China Railway
China State Railway Group Company, Ltd., doing business as China Railway or CR, is a state-owned sole proprietorship enterprise that undertakes railway passenger and cargo transportation services in the People's Republic of China and is a state-owned industrial enterprise established under the "Law of the People's Republic of China on All-Ownership Industrial Enterprises." The Ministry of Finance acts on behalf of the State Council to perform the duties of shareholders.[2] It used to be part of the now defunct Ministry of Railways. China Railway operates passenger and freight transport via 21 subsidiaries.
.jpg.webp) Headquarters of the corporation | |
| China Railway (CR) | |
Native name | Chinese: 中国国家铁路集团有限公司 |
| Formerly | China Railway Corporation (2013–2019) |
| Type | State-owned limited company |
| Industry | Rail transport |
| Predecessor | Ministry of Railways |
| Founded |
|
| Headquarters | , |
Area served | China |
Key people | Lu Dongfu (Chairman) Yang Yudong (General Manager) |
| Services | Passenger rail Freight rail |
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owner | Ministry of Finance of China |
Number of employees | 2 million approx. (2013) |
| Divisions | Railway operations |
| Subsidiaries | 16 bureau 5 companies |
| Website | Corporate website Customer portal |
| Footnotes / references source[1] | |
| China State Railway Group Co.,Ltd. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 中国国家铁路集团有限公司 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 中國國家鐵路集團有限公司 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | China State Railway Group Limited Company | ||||||
| |||||||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 国铁集团 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 國鐵集團 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | State Railway Group | ||||||
| |||||||
China Railway previously had its own railway police force, prosecutors office and court system. The police department of the railway is still under the control of the company. The status of the police is civil service of Ministry of Public Security, but they are still paid and managed by the company. [3]
History
On June 18, 2019, China Railway Corporation is reorganized as China State Railway Group Co., Ltd. under China's Corporate Law, instead of Industrial Enterprises Owned by the Whole People Law. It means the Ministry of Finance would act as an investor on behalf of the state and the company would be led by a board and managed by board-chosen executives.[4][5]
Logo
The China Railway logo was designed by Chen Yuchang (Chinese: 陈玉昶) (1912-1969), officially adopted on 22 January 1950. The whole logo represents the front of a locomotive. The upper part of the logo represents the Chinese character 人 (people), while the lower part represents the transversal surface of a rail. The logo means that China's railway belongs to the people.[6][7][8] The lower part represents the character 工 (labour), means that China's railway belongs to the working class.
The "CR" logo is used on the Fuxing (train) along with the China Railway logo.[9]
Companies
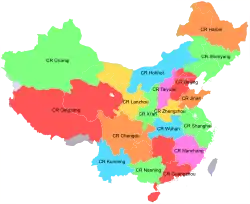
There are 21 primary subsidiary companies under China Railway. As of 2008, approximately 2 million people work in China Railway.
| Business | Company | Provinces of operation | Regions of operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger | China Railway Harbin Group Company (CR Harbin) |
Northeastern Inner Mongolia(Hulunbuir and part of Xingan League), Heilongjiang | Northeast China |
| China Railway Shenyang Group Company (CR Shenyang) |
Liaoning, Jilin, Southeastern Inner Mongolia(Chifeng, Tongliao and part of Xingan League), southern Heilongjiang, northeastern Hebei | ||
| China Railway Beijing Group Company (CR Beijing) |
Beijing, Hebei, Tianjin, western Shandong, northern Henan, eastern Shanxi |
North China | |
| China Railway Hohhot Group Company (CR Hohhot) |
Inner Mongolia | ||
| China Railway Taiyuan Group Company (CR Taiyuan) |
Shanxi | ||
| China Railway Jinan Group Company (CR Jinan) |
Shandong | East China | |
| China Railway Shanghai Group Company (CR Shanghai) |
Shanghai, Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang | ||
| China Railway Nanchang Group Company (CR Nanchang) |
Jiangxi, Fujian, parts of Hubei and Hunan | ||
| China Railway Guangzhou Group Company (CR Guangzhou) |
Guangdong, Hunan, Hainan | South China | |
| China Railway Nanning Group Company (CR Nanning) |
Guangxi, western Guangdong | ||
| China Railway Wuhan Group Company (CR Wuhan) |
Hubei, southern Henan | Central China | |
| China Railway Zhengzhou Group Company (CR Zhengzhou) |
Henan, Shanxi | ||
| China Railway Chengdu Group Company (CR Chengdu) |
Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, parts of Yunnan and Hubei | Southwest China | |
| China Railway Kunming Group Company (CR Kunming) |
Yunnan, parts of Sichuan and Guizhou | ||
| China Railway Qingzang Group Company (CR Qingzang) |
Tibet | ||
| Qinghai | Northwest China | ||
| China Railway Lanzhou Group Company (CR Lanzhou) |
Gansu, Ningxia, parts of Inner Mongolia | ||
| China Railway Ürümqi Group Company (CR Ürümqi) |
Xinjiang, parts of Gansu | ||
| China Railway Xi'an Group Company (CR Xi'an) |
Shaanxi,northeast Sichuan | ||
| Freight | China Railway Special Cargo Service Company (CRSCS) |
Nationwide | |
| China Railway Express Company (CRE) | |||
| China Railway Container Transport Company (CRCT) | |||
Second tier subsidiaries
| Parent | Subsidiary | Operational line |
|---|---|---|
| CR Guangzhou | Guangshen Railway Company | Guangzhou–Shenzhen railway |
| Guangmeishan Railway Company | Guangzhou–Meizhou–Shantou railway | |
| Sanmao Company | Sanshui–Maoming railway | |
| Shichang Railway Company | Shimen–Changsha railway | |
| Yuehai Railway Company | Guangdong–Hainan railway | |
| CR Kunming | Shuibai Railway Company | Liupanshui–Baiguo railway |
| CR Nanchang | Wuyishan Railway Company | Hengfeng–Nanping railway |
| Quanzhou Railway Company | Zhangping–Longyan–Kanshi railway | |
| Longyan Railway Company | Zhangping–Quanzhou–Xiaocuo railway | |
| Xiamen Haicang Railway Company | Haicang branch railway | |
| CR Shanghai | Xiaoyong Railway Company | Xiaoshan–Ningbo railway |
| Hejiu Railway Company | Hefei–Jiujiang railway | |
| Xinchang Railway Company | Xinyi–Changxing railway | |
| Jinwen Railway Company | Jinhua–Wenzhou railway | |
| Ningqi Railway Company | Nanjing–Qidong railway | |
| Ninghe Railway Company | Hefei–Nanjing passenger railway | |
| Hewu Railway Company | Hefei–Wuhan high-speed railway | |
| CR Taiyuan | Daqin Railway Company | Datong–Qinhuangdao railway |
| CR Wuhan | Huhanrong Railway Hubei Company | Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu high-speed railway (Hubei section) |
| Luofu Railway Company | Luohe–Fuyang railway | |
| CR Xi'an | Xiyan Railway Company | Xi'an–Yan'an railway |
| CR Zhengzhou | Anli Branch Line Company | Anyang–Lizhen railway |
| Tanghe Branch Line Company | Tangyin–Hebi railway |
International operations
International passenger trains
China Railway operates the passenger trains from China to Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, North Korea and Vietnam. Currently all international passenger trains are suspended due to COVID-19 pandemics in Asia.

 The Beijing–UlaanBaatar–Moscow passenger train
The Beijing–UlaanBaatar–Moscow passenger train
Services to Europe (New Silk Route)
As of 2017 China Railway ran goods services to 15 European cities, including routes to Madrid and Hamburg and the experimental East Wind service to London to test demand.[10] The Chinese government refers to the two-week 12,000 km (7,500 mi) route, starting at Yiwu and with trains to London traversing Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Poland, Germany, Belgium and France, as the Belt and Road Initiative.[11] Containers must be transferred several times, as different, incompatible, rail gauges are used in different regions, and the same rolling stock cannot be used throughout.
Africa
China has been investing in and helping to rebuild railways in Africa.[12][13] Below is an incomplete list of rail projects.
List of director generals
- Sheng Guangzu (2013-2016)
- Lu Dongfu (2016-2018)
- Yang Yudong (2018-)
Footnotes
- Including revenue from "Railway Construction Fund"
- EBIT, including revenue from "Railway Construction Fund" but excluding contribution to "Water Conservancy Construction Fund"
See also
References
- 中国铁路总公司2015年年度报告 [China Railway Corporation 2015 Annual Report] (in Chinese). archive of Shangjai Clearing House. April 29, 2016. Retrieved May 6, 2016.
- "国家铁路局". www.nra.gov.cn. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
- 铁路公安转制公务员 中铁总公司“企业代管”八万警察 Archived March 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, 《中国经营报》,2013-08-31
- "China renames, restructures railway corporation in reform push". Reuters. June 18, 2019. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- 樊, 曦 (June 18, 2019). "中国国家铁路集团有限公司在京挂牌成立". Xinhuanet (in Chinese). Xinhua News Agency.
- "中国铁路标志的设计者——陈玉昶 60年前的标志还是这么简洁、漂亮!_刘逸设计_新浪博客". Blog.sina.com.cn. March 13, 2013. Retrieved July 31, 2015.
- "Rologo 标志共和国 | 专注于Logo的网站_Logo设计_Logo欣赏 » 中国铁路标志的设计者——陈玉昶". Rologo.com. Retrieved July 31, 2015.
- 路徽的来历.
- 天津站的复兴号CR400AF标准动车组.
- Tracy McVeigh (January 14, 2017). "Silk Road route back in business as China train rolls into London". The Guardian. Retrieved January 15, 2017.
- "Travelling from China to London - BBC News". BBC. January 18, 2017. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- O'Dowd, Emily. "Special report: How five major African rail projects are supported by China". Retrieved September 18, 2018.
- Kacungira, Nancy (June 8, 2017). "Is Kenya's new railway good value for money?". BBC News. Retrieved September 18, 2018.
- "The Report: Algeria 2010 page 165". Oxford Publishing Group. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "Chinese Funded Railways". CNN. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "Government Signs Commercial Contract for the Nairobi to Malaba SGR Section with CCCC". Kenya Railways. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "Mali signs $11bn agreements with China for new rail projects". Railway Technology. September 16, 2014. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "China to build major new African railway from Mali to the coast". Global Construction Review. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "CCECC sign $11.117 billion Lagos-Calabar Rail Contract line". The Guardian. July 2, 2016. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "Abuja-Kaduna Rail line". Railway Technology. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- "Construction of railway from Khartoum to Port Sudan". Aiddata. Archived from the original on January 9, 2017. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- David Lumu, and Samuel Balagadde (August 30, 2014). "Chinese Firm CHEC Given US$8 Billion Railway Deal". New Vision (Kampala). Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- Jin, Haixing (March 31, 2015). "China's Xi Finds Eight Good Reasons to Host Uganda's President". Bloomberg News. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- Monitor Reporter, . (March 30, 2015). "Museveni Signs Deal With Chinese Company To Construct Kasese Railway Line". Daily Monitor (Kampala). Retrieved April 1, 2015.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
External links
- (in Chinese) China Railway official website
- (in Chinese) China Railway Corporation official website
