports organization |
| Headquarters | Miami, Florida, United States |
| Coordinates | 25.773°N 80.138°W |
Region | North America (the Caribbean, Central America, and Northern America) South America (The Guianas) |
Membership | 41 member associations |
Official language | |
| Victor Montagliani | |
General Secretary | Philippe Moggio |
Parent organization | FIFA |
| Subsidiaries | |
| Website | CONCACAF.com |
| FIFA confederations |
|---|
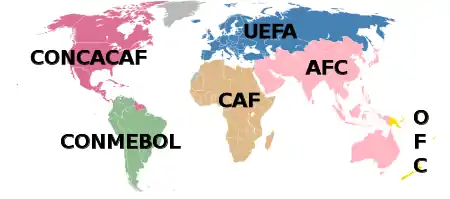 |
| AFC, CAF, CONCACAF |
| CONMEBOL, OFC, UEFA |
The CONCACAF was founded in its current form on 18 September 1961 in Mexico City, Mexico, with the merger of the NAFC and the CCCF, which made it one of the then five, now six, continental confederations affiliated with FIFA. Canada, Costa Rica, Cuba, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Netherlands Antilles (Curaçao), Nicaragua, Panama, Suriname and United States were founding members.[5]
The CONCACAF is the third-most successful FIFA confederation. Mexico dominated CONCACAF men's competition early on and has won the most Gold Cups since the beginning of the tournament in its current format. The Mexico national football team is the only CONCACAF team to win an official FIFA tournament by winning the 1999 FIFA Confederations Cup. Mexico and the U.S. have won all but one of the editions of the CONCACAF Gold Cup. In recent years Costa Rica and Panama have become powers in the region; in 2014, Costa Rica became the 4th CONCACAF country after the United States, Cuba, and Mexico to make the World Cup quarterfinals, while Panama became the eleventh country from the confederation to participate in the World Cup in 2018. The United States has been very successful in the women's game, being the only CONCACAF member to win all three major worldwide competitions in women's football — the World Cup (4), the Olympics (4), and the Algarve Cup (10). Canada is the only other member to win at least one of the major competitions, winning the Algarve Cup in 2016.
Governance
The CONCACAF is led by a General Secretary, Executive Committee, Congress, and several standing committees. The Executive Committee is composed of eight members — one president, three vice-presidents, three members, and one female member.[6] Each of the three geographic zones in CONCACAF is represented by one vice-president and one member. The Executive Committee carries out the various statutes, regulations, and resolutions.
Leadership
.svg.png.webp)
The first leader of CONCACAF was Costa Rican Ramón Coll Jaumet; he had overseen the merger between the North American Football Confederation (NAFC) and the Confederación Centroamericana y del Caribe de Fútbol (CCCF). In 1969, he was succeeded in the role by Mexican Joaquín Soria Terrazas, who served as president for 21 years.
His successor Jack Warner was the CONCACAF president from 1990 to 2011, also for 21 years. Warner was suspended as president on 30 May 2011 due to his temporary suspension from football-related activity by FIFA following corruption allegations.[7] Chuck Blazer was the General Secretary during the same period.[8]
On 20 June 2011, Jack Warner resigned from the presidency of CONCACAF, and removed himself from all participation in football, in the wake of the corruption investigation resulting from 10 May 2011 meeting of the Caribbean Football Union.[9] The vice-president of CONCACAF, Alfredo Hawit, acted as president until May 2012.[10]
In May 2012, Cayman Islands banker Jeffrey Webb was installed as President of CONCACAF. On 27 May 2015, Webb was arrested in Zurich, Switzerland on corruption charges in the U.S.
Victor Montagliani, leader of the Canadian Soccer Association, was elected as president of CONCACAF in May 2016.[11]
Current leaders
| Name[12][13] | Nation | Position |
|---|---|---|
| Victor Montagliani | President | |
| Rodolfo Villalobos | Vice president | |
| Sunil Gulati | Vice president | |
| Randolph Harris | Vice president | |
| Yon de Luisa | Vice president | |
| Philippe Moggio | General secretary | |
| Jason Roberts | Technical Director | |
| Sonia Bien-Aime | Member | |
| Jorge Salomon | Member |
Corporate structure
CONCACAF is a non-profit company registered in Nassau, Bahamas.
The headquarters of the CONCACAF are located in Miami, United States. Previously it had been the Admiral Financial Center, George Town, Cayman Islands—the home city of former CONCACAF president Jeffrey Webb and prior to that, they were based in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago under the presidency of Jack Warner. The administration office of CONCACAF was previously located in Trump Tower, New York when Chuck Blazer was the General Secretary.
In February 2017, a satellite office was opened in Kingston, Jamaica.[14] In July 2017, a second satellite office was opened in Guatemala City, which is shared with UNCAF,[15] and most recently another satellite office for the FIFA Caribbean Development Office[16][17] was opened in Bridgetown, Barbados' suburb of Welches.[18][19]
Members
CONCACAF has 41 member associations:[20]
| Code | Association | National teams | Founded | FIFA affiliation | CONCACAF affiliation | IOC member |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North American Zone (NAFU) (3) | ||||||
| CAN | (M, W) | 1912 | 1913 | 1961 | Yes | |
| MEX | (M, W) | 1922 | 1929 | 1961 | Yes | |
| USA | (M, W) | 1913 | 1914 | 1961 | Yes | |
| Central American Zone (UNCAF) (7) | ||||||
| BLZ | (M, W) | 1980 | 1986 | 1986 | Yes | |
| CRC | (M, W) | 1921 | 1927 | 1961 | Yes | |
| SLV | (M, W) | 1935 | 1938 | 1961 | Yes | |
| GUA | (M, W) | 1919 | 1946 | 1961 | Yes | |
| HON | (M, W) | 1935 | 1951 | 1961 | Yes | |
| NCA | (M, W) | 1931 | 1950 | 1961 | Yes | |
| PAN | (M, W) | 1937 | 1938 | 1961 | Yes | |
| Caribbean Zone (CFU) (31) | ||||||
| AIA | (M, W) | 1990 | 1996 | 1996 | No | |
| ATG | (M, W) | 1928 | 1972 | between 1961 and 1973 | Yes | |
| ARU | (M, W) | 1932 | 1988 | 1986 | Yes | |
| BAH | (M, W) | 1967 | 1968 | between 1961 and 1973 | Yes | |
| BRB | (M, W) | 1910 | 1968 | 1967 | Yes | |
| BER | (M, W) | 1928 | 1962 | 1967 | Yes | |
| BOE | (M, W) | 1960 | N/A | 2014 | No | |
| VGB | (M, W) | 1974 | 1996 | 1996 | Yes | |
| CAY | (M, W) | 1966 | 1992 | 1990 | Yes | |
| CUB | (M, W) | 1924 | 1929 | 1961 | Yes | |
| CUW | (M, W) | 1921 | 1932 | 1961 | No | |
| DMA | (M, W) | 1970 | 1994 | 1994 | Yes | |
| DOM | (M, W) | 1953 | 1958 | 1964 | Yes | |
| GUF | (M, W) | 1962 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| GRN | (M, W) | 1924 | 1978 | 1978 | Yes | |
| GLP | (M, W) | 1958 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| GUY | (M, W) | 1902 | 1970 | between 1969 and 1971 | Yes | |
| HAI | (M, W) | 1904 | 1934 | 1961 | Yes | |
| JAM | (M, W) | 1910 | 1962 | 1963 | Yes | |
| MTQ | (M, W) | 1953 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| MSR | (M, W) | 1994 | 1996 | 1996 | No | |
| PUR | (M, W) | 1940 | 1960 | 1964 | Yes | |
| SKN | (M, W) | 1932 | 1992 | 1992 | Yes | |
| LCA | (M, W) | 1979 | 1988 | 1986 | Yes | |
| SMN | (M, W) | 1999 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| VIN | (M, W) | 1979 | 1988 | 1986 | Yes | |
| SMA | (M, W) | 1986 | N/A | 2013 | No | |
| SUR | (M, W) | 1920 | 1929 | 1961 | Yes | |
| TRI | (M, W) | 1908 | 1964 | 1964 | Yes | |
| TCA | (M, W) | 1996 | 1998 | 1996 | No | |
| VIR | (M, W) | 1992 | 1998 | 1987 | Yes | |
M = Men's National Team. W = Women's National Team
N/A: not applicable, not available or no answer.
- Full CONCACAF member, but not a FIFA member.
Bonaire were promoted from an association member to a full member at the XXIX Ordinary CONCACAF Congress in São Paulo on 10 June 2014.
Teams not affiliated to the IOC are not eligible to participate in the Summer Olympics football tournament, as a result, they do not participate in the CONCACAF Men's Pre-Olympic Tournament or the CONCACAF Women's Pre-Olympic Tournament.
Non-members
Some territories in the North, Central American and Caribbean region have national teams with no affiliation. All play infrequently and/or are in the early stages of being founded.
- Although one of the three special municipalities of the Netherlands in the region is a member of CONCACAF (
 Bonaire), the other two are not.
Bonaire), the other two are not.
 Saba
Saba Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius
- Although one of the three overseas collectivities of France in the region is a member of CONCACAF (
 Saint Martin), the other two are not.
Saint Martin), the other two are not.
The Football Association of Saint Pierre and Miquelon is expected to build a suitable venue with the goal of becoming a member of CONCACAF in September 2021.[21][22]
Membership relation
Elections at the CONCACAF Congress are mandated with a one-member, one-vote rule. The North American Football Union is the smallest association union in the region with only three members, but its nations have strong commercial and marketing support from sponsors and they are the most populous nations in the region.
The Caribbean Football Union has the ability to outvote NAFU and UNCAF with less than half of its membership. Consequently, there is a fractious relationship between members of CFU, UNCAF and NAFU. This provoked former Acting-President Alfredo Hawit to lobby for the CONCACAF Presidency to be rotated between the three unions in CONCACAF in 2011.
Trinidad's Jack Warner presided over CONCACAF for 21 years, and there was little that non-Caribbean nations could do to elect an alternative. Under Warner, the CFU members voted together as a unit with Warner acting as a party whip. It happened with such regularity that sports political commentators referred to the CFU votes as the "Caribbean bloc" vote. Warner rejected the idea in 1993 of merging several smaller nations' national teams into a Pan-Caribbean team. His reasoning was that the nations were more powerful politically when separate than when together. He commented that "being small is never a liability in this sport".[23]
Competitions
CONCACAF continental competitions
|
National teams:
|
Clubs:
Defunct
|
Intercontinental: Defunct
|
Defunct competitions
|
The Gold Cup and the Champions League are the two most visible CONCACAF tournaments.[20]
CONCACAF Gold Cup
The CONCACAF Gold Cup, held since 1991, is the main association football competition of the men's national football teams governed by CONCACAF. The Gold Cup is CONCACAF's flagship competition, and generates a significant part of CONCACAF's revenue.[24]
The Gold Cup determines the regional champion of North America, Central America, and the Caribbean, and is held every two years. Starting with the 2019 edition, 16 teams compete for the Gold Cup (up from 12).
CONCACAF Nations League
All men's national teams of member associations take part in the CONCACAF Nations League, a competition created in 2017. National teams are placed into tiers and play matches against teams in the same tier. At the end of each season, teams can be promoted to the tier above or relegated to the tier below depending upon their results.
CONCACAF Champions League
The CONCACAF Champions League, originally known as the CONCACAF Champions' Cup, is an annual continental club association football competition organized by CONCACAF since 1962 for the top football clubs in the region. It is the most prestigious international club competition in North American football. The winner of the Champions League qualifies for the FIFA Club World Cup. The knockout tournament spans February through April.[25]
Since 2018, 16 teams compete in each Champions League; at least 9 from North America, at least 1 from the Caribbean and the remaining 6 from varying CONCACAF countries. The North American teams from Major League Soccer and Liga MX qualify through their national leagues or other national tournaments, while the Caribbean team qualifies through the Caribbean Club Championship; the remaining six teams qualify through the CONCACAF League.
The title has been won by 28 clubs, 13 of which have won the title more than once. Mexican clubs have accumulated the highest number of victories, with 36 titles. The second most successful league has been Costa Rica's Primera División with six titles in total. The most successful club is Club América from Mexico, with seven titles; fellow Mexico side Cruz Azul is just behind with six.
CONCACAF League
Eighteen clubs from Central America, three from the Caribbean, and one from Canada compete in the 2017-established CONCACAF League. The top six teams of the competition are awarded a place in the following year's CONCACAF Champions League.
Current title holders
Titles by nation
| Nation | Men | Women | Futsal | Beach | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | League | U20 | U17 | U15 | Gold | League | U20 | U17 | U15 | Men's | Men's | ||
| 11 | – | 13 | 8 | 1 | – | – | 1 | – | 1 | – | 4 | 39 | |
| 6 | – | 2 | 3 | – | 8 | – | 6 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 35 | |
| 2 | – | 2 | – | – | 2 | – | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | – | 10 | |
| 3 | – | 2 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3 | – | 9 | |
| 1 | – | 2 | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 4 | |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | 2 | |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | |
CONMEBOL tournaments
The following CONMEBOL tournaments have had CONCACAF competitors:
National teams
Clubs
- Copa Libertadores – (1998–2017)
- Copa Sudamericana – (2005–2008)
- Copa Merconorte – (2000–2001) (defunct)
Rankings
Men's national teams
FIFA World RankingsRankings are calculated by FIFA.
Top ranked men's national teams by FIFA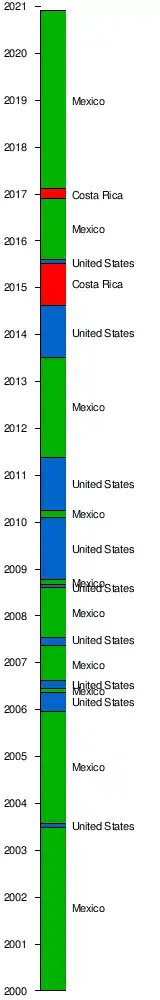
|
CONCACAF Ranking IndexThe Ranking Index is calculated by CONCACAF.[26]
Women's national teams
CONCACAF Ranking IndexThe Ranking Index is calculated by CONCACAF.
Men's Futsal
Women's Futsal
Beach soccer national teamsRankings are calculated by Beach Soccer Worldwide (BSWW). Top ten, last updated 13 March 2018
CorruptionAt the CONCACAF Congress in May 2012 in Budapest, Hungary, legal counsel John P. Collins informed the members of CONCACAF of several financial irregularities. Collins revealed that Jack Warner, the former CONCACAF President, had registered the $22 million 'Dr. João Havelange Centre of Excellence' development in Port-of-Spain under the name of two companies that Warner owned.[27] In addition, Warner had secured a mortgage against the asset in 2007 which the CONCACAF members were also unaware of; the mortgage was co-signed by Lisle Austin, a former vice-president of CONCACAF.[27] The loan defaulted. Collins also revealed that CONCACAF, despite most of its income coming from the United States, had not paid any tax to the Internal Revenue Service since at least 2007 and had never filed a return in the United States.[28] Although CONCACAF is a registered non-profit organization in the Bahamas and headquartered in Port-of-Spain, Trinidad, they have an administration office in New York, and BDO and CONCACAF invited the IRS to investigate potential liabilities. It is thought that CONCACAF may have to pay up to $2 million plus penalties. Chuck Blazer stated that a full financial audit into CONCACAF by New-York based consultancy BDO was delayed due to the actions of Jack Warner and his personal accountant, and the accounts could not be "signed off" as a consequence.[28] In addition, Blazer is to sue CONCACAF for unpaid commission of sponsorship and marketing deals which he had made in 2010 during his time as General Secretary.[27] Blazer received a 10% commission on any deal that he made on behalf of CONCACAF.[29] The Bermuda FA asked members of CONCACAF to lobby FIFA to remove Blazer from his position on the FIFA Executive Committee. Blazer suggested that it was less to do with financial irregularities and more for his role in the removal of Jack Warner in the Caribbean Football Union corruption scandal: "I spent 21 years building the confederation and its competitions and its revenues and I'm the one responsible for its good levels of income . . . I think this is a reflection of those who were angry at me having caused the action against Warner. This is also a reaction by people who have their own agenda."[29] Jack Warner presided over CONCACAF for 21 years. Warner was one of the most controversial figures in world football. Warner was suspended as president on 30 May 2011 due to his temporary suspension from football-related activity by FIFA following corruption allegations.[7] A power struggle developed at CONCACAF following the allegations against Warner. The allegations against Warner were reported to the FIFA Ethics Committee by Chuck Blazer, the secretary general of CONCACAF. The acting president of CONCACAF, Lisle Austin, sent Blazer a letter saying he was "terminated as general secretary with immediate effect".[30] Austin described Blazer's actions as "inexcusable and a gross misconduct of duty and judgement" and said the American was no longer fit to hold the post.[31] The executive committee of CONCACAF later issued a statement saying that Austin did not have the authority to fire Blazer, and the decision was unauthorized.[30] On 20 June 2011, Jack Warner resigned from the presidency of CONCACAF, all posts with FIFA, and removed himself from all participation in football, in the wake of the corruption investigation resulting from 10 May 2011 meeting of the Caribbean Football Union.[9] The vice-president of CONCACAF, Alfredo Hawit, acted as president until May 2012.[10] Indicted CONCACAF individualsSeveral CONCACAF officials have been indicted.[32][33]
Hall of fame
Source:[36]
Team of the CenturyThe CONCACAF Team of the Century was announced as part of the festivities associated with the 1998 FIFA World Cup in France.[37]
President's award
Major tournament records
For each tournament, the flag of the host country and the number of teams in each finals tournament (in brackets) are shown. FIFA World CupOnly eleven CONCACAF members have ever reached the FIFA World Cup since its inception in 1930, six of them accomplishing the feat only once. No team from the region has ever reached the final at the World Cup, but the United States reached the semifinals in the inaugural edition, for which they were awarded third place. CONCACAF members have reached the quarterfinals five times: Cuba in 1938, Mexico as hosts in 1970 and 1986, the United States in 2002, and most recently, Costa Rica in 2014. Jamaica is the smallest country to ever win a World Cup match, by virtue of their 2–1 victory over Japan in 1998. The following table shows the CONCACAF representatives at each edition of the World Cup, sorted by number of appearances:
FIFA World Cup hostingCONCACAF nations have hosted the FIFA World Cup three times. The 1970 FIFA World Cup took place in Mexico, the first World Cup tournament to be staged in North America, and the first held outside Europe and South America. Mexico was chosen as the host nation in 1964 by FIFA's congress ahead of the only other submitted bid from Argentina.[41] The tournament was won by Brazil. The victorious team led by Carlos Alberto, and featuring players such as Pelé, Gérson, Jairzinho, Rivelino, and Tostão, is often cited as the greatest-ever World Cup team.[42][43][44] They achieved a perfect record of wins in all six games in the finals.[45] Despite the issues of altitude and high temperature, the finals produced attacking football which created an average goals per game record not since bettered by any subsequent World Cup Finals.[46][47][48] The 1970 Finals attracted a new record television audience for the FIFA World Cup[49] and, for the first time, in colour.[50][51] In 1986, Mexico became the first country to host the FIFA World Cup twice when it stepped in to stage the 1986 FIFA World Cup after the original host selection, Colombia, suffered financial problems.[41] Colombia was originally chosen as hosts by FIFA in June 1974. However, the Colombian authorities eventually declared in November 1982 that they could not afford to host the World Cup because of economic concerns. Mexico was selected on 20 May 1983 as the replacement hosts, beating the bids of Canada and the United States, and thereby became the first nation to host two World Cups. This second World Cup in Mexico came 16 years after the first one in 1970. The United States won the right to host the 1994 FIFA World Cup, defeating bids from Brazil and Morocco.[52] The vote was held in Zurich on 4 July 1988, and only took one round with the United States bid receiving a little over half of the votes by the Exco members.[52] FIFA hoped that by staging the world's most prestigious football tournament there, it would lead to a growth of interest in the sport; one condition FIFA imposed was the creation of a professional football league, Major League Soccer, starting in 1996. The U.S. staged a hugely successful tournament, with average attendance of nearly 69,000 breaking a record that surpassed the 1966 FIFA World Cup average attendance of 51,000 thanks to the large seating capacities the American stadiums provided for the spectators in comparison to the smaller venues of Europe and Latin America. To this day, the total attendance for the final tournament of nearly 3.6 million remains the highest in World Cup history, despite the expansion of the competition to 32 teams at the 1998 World Cup.[53][54] Canada, Mexico, and the United States have won the bidding to host the 2026 FIFA World Cup, competing against a Moroccan bid.[55] FIFA Women's World Cup
Olympic Games For Men
Olympic Games For Women
CONCACAF Gold Cup
Copa AméricaMexico has finished runners up twice and 3rd place three times at the Copa América making El Tri the most successful non-CONMEBOL nation. The US national team have reached the semifinal stage in the South American tournament twice, followed by Honduras who have reached it once. Costa Rica has reached the quarter finals twice.
CONCACAF Women's Championship
FIFA U-20 World Cup
FIFA U-20 Women's World Cup
FIFA U-17 World Cup
FIFA U-17 Women's World Cup
FIFA Futsal World Cup
FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup
Former tournamentsFIFA Confederations Cup
See alsoCONCACAF
Related linksReferences
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||