Control chart
Control charts, also known as Shewhart charts (after Walter A. Shewhart) or process-behavior charts, are a statistical process control tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of control. It is more appropriate to say that the control charts are the graphical device for Statistical Process Monitoring (SPM). Traditional control charts are mostly designed to monitor process parameters when underlying form of the process distributions are known. However, more advanced techniques are available in the 21st century where incoming data streaming can-be monitored even without any knowledge of the underlying process distributions. Distribution-free control charts are becoming increasingly popular.
| Control chart | |
|---|---|
 | |
| One of the Seven basic tools of quality | |
| First described by | Walter A. Shewhart |
| Purpose | To determine whether a process should undergo a formal examination for quality-related problems |
Overview
If analysis of the control chart indicates that the process is currently under control (i.e., is stable, with variation only coming from sources common to the process), then no corrections or changes to process control parameters are needed or desired. In addition, data from the process can be used to predict the future performance of the process. If the chart indicates that the monitored process is not in control, analysis of the chart can help determine the sources of variation, as this will result in degraded process performance.[1] A process that is stable but operating outside desired (specification) limits (e.g., scrap rates may be in statistical control but above desired limits) needs to be improved through a deliberate effort to understand the causes of current performance and fundamentally improve the process.[2]
The control chart is one of the seven basic tools of quality control.[3] Typically control charts are used for time-series data, though they can be used for data that have logical comparability (i.e. you want to compare samples that were taken all at the same time, or the performance of different individuals); however the type of chart used to do this requires consideration.[4]
History
The control chart was invented by Walter A. Shewhart working for Bell Labs in the 1920s.[5] The company's engineers had been seeking to improve the reliability of their telephony transmission systems. Because amplifiers and other equipment had to be buried underground, there was a stronger business need to reduce the frequency of failures and repairs. By 1920, the engineers had already realized the importance of reducing variation in a manufacturing process. Moreover, they had realized that continual process-adjustment in reaction to non-conformance actually increased variation and degraded quality. Shewhart framed the problem in terms of Common- and special-causes of variation and, on May 16, 1924, wrote an internal memo introducing the control chart as a tool for distinguishing between the two. Shewhart's boss, George Edwards, recalled: "Dr. Shewhart prepared a little memorandum only about a page in length. About a third of that page was given over to a simple diagram which we would all recognize today as a schematic control chart. That diagram, and the short text which preceded and followed it set forth all of the essential principles and considerations which are involved in what we know today as process quality control."[6] Shewhart stressed that bringing a production process into a state of statistical control, where there is only common-cause variation, and keeping it in control, is necessary to predict future output and to manage a process economically.
Shewhart created the basis for the control chart and the concept of a state of statistical control by carefully designed experiments. While Shewhart drew from pure mathematical statistical theories, he understood that data from physical processes typically produce a "normal distribution curve" (a Gaussian distribution, also commonly referred to as a "bell curve"). He discovered that observed variation in manufacturing data did not always behave the same way as data in nature (Brownian motion of particles). Shewhart concluded that while every process displays variation, some processes display controlled variation that is natural to the process, while others display uncontrolled variation that is not present in the process causal system at all times.[7]
In 1924, or 1925, Shewhart's innovation came to the attention of W. Edwards Deming, then working at the Hawthorne facility. Deming later worked at the United States Department of Agriculture and became the mathematical advisor to the United States Census Bureau. Over the next half a century, Deming became the foremost champion and proponent of Shewhart's work. After the defeat of Japan at the close of World War II, Deming served as statistical consultant to the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers. His ensuing involvement in Japanese life, and long career as an industrial consultant there, spread Shewhart's thinking, and the use of the control chart, widely in Japanese manufacturing industry throughout the 1950s and 1960s.
Chart details
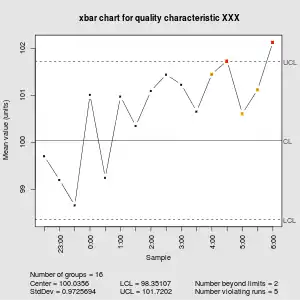
A control chart consists of:
- Points representing a statistic (e.g., a mean, range, proportion) of measurements of a quality characteristic in samples taken from the process at different times (i.e., the data)
- The mean of this statistic using all the samples is calculated (e.g., the mean of the means, mean of the ranges, mean of the proportions)
- A center line is drawn at the value of the mean of the statistic
- The standard deviation (e.g., sqrt(variance) of the mean) of the statistic is also calculated using all the samples
- Upper and lower control limits (sometimes called "natural process limits") that indicate the threshold at which the process output is considered statistically 'unlikely' and are drawn typically at 3 standard deviations from the center line
The chart may have other optional features, including:
- Upper and lower warning or control limits, drawn as separate lines, typically two standard deviations above and below the center line
- Division into zones, with the addition of rules governing frequencies of observations in each zone
- Annotation with events of interest, as determined by the Quality Engineer in charge of the process' quality
- Action on special causes
(n.b., there are several rule sets for detection of signal; this is just one set. The rule set should be clearly stated.)
- Any point outside the control limits
- A Run of 7 Points all above or all below the central line - Stop the production
- Quarantine and 100% check
- Adjust Process.
- Check 5 Consecutive samples
- Continue The Process.
- A Run of 7 Point Up or Down - Instruction as above
Chart usage
If the process is in control (and the process statistic is normal), 99.7300% of all the points will fall between the control limits. Any observations outside the limits, or systematic patterns within, suggest the introduction of a new (and likely unanticipated) source of variation, known as a special-cause variation. Since increased variation means increased quality costs, a control chart "signaling" the presence of a special-cause requires immediate investigation.
This makes the control limits very important decision aids. The control limits provide information about the process behavior and have no intrinsic relationship to any specification targets or engineering tolerance. In practice, the process mean (and hence the centre line) may not coincide with the specified value (or target) of the quality characteristic because the process design simply cannot deliver the process characteristic at the desired level.
Control charts limit specification limits or targets because of the tendency of those involved with the process (e.g., machine operators) to focus on performing to specification when in fact the least-cost course of action is to keep process variation as low as possible. Attempting to make a process whose natural centre is not the same as the target perform to target specification increases process variability and increases costs significantly and is the cause of much inefficiency in operations. Process capability studies do examine the relationship between the natural process limits (the control limits) and specifications, however.
The purpose of control charts is to allow simple detection of events that are indicative of actual process change. This simple decision can be difficult where the process characteristic is continuously varying; the control chart provides statistically objective criteria of change. When change is detected and considered good its cause should be identified and possibly become the new way of working, where the change is bad then its cause should be identified and eliminated.
The purpose in adding warning limits or subdividing the control chart into zones is to provide early notification if something is amiss. Instead of immediately launching a process improvement effort to determine whether special causes are present, the Quality Engineer may temporarily increase the rate at which samples are taken from the process output until it is clear that the process is truly in control. Note that with three-sigma limits, common-cause variations result in signals less than once out of every twenty-two points for skewed processes and about once out of every three hundred seventy (1/370.4) points for normally distributed processes.[8] The two-sigma warning levels will be reached about once for every twenty-two (1/21.98) plotted points in normally distributed data. (For example, the means of sufficiently large samples drawn from practically any underlying distribution whose variance exists are normally distributed, according to the Central Limit Theorem.)
Choice of limits
Shewhart set 3-sigma (3-standard deviation) limits on the following basis.
- The coarse result of Chebyshev's inequality that, for any probability distribution, the probability of an outcome greater than k standard deviations from the mean is at most 1/k2.
- The finer result of the Vysochanskii–Petunin inequality, that for any unimodal probability distribution, the probability of an outcome greater than k standard deviations from the mean is at most 4/(9k2).
- In the Normal distribution, a very common probability distribution, 99.7% of the observations occur within three standard deviations of the mean (see Normal distribution).
Shewhart summarized the conclusions by saying:
... the fact that the criterion which we happen to use has a fine ancestry in highbrow statistical theorems does not justify its use. Such justification must come from empirical evidence that it works. As the practical engineer might say, the proof of the pudding is in the eating.[9]
Although he initially experimented with limits based on probability distributions, Shewhart ultimately wrote:
Some of the earliest attempts to characterize a state of statistical control were inspired by the belief that there existed a special form of frequency function f and it was early argued that the normal law characterized such a state. When the normal law was found to be inadequate, then generalized functional forms were tried. Today, however, all hopes of finding a unique functional form f are blasted.
The control chart is intended as a heuristic. Deming insisted that it is not a hypothesis test and is not motivated by the Neyman–Pearson lemma. He contended that the disjoint nature of population and sampling frame in most industrial situations compromised the use of conventional statistical techniques. Deming's intention was to seek insights into the cause system of a process ...under a wide range of unknowable circumstances, future and past.... He claimed that, under such conditions, 3-sigma limits provided ... a rational and economic guide to minimum economic loss... from the two errors:
- Ascribe a variation or a mistake to a special cause (assignable cause) when in fact the cause belongs to the system (common cause). (Also known as a Type I error or False Positive)
- Ascribe a variation or a mistake to the system (common causes) when in fact the cause was a special cause (assignable cause). (Also known as a Type II error or False Negative)
Calculation of standard deviation
As for the calculation of control limits, the standard deviation (error) required is that of the common-cause variation in the process. Hence, the usual estimator, in terms of sample variance, is not used as this estimates the total squared-error loss from both common- and special-causes of variation.
An alternative method is to use the relationship between the range of a sample and its standard deviation derived by Leonard H. C. Tippett, as an estimator which tends to be less influenced by the extreme observations which typify special-causes.
Rules for detecting signals
The most common sets are:
- The Western Electric rules
- The Wheeler rules (equivalent to the Western Electric zone tests[10])
- The Nelson rules
There has been particular controversy as to how long a run of observations, all on the same side of the centre line, should count as a signal, with 6, 7, 8 and 9 all being advocated by various writers.
The most important principle for choosing a set of rules is that the choice be made before the data is inspected. Choosing rules once the data have been seen tends to increase the Type I error rate owing to testing effects suggested by the data.
Alternative bases
In 1935, the British Standards Institution, under the influence of Egon Pearson and against Shewhart's spirit, adopted control charts, replacing 3-sigma limits with limits based on percentiles of the normal distribution. This move continues to be represented by John Oakland and others but has been widely deprecated by writers in the Shewhart–Deming tradition.
Performance of control charts
When a point falls outside the limits established for a given control chart, those responsible for the underlying process are expected to determine whether a special cause has occurred. If one has, it is appropriate to determine if the results with the special cause are better than or worse than results from common causes alone. If worse, then that cause should be eliminated if possible. If better, it may be appropriate to intentionally retain the special cause within the system producing the results.
Even when a process is in control (that is, no special causes are present in the system), there is approximately a 0.27% probability of a point exceeding 3-sigma control limits. So, even an in control process plotted on a properly constructed control chart will eventually signal the possible presence of a special cause, even though one may not have actually occurred. For a Shewhart control chart using 3-sigma limits, this false alarm occurs on average once every 1/0.0027 or 370.4 observations. Therefore, the in-control average run length (or in-control ARL) of a Shewhart chart is 370.4.
Meanwhile, if a special cause does occur, it may not be of sufficient magnitude for the chart to produce an immediate alarm condition. If a special cause occurs, one can describe that cause by measuring the change in the mean and/or variance of the process in question. When those changes are quantified, it is possible to determine the out-of-control ARL for the chart.
It turns out that Shewhart charts are quite good at detecting large changes in the process mean or variance, as their out-of-control ARLs are fairly short in these cases. However, for smaller changes (such as a 1- or 2-sigma change in the mean), the Shewhart chart does not detect these changes efficiently. Other types of control charts have been developed, such as the EWMA chart, the CUSUM chart and the real-time contrasts chart, which detect smaller changes more efficiently by making use of information from observations collected prior to the most recent data point.[11]
Many control charts work best for numeric data with Gaussian assumptions. The real-time contrasts chart was proposed to monitor process with complex characteristics, e.g. high-dimensional, mix numerical and categorical, missing-valued, non-Gaussian, non-linear relationship.[11]
Criticisms
Several authors have criticised the control chart on the grounds that it violates the likelihood principle. However, the principle is itself controversial and supporters of control charts further argue that, in general, it is impossible to specify a likelihood function for a process not in statistical control, especially where knowledge about the cause system of the process is weak.
Some authors have criticised the use of average run lengths (ARLs) for comparing control chart performance, because that average usually follows a geometric distribution, which has high variability and difficulties.
Some authors have criticized that most control charts focus on numeric data. Nowadays, process data can be much more complex, e.g. non-Gaussian, mix numerical and categorical, or be missing-valued.[11]
Types of charts
| Chart | Process observation | Process observations relationships | Process observations type | Size of shift to detect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| and R chart | Quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Independent | Variables | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| and s chart | Quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Independent | Variables | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| Shewhart individuals control chart (ImR chart or XmR chart) | Quality characteristic measurement for one observation | Independent | Variables† | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| Three-way chart | Quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Independent | Variables | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| p-chart | Fraction nonconforming within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes† | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| np-chart | Number nonconforming within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes† | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| c-chart | Number of nonconformances within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes† | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| u-chart | Nonconformances per unit within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes† | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
| EWMA chart | Exponentially weighted moving average of quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes or variables | Small (< 1.5σ) |
| CUSUM chart | Cumulative sum of quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Independent | Attributes or variables | Small (< 1.5σ) |
| Time series model | Quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Autocorrelated | Attributes or variables | N/A |
| Regression control chart | Quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup | Dependent of process control variables | Variables | Large (≥ 1.5σ) |
†Some practitioners also recommend the use of Individuals charts for attribute data, particularly when the assumptions of either binomially distributed data (p- and np-charts) or Poisson-distributed data (u- and c-charts) are violated.[12] Two primary justifications are given for this practice. First, normality is not necessary for statistical control, so the Individuals chart may be used with non-normal data.[13] Second, attribute charts derive the measure of dispersion directly from the mean proportion (by assuming a probability distribution), while Individuals charts derive the measure of dispersion from the data, independent of the mean, making Individuals charts more robust than attributes charts to violations of the assumptions about the distribution of the underlying population.[14] It is sometimes noted that the substitution of the Individuals chart works best for large counts, when the binomial and Poisson distributions approximate a normal distribution. i.e. when the number of trials n > 1000 for p- and np-charts or λ > 500 for u- and c-charts.
Critics of this approach argue that control charts should not be used when their underlying assumptions are violated, such as when process data is neither normally distributed nor binomially (or Poisson) distributed. Such processes are not in control and should be improved before the application of control charts. Additionally, application of the charts in the presence of such deviations increases the type I and type II error rates of the control charts, and may make the chart of little practical use.
See also
References
- McNeese, William (July 2006). "Over-controlling a Process: The Funnel Experiment". BPI Consulting, LLC. Retrieved 2010-03-17.
- Wheeler, Donald J. (2000). Understanding Variation. Knoxville, Tennessee: SPC Press. ISBN 978-0-945320-53-1.
- Nancy R. Tague (2004). "Seven Basic Quality Tools". The Quality Toolbox. Milwaukee, Wisconsin: American Society for Quality. p. 15. Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- A Poots, T Woodcock (2012). "Statistical process control for data without inherent order". BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 12. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-12-86. PMC 3464151. PMID 22867269.
- "Western Electric History". www.porticus.org. Archived from the original on 2011-01-27. Retrieved 2015-03-26.
- "Western Electric – A Brief History". Archived from the original on 2008-05-11. Retrieved 2008-03-14.
- "Why SPC?" British Deming Association SPC Press, Inc. 1992
- Wheeler, Donald J. (1 November 2010). "Are You Sure We Don't Need Normally Distributed Data?". Quality Digest. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- Shewhart, W A (1931). Economic Control of Quality of Manufactured Product. Van Nordstrom. p. 18.
- Wheeler, Donald J.; Chambers, David S. (1992). Understanding statistical process control (2 ed.). Knoxville, Tennessee: SPC Press. p. 96. ISBN 978-0-945320-13-5. OCLC 27187772.
- Deng, H.; Runger, G.; Tuv, E. (2012). "System monitoring with real-time contrasts". Journal of Quality Technology. 44 (1). pp. 9–27. doi:10.1080/00224065.2012.11917878.
- Wheeler, Donald J. (2000). Understanding Variation: the key to managing chaos. SPC Press. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-945320-53-1.
- Staufer, Rip. "Some Problems with Attribute Charts". Quality Digest. Retrieved 2 Apr 2010.
- Wheeler, Donald J. "What About Charts for Count Data?". Quality Digest. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
Bibliography
- Deming, W. E. (1975). "On probability as a basis for action". The American Statistician. 29 (4): 146–152. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.470.9636. doi:10.2307/2683482. JSTOR 2683482.
- Deming, W. E. (1982). Out of the Crisis: Quality, Productivity and Competitive Position. ISBN 978-0-521-30553-2.
- Deng, H.; Runger, G.; Tuv, Eugene (2012). "System monitoring with real-time contrasts". Journal of Quality Technology. 44 (1): 9–27. doi:10.1080/00224065.2012.11917878.
- Mandel, B. J. (1969). "The Regression Control Chart". Journal of Quality Technology. 1 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1080/00224065.1969.11980341.
- Oakland, J. (2002). Statistical Process Control. ISBN 978-0-7506-5766-2.
- Shewhart, W. A. (1931). Economic Control of Quality of Manufactured Product. ISBN 978-0-87389-076-2.
- Shewhart, W. A. (1939). Statistical Method from the Viewpoint of Quality Control. ISBN 978-0-486-65232-0.
- Wheeler, D. J. (2000). Normality and the Process-Behaviour Chart. ISBN 978-0-945320-56-2.
- Wheeler, D. J.; Chambers, D. S. (1992). Understanding Statistical Process Control. ISBN 978-0-945320-13-5.
- Wheeler, Donald J. (1999). Understanding Variation: The Key to Managing Chaos (2nd ed.). SPC Press. ISBN 978-0-945320-53-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Control charts. |
