Comparative officer ranks of World War I
The following table shows comparative officer ranks of several Allied and Central powers during World War I. Not all combatant countries are shown in the table. For modern ranks refer to List of comparative military ranks. See also: Comparative officer ranks of World War II
Table
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[lower-alpha 1][1] |
No equivalent | |||||||||||||||
| Feldmarschall Tábornagy |
Generaloberst Vezérezredes |
General der Waffengattung Tábornok |
Feldmarschall-Leutnant Altábornagy |
Generalmajor Vezérőrnagy |
Oberst Ezredes |
Oberstleutnant Alezredes |
Major Őrnagy |
Hauptmann / Rittmeister Százados / Kapitány |
Oberleutnant Főhadnagy |
Leutnant Hadnagy | ||||||
[lower-alpha 1][1] |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Großadmiral Vezérőrnagy |
Admiral Tengernagy |
Vizeadmiral Altengernagy |
Kontreadmiral Ellentengernagy |
Linienschiffkapitän Sorhajókapitány |
Fregattenkapitän Fregattkapitány |
Korvettenkapitän Korvettkapitány |
Linienschiffsleutnant Sorhajóhadnagy |
Fregattenleutnant Fregatthadnagy |
Korvettenleutnant Korvetthadnagy |
Seekadett | ||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[2] |
_OF-10.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-9.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-8.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-7.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-6.svg.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
.png.webp) |
No equivalent | ||||
| Field Marshal | General | Lieutenant-General | Major-General | Brigadier-General | Colonel | Lieutenant-Colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | ||||||
[2] |
_OF-10.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-9.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-8.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-7.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-7.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-6.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-5.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-4.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-3.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-2.svg.png.webp) |
_OF-1b.svg.png.webp) |
 | ||||
| Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice-Admiral | Rear-Admiral | Commodore 1st class[3] | Commodore 2nd class | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant Commander | Lieutenant | Sub-Lieutenant | Chief Commissioned Warrant Officer | Commissioned Warrant Officer/ Midshipman | ||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[4] |
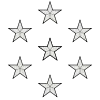 |
[lower-alpha 2][5] | 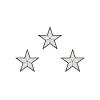 |
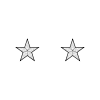 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Maréchal de France[lower-alpha 3] | Général de division ayant un commandement supérieur (général) |
Général de division (lieutenant-général) |
Général de brigade (major-général) |
Colonel | Lieutenant-Colonel | Commandant | Capitaine | Lieutenant | Sous-Lieutenant | Aspirant | ||||||
[4] |
 |
[lower-alpha 2] |  |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Amiral de France[lower-alpha 3] | Vice-amiral ayant un commandement supérieur (amiral) |
Vice-amiral | Contre-amiral | Capitaine de vaisseau | Capitaine de frégate | Capitaine de corvette | Lieutenant de Vaisseau | Enseigne de vaisseau de 1re classe | Enseigne de vaisseau de 2e classe | Aspirant | ||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[6] |
 |
 |
_1918.gif) |
.gif) |
.gif) |
.gif) |
.gif) |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | |||||
| Generalfeldmarschall | Generaloberst mit dem Rang als Generalfeldmarschall | Generaloberst | General der Waffengattung | Generalleutnant | Generalmajor | Oberst | Oberstleutnant | Major | Hauptmann / Rittmeister | Oberleutnant | Leutnant | |||||
[6][7] |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Großadmiral | Admiral | Vizeadmiral | Konteradmiral | Kommodore | Kapitän zur See | Fregattenkapitän | Korvettenkapitän | Kapitänleutnant | Oberleutnant zur See | Leutnant zur See | Seekadett | |||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[8] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||
| Generale d'Esercito | Tenente Generale
|
Tenente Generale
|
Maggior Generale
|
Brigadier Generale | Colonello | Tenente Colonello | Maggiore | Capitano | Tenente | Sottotenente | Aspirante | |||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Ammiraglio | Vice Ammiraglio | Contrammiraglio | Sottoammiraglio | Capitano di Vascello | Capitano di Frigata | Capitano di Corvetta | Tenente di Vascello | Sottotenent di Vascello | Guardiamarina | Aspirante Guardiamarina | ||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[9] |
 |
No equivalent | ||||||||||||||
| Daigensui-Rikugun-Taishō 大元帥陸軍大将 |
Gensui-Rikugun-Taishō 元帥陸軍大将 |
Rikugun-Taishō 陸軍大将 |
Rikugun-Chūjō 陸軍中将 |
Rikugun-Shōshō 陸軍少将 |
Rikugun-Taisa 陸軍大佐 |
Rikugun-Chūsa 陸軍中佐 |
Rikugun-Shōsa 陸軍少佐 |
Rikugun-Tai-i 陸軍大尉 |
Rikugun-Chūi 陸軍中尉 |
Rikugun-Shōi 陸軍少尉 |
Jun-i 准尉 | |||||
[9] |
 |
  |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
.png.webp) | |||
| Daigensui-Kaigun-Taishō 大元帥海軍大将 |
Gensui-kaigun-Taishō 元帥海軍大将 |
Kaigun-Taishō 海軍大将 |
Kaigun-Chūjō 海軍中将 |
Kaigun-Shōshō 海軍少将 |
Kaigun-Daisa 海軍大佐 |
Kaigun-Chūsa 海軍中佐 |
Kaigun-Shōsa 海軍少佐 |
Kaigun-Dai-i 海軍大尉 |
Kaigun-Chūi 海軍中尉 |
Kaigun-Shōi 海軍少尉 |
Hēsōchō 兵曹長 | |||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[lower-alpha 4][10] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
||||||||
| Müşir | Birinci Ferik | Ferik | Mirliva | Miralay | Kaymakam | Binbaşı | Kolağası | Yüzbaşı | Mülazım-ı evvel | Mülazım-ı sani | ||||||
[11] |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | ||||||||||||
| Müşir Amiral | Birinci Ferik Amiral | Ferik Amiral | Liva Amiral | Kalyon Kaptanı | Fırkateyn Kaptanı | Korvet Kaptanı | Yüzbaşı | Mülazım | ||||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[12] |
 |
No equivalent |  |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Marechal[lower-alpha 5] | General[lower-alpha 6] | Brigadeiro | Coronel | Tenente-coronel | Major | Capitão | Tenente | Alferes | Aspirante | |||||||
[12] |
No equivalent | |||||||||||||||
| Almirante[lower-alpha 5] | Vice-almirante | Contra-almirante | Capitão de mar e guerra | Capitão de fragata | Capitão-tenente | Primeiro-tenente | Segundo-tenente | Guarda-marinha | Aspirante | |||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[lower-alpha 7] [13] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||
| Generalfeldmarschall | General roda voisk | General-leytenant | General-mayor | Polkovnik[lower-alpha 8] | Podpolkovnik / Voyskovoy starshina | Kapitan / Rotmistr / Esaul | Shtabs-kapitan / Shtabs-rotmistr / Podesaul | Poruchik / Sotnik | Podporuchik / Kornet / Korunzhy | Praporshik | ||||||
[13] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | ||||||
| General-admiral | Admiral | Vitse-admiral | Kontr-admiral | Kapitan 1-go ranga | Kapitan 2-go ranga | Starshy leytenant | Leytenant | Michman | ||||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[14] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | ||||||
| Bojni Vojvoda[lower-alpha 9] | General[lower-alpha 10] | Pukovnik | Potpukovnik | Major | Kapetan 1. klase | Kapetan 2. klase | Poručnik | Potporučnik | ||||||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
[15] |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | ||||||||||||
| General of the Armies[lower-alpha 11] | General | Lieutenant General | Major General | Brigadier General | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | First Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | ||||||
[15] |
  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Various | ||||
| Admiral of the Navy[lower-alpha 11] | Admiral | Vice Admiral | Rear Admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant Commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Ensign | Midshipman | |||||
| General officers | Field officers | Junior officers | ||||||||||||||
Notes
- Austro-Hungarian ranks are shown in both German and Hungarian, as would have been contemporary practice.
- One horizontal bar under or above the three-star.
- Maréchal de France and Amiral de France were as much a dignity of state as a military title. Thus British Field Marshals consulted with French Generals in 1914. The elevation of Joffre to Maréchal in 1916 actually marked a diminution of his powers of command. There was no Amiral de France alive during World War I.
- Military personnel in the Ottoman Empire were assigned different duties according to their capabilities in order to administer the Armed Forces and particularly to be successful in battle. They were given various ranks so that they could conduct relations with each other and be fully aware of their duties. The issue of what sort of duties should be allocated to which unit or to which military institution used to be determined by the ranking within the Armed Forces. In Islamic countries, certain 'degrees', instead of ranks, were given in accordance with the categorization of government duties. In the course of time, these 'degrees' had taken on certain characteristics. In the Ottoman Empire, besides the ranks that were awarded after passing through certain stages of promotion, there was also the rank of "Pasha" that was given directly by the Ottoman Sultan. This rank, which continued until the establishment of the Republic of Turkey, was also given to civilian administrators who were approved of and found suitable. After the establishment of the Republic, the Sultanate was abolished, and the title became synonymous with the General rank, restricted to the Armed Forces only. Paymaster of a regiment - Captain of the Right Wing (Alay Emini - Sağ Kolağası): The rank of the Captain of the Right Wing was very high. The rank of the Adjutant and Paymaster of a regiment was also high but such individuals were not from the military class and they dealt with clerical duties and equipment needed by the regiment. Captain of the Wing - The Captain of the Left Wing- (Kolağası - Sol Kolağası): Captain of the Wing or the Captain of the Left Wing was the senior Captain. If he was educated in the regiment, he was called "Ağa" but if he was the son of a pasha, he was called "Bey".
- Almirante and Marechal were only honorary ranks, not held by anyone during World War I.
- The Portuguese Army had the particularity of having only a single rank of General Officer. A Portuguese General could be assigned to command from a brigade to the entire Army.
- For transliterations, refer to History of Russian military ranks.
- Army/cavalry ranks. Cossack cavalry had distinct ranks below Podpolkovnik: войсково́й старшина́ (Voiskovoy Starshina), есау́л (Yesaul), подъесау́л (Sub-Yesaul), со́тник (Sotnik), хору́нжий (Khorunzhiy)
- Field Marshal of Serbia (Voivode) was the highest rank in the army of the Kingdom of Serbia. Radomir Putnik held title from beginning of the war since he was promoted in 1912.
- Like the Portuguese Army, the Serbian Army had only a single rank of General Officer. A Serbian General could be assigned to command from a division to the entire Army.
- The US rank Admiral of the Navy was a unique rank created for Admiral George Dewey after the Spanish–American War; it has never been held by any other person and debate still goes on over whether it was a "five-star" or "six-star" rank. General of the Armies is similarly ambiguous; it was granted to General Pershing at the end of the war, and previously had been held (or a rank of the same name had been held) by Generals Grant and Sherman after the Civil War, but its equivalency to modern ranks is disputed.
References
- Over the Front. "Austro-Hungarian Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "British Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- http://www.naval-history.net/WW1NavyBritish-Ranks.htm
- Over the Front. "French Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- CAIRN.INFO. "Général de corps d'armée". CAIRN INFO.
- Over the Front. "German Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Strauß, Matthias. "Dienstgrade und Uniformen". kleiner-kreuzer-dresden.de (in German). Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "Italian Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "Japanese Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- "1909 TILL 1918 OTTOMAN RANK INSIGNIA". ottoman-uniforms.com. Ottoman Uniforms. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- "1916 TILL 1918 OTTOMAN NAVY". ottoman-uniforms.com. Ottoman Uniforms. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "Portuguese Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "Russian Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "Serbian Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- Over the Front. "American Ranks". Over the Front. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.